Reasons for the development of pathology. Symptoms Possible complications of lymphangioma Diagnosis of pathology and treatment methods
Lymphangioma
or lymphatic malformation - the scientific definition of pathology, is a benign tumor formed in the plexus of lymphatic vessels of connective tissue.
At present, the true causes of the tumor have not been established. There is an opinion among doctors that lymphangioma
is a real benign tumor that develops in the body due to the existing conditions. On the other hand, there is an opinion that the pathology is a congenital malformation of the lymphatic system. The neoplasm consists of cysts of various sizes. The most common manifestation of tumor development are nodes with a diameter of 0.2-0.3 cm. However, in medical practice there are cases of the presence of large formations as a result of malformation of the lymphatic system, which are detected upon visual examination. A benign tumor most often develops in childhood. In some cases, the pathology is a congenital form of the disease.
According to the Ministry of Health, lymphangioma
occurs quite often. Every tenth case from the general picture of the development of tumors in children is associated with a benign neoplasm in the lymphatic system. There is a clear division into primary tumors and secondary neoplasms. The secondary form of tumor growth is observed as a result of infectious diseases suffered by the child and complications arising in connection with this.
Reasons for the development of pathology. Symptoms
It was said earlier that at present there is no clear idea about the reasons for the development of benign neoplasms of the lymphatic system. As a result of examination of patients, it was found that lymphangioma
most often becomes the result of the development of a congenital malformation of the lymphatic system. In some cases, the pathology forms during the prenatal period and begins to develop intensively immediately after the birth of the child. Often, a benign tumor of the lymphatic system develops against the background of other abnormalities of the body. The congenital nature of the pathology, in accordance with the latest scientific developments and guesses of medical scientists, can be influenced by a poor environmental situation for the expectant mother, including exposure to gamma radiation. Other indirect factors influencing the formation of pathology may be poor heredity and complications resulting from severe systemic and infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother.
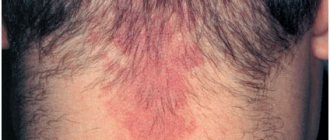
The symptoms of the pathology are pronounced. With the development of a tumor at an early age, the child experiences the appearance of compactions in the neck, in the oral cavity, and somewhat less often in the internal organs and in the peritoneum. There are cases of nodules developing in other parts of the patient’s body. The tumor is localized in the subcutaneous fatty tissue. Depending on the symptoms, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- capillary lymphangioma
; - cavernous lymphangioma
; - cystic lymphangioma
.
Capillary or simple pathologies include neoplasms, the location of which most often is the oral cavity, tongue, and the inner surface of the child’s cheeks. From a clinical point of view, the neoplasms in this case look like swellings measuring 203 cm, soft to the touch and with an unchanged color. There is no pain when palpating the tumors. A detailed analysis can reveal the structure of the seals, consisting of a network of capillaries, a large number of lymphoid cells and connective tissue.
The second type of pathology, cavernous lymphangioma
manifests itself in the form of bubbles on the surface of the skin, the size of which is 2-5 cm. Bubbles, as a rule, appear in the soft subcutaneous tissues in the areas of the largest plexus of the lymphatic system, neck, chest area, on the side of the body, on the arms and legs.
The third type of pathology, cystic lymphangiomas, is much more common in medical practice. Neoplasms develop at the site of the plexus of lymph nodes. Large, spherical formations can occur in the submandibular region, armpits, or in the area of the ears. Unlike the previous two types of pathology, cystic lymphangioma
is characterized by rapid growth, which is caused by the rapid filling of the cyst cavities with fluid. As a result of cyst rupture, abscesses and infection of the body often occur.
A distinctive feature of the first two types of the disease is the ability to stop tumor growth on its own. Regression in tumor development, ending with scarring, is often observed. Detected lymphangioma
in childhood it develops rather slowly, the process of which accelerates during puberty. The reasons explaining such dynamics are not fully understood. There is an opinion among doctors that the activation of tumor growth with the onset of puberty is associated with the impact of the developing secretory system of the body on the state of the lymphatic system.
Why choose Top Ichilov clinic
- The most modern methods of treating lymphangioma in Israel
- Possibility of non-surgical treatment
- Fast and high-quality diagnostics with a second opinion
- Comfortable conditions for staying in the hospital: comfortable and clean rooms, equipped with everything necessary, polite medical staff
- Loyal prices, flexible payment system
- Personal case manager, organizing the process of diagnosis and treatment, as well as taking upon himself the solution of all everyday problems
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(3 votes, average: 3.7 out of 5)
Possible complications with lymphangioma
Despite its benign nature, lymphangioma
poses a serious danger to the body. The main danger is due to the threat to the body during childbirth, both for the mother and for the unborn child. The pathology poses a danger not only to newborns, but also to adolescent children, causing serious harm to their health. Neoplasms that arise in the fetus create difficulties for the woman in labor during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal. Often there is compression of neighboring organs, displacement of tissues, causing congenital hypoxia and coronary heart disease and other organs in the newborn.
