MCV in a blood test is one of the most important erythrocyte indices. It reflects the average volume of a red blood cell and is calculated by dividing the hematocrit by the number of red blood cells. The result is expressed in cubic microns or femtoliters.
Another way to obtain this indicator is to multiply the hematocrit by 10 and divide the resulting number by the number of red blood cells contained in one cubic millimeter of blood.
It is important to consider that in some cases the mcv test will produce invalid data. For example, in sickle cell disease, large numbers of abnormal, misshapen red blood cells circulate in the bloodstream. Therefore, the indices obtained by calculation will in this case be uninformative.
Description of the analysis
The mcv value is calculated based on data obtained from a general blood test. This is one of the most widespread and frequently prescribed laboratory tests. It allows you to comprehensively assess the condition of the entire hematopoietic system.
Erythrocyte indices, which are part of a general blood test, allow one to diagnose and classify various anemias with fairly high accuracy. Thanks to this, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
Since the analysis is simple, inexpensive and publicly available, it is used as a screening technique for identifying disorders in the hematopoietic system. Another advantage of the technique is the possibility of dynamic monitoring of the effectiveness of the treatment and timely adjustment of the dosages of drugs prescribed to the patient.
The result of the study may be affected by the presence of severe leukocytosis, a large number of reticulocytes, and a significant excess of normal glucose levels. All these conditions lead to an increase in the average size of the red blood cell.
It should also be taken into account that a simultaneous increase in macrocytic (large) and microcytic (small) red blood cells can create the appearance of normality. This is due to the fact that mcv is a calculated indicator that does not always reflect the objective state of blood cells. To identify abnormalities in such cases, direct microscopy of a blood smear taken from the subject is required.
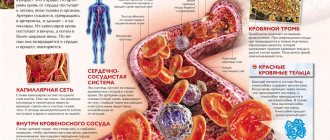
Red blood cells and their function in the body
Red blood cells are a cellular unit of blood, the main purpose of which is to saturate the body with all components of the inhaled air. They carry oxygen molecules from lung tissue to internal organs, as well as other parts of the body.
In the opposite direction, red cells remove carbon dioxide from the body, formed after absorbing air. Oxygen delivery is carried out by hemoglobin proteins, which make up 98% of the total mass of protein compounds in red blood cells.
When hemoglobin concentration decreases, the transport function of blood cells is disrupted. Therefore, these indicators must be constantly monitored.
Preparing for analysis
In most cases, blood for analysis is taken from a vein. It is permissible to take capillary blood from children under 3 years of age and from adults for special indications. The analysis is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach; the fasting period should be at least 8 hours.
Before blood sampling, it is forbidden to eat food or any drinks; you can drink plain water. There is no need to follow a diet a few days before the test, but you should exclude alcoholic drinks and fatty foods. It is undesirable to be exposed to high physical and psycho-emotional stress, which may affect the reliability of the analysis results.
In the process of preparing for the blood sampling procedure, the patient should be warned about possible unpleasant sensations when applying a tourniquet and during vein puncture.
Necessary therapy for a low MNCH index
If a reduced level of concentration of iron-containing protein in such elements is detected, medical professionals prescribe therapeutic treatment using medications that can increase the level of MNCH.
Having determined the reasons for the decrease in MNCH levels, doctors develop an individual therapeutic treatment plan. The basis of this treatment are:
- A vitamin complex with an element of group “B” included in its composition;
- Mineral components and additives;
- Preparations rich in components such as folic acid and iron.
With the described deficiency of pigment in the cells, patients under 3 years of age are recommended to take drugs in the form of Ferum, Lek, Actifferin, while older children are advised to take drugs in the form of Totem, Ferroplex, Tardiferon. The purpose of these particular drugs is due to the content of natural elements in their composition, which during the treatment process in no way can harm the child’s still fragile body.
The treatment process for the adult generation is based on the same medications, but in a much higher dosage. The duration of the prescribed course of treatment varies from 1 to 3 months, and the frequency of administration and individual dosage is calculated by the attending doctor, taking into account all the characteristics of the body of a particular patient, as well as based on the reasons that led to this condition.
The above-described therapy is complemented by the inclusion in the patient’s daily menu of foods rich in elements in the form of iron and folic acid.
MCV blood test interpretation
The normal mcv value for people from 18 to 45 years old is considered to be in the range from 84 to 99 µm3. The mcv rate changes quite a lot over the course of a person’s life. For newborns, up to 112 µm3 is considered normal, then, as they grow older, the average volume of red blood cells quickly decreases. Therefore, already for teenagers 12-15 years old, the range from 73 to 95 cubic micrometers is considered normal.
In general, it can be said that the volume of red blood cells is maximum in newborns and decreases slowly throughout life. Moreover, the fact that most red blood cells have a normal volume does not exclude the presence of pathologies associated with the hematopoietic system. For example, normocytic anemias are quite common - blood diseases that do not affect the average volume of red blood cells.