Lymphangioma that appeared after birth in a newborn
, gives every reason to suspect that the child has serious impairments in the functionality of vital organs. Over time, complete loss of functionality of individual organs may occur. Based on the fact that the defect during birth affects organs in the head and neck area, the newborn may have problems with the respiratory process and make it difficult to swallow.
The most common complication resulting from developing pathology is lymphatic malformation, formed as a result of any inflammatory process. Complications can arise as a result of otitis media, acute respiratory viral infections, respiratory diseases, and lymphadenitis. One of the severe complications, the likelihood of which increases as a result of the development of a benign tumor in the lymphatic system, is the leakage of lymph into the chest and peritoneum, which poses a threat to the patient’s life.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease may vary depending on where the hemlymphangioma is located. The severity of symptoms is influenced by the degree of development of the pathology, the size of the tumor and the characteristics of the body.
Small tumors cause almost no discomfort. But with bulky tumors, many disorders occur.
Common signs of lymphangioma include:
- swelling in the location area;
- swelling of the skin;
- change color ;
- formation of blisters or ulcers;
- deformation .
Additional symptoms can be varied, due to the different location of the tumor. For example, if neoplasia is near the eye, vision may be impaired, and if it is on the tongue, speech problems may arise. The larger the tumor, the more pressure it exerts on surrounding tissue. This leads to increased symptoms.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Usually the tumor is detected before additional manifestations occur. Such a neoplasm is difficult to miss.
FIBROHISTIOCYTIC TUMORS AND TUMOR-LIKE LESIONS
Xanthoma
A rare disease, most often localized in the skin. Occurs in people with impaired lipid metabolism, usually multiple. Also localized in tendons. Presented by small nodules, partly of the xanthelasma type.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma
A small nodule in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue. Disappears spontaneously.
Fibrous histiocytoma
It is more common in middle age and is localized mainly on the lower extremities. Usually has the shape of a dense knot up to 10 cm, grows slowly. After surgical removal, recurrences are rare.
Forecast
This disease is not life-threatening, and the prognosis, if present, is usually favorable. But this is only true in situations where the pathology was identified at an early stage of its development. Therefore, patients should consult a doctor when the first symptoms are detected. Since the disease often occurs in children, parents need to monitor pathological symptoms.
Timely contact with a doctor allows you to get the necessary help before the tumor can cause significant harm. In most cases, the patient can be cured without consequences.
With the right approach, the tumor is removed, and the child’s further development proceeds according to the norms. Lymphangioma is almost not prone to recurrence - cases of tumor re-formation are less than 10%.
At an advanced stage of the disease, the prognosis is less favorable. It depends on the location of the tumor and its size. If a large tumor is located in a dangerous area, the situation may worsen in terms of complications. But even in these cases, proper therapy can cure the patient and provide him with a normal lifestyle.
Treatment
If the lymphangioma does not cause significant discomfort and is small in size, doctors use observation tactics. As the tumor grows, various complications arise, since the pathological tissue puts pressure on neighboring areas and nerves. In this case, the neoplasia is removed surgically.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Indications for intervention are the following:
- Rapid growth .
- Dangerous location of the tumor.
- Significant deterioration quality of life.
If such circumstances exist, the doctor decides to perform the operation. During this procedure, the tumor is removed completely or partially. This can be done using a laser, electrocoagulation or liquid nitrogen.
Radio wave exposure is also used. Excision is performed only in relation to pathological tissues, trying not to affect healthy areas. To prevent leakage of lymph or re-formation of the tumor, stitches are placed.
A new method of exposure is sclerotherapy. It involves the introduction of special substances into the affected area that cause blood vessels to stick together.
Thanks to this, the feeding of the tumor stops, and the tumor dies. It may leave a small scar, which can be removed surgically. This method of treatment is used for small lymphangiomas located on the face.
Chemotherapy is almost never used for this disease due to its low effectiveness. The inflammatory process in lymphangioma is treated using conservative methods.
The main group of drugs used is anti-inflammatory. They stop the pathological process and relieve negative symptoms. In addition to these, antibiotics are prescribed to destroy the source of infection.
It is advisable to use both systemic and local medications. If necessary, agents are used to help remove toxic substances from the body. It is also important to strengthen the immune system, which is done with the help of biostimulants and vitamins.
Conservative therapy can be changed as preparation for surgery or to consolidate the results.
BENIGN TUMORS OF MUSCLE TISSUE
Tumors of muscle tissue are divided into smooth muscle tumors - leiomyomas, and striated muscle tumors - rhabdomyomas. Tumors are quite rare.
Leiomyoma
Mature benign tumor. Occurs at any age in both sexes. It is often multiple. The tumor can become malignant. Treatment is surgical.
Leiomyoma, developing from the muscular wall of small vessels - small, often multiple, poorly demarcated and slowly growing nodes, often with ulcerated skin, is clinically very similar to Kaposi's sarcoma.
Genital leiomyoma is formed from the muscular lining of the scrotum, labia majora, perineum, and