Most often, such anemia occurs after serious blood loss, during the process of recovery from conditions associated with iron deficiency. Often normocytic anemia indicates suppression of the functions of the red bone marrow, severe liver and kidney diseases. Less commonly, it is a manifestation of other pathological processes, such as hemoglobinopathy. But do not confuse MCV and MCHC, as these are two different indicators.
MCH norm indicators
The average amount of hemoglobin in one red blood cell varies depending on age and gender. Its average value in a healthy adult is from 27 to 31 picograms (pg). The highest rates are observed in infants under 14 days of age. They can vary from 30 to 37 pg and, as they grow older, gradually decrease and are compared with the norm for adults. Norms for women
| Woman's age, years | Norm MCH per red blood cell (in pg) |
| 16-18 | 26-34 |
| 19-45 | 27-35 |
| 46-60 | 27-34 |
| After 60 | 27-35 |
The norms for men are approximately the same as for women. Minimal deviations are observed. 46-6027-34 After 6027-35
| Man's age, years | Norm MCH per red blood cell (in pg) |
| 16-18 | 27-32,5 |
| 19-45 | 27-34 |
| 46-60 | 27-35 |
| After 60 | 27-34,5 |
Norms for children. It should be noted that these indicators are unstable; they can change within a matter of hours or days.
| Child's age, years | Norm MCH per red blood cell (in pg) |
| 1-4 months | 27-32 |
| 1-3 years | 23-31 |
| 7-15 years | 26-32 |
MCV in blood test is increased
If the decoding of the mcv blood test showed an increase above 100 µm3, this is a sign of the development of anemia associated with a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12. As a result, the formation of red blood cells is disrupted. They increase in volume, but do not cope well with the function of transporting oxygen. Simultaneously with the increase in the size of red blood cells, hemoglobin levels often decrease. This combination of signs is clearly detected by a general blood test and serves as a fairly reliable diagnostic factor.
An increase in mcv can also be a manifestation of other diseases, including very serious ones. These include liver and bone marrow diseases, hemolytic conditions, and myelodysplastic conditions.
An increase in mcv in a blood test does not always indicate the development of anemia or other serious pathologies. Values above 100 µm3 can be observed in people who abuse alcohol for a long time, smokers with many years of experience, as well as with chronic dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
How the research is carried out
To obtain data on MSI in a blood test, blood is drawn from a vein. In rare cases, it is possible to use finger capillaries (nowadays they are practically not used, as they are less accurate and informative). This procedure is performed by a nurse or laboratory worker who has the appropriate education and license to carry out this activity. Its duration is no more than 5 minutes and is accompanied by slight pain and discomfort at the puncture site. However, the discomfort quickly disappears, and a small bruise may remain at the puncture site. Persons who are afraid of the sight of blood are strongly advised to turn away and not look at the hand until the end of the procedure. But to prevent loss of consciousness and quickly restore consciousness, a cotton pad and ammonia are always present in the office. Blood sampling is carried out in several successive stages:
- Applying a rubber or fabric tourniquet with clamps to the forearm of the patient, who must work his fists a little (clench and unclench his hand several times to better fill the vessels).
- The technician or nurse selects the most appropriate vein and cleans the skin with an alcohol swab.
- Inserting a needle into a vein, through which blood flows into a syringe or special tube. Often, no more than 5 ml is collected.
- Remove the needle and apply cotton wool soaked in alcohol to the puncture site.
To prevent bruising or bruising, the patient is asked to press his forearm to his shoulder for a few minutes. At this point, the procedure ends and the medical worker signs the tube, after which the resulting material is placed in the analyzer. Its use makes it possible to automatically count all types of blood cells, including red blood cells. The obtained data is sent to the attending physician, after which the MCH blood test begins to be deciphered.
MCV reduced
A decrease in the average volume of red blood cells most often occurs with the development of iron deficiency anemia. They can develop as a result of exposure to various factors, such as:
- Chronic blood loss.
- Lack of iron in the diet.
- Impaired absorption of iron in the intestines.
A decrease in the volume of red blood cells is observed in a variety of chronic diseases - long-term infections, oncological pathologies. Rarely, a congenital decrease in mcv is possible, for example, with thalassemia. This is a group of genetic pathologies that occur when the synthesis of hemoglobin globin chains is disrupted.
If the synthesis of the alpha chain is impaired, alpha thalassemia develops. This is a relatively mild pathology, characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin to 70-90 g/l and a decrease in the mcv index. This form of the disease often does not manifest itself in any way and is detected by chance, when studying laboratory blood parameters.
Beta thalassemia, which occurs when the synthesis of the hemoglobin beta chain is impaired, is much more severe. If defective genes were inherited from one of the parents, it is manifested by a decrease in the mcv index and hemoglobin level. When defective genes are passed on from both parents, Cooley's anemia develops. It is characterized by an extremely severe course; red blood cells not only sharply decrease in volume, but are also quickly destroyed. This leads to enlargement of the liver and spleen and disruption of their functions. To maintain life, such patients require regular blood transfusions, and a complete cure is possible with a bone marrow transplant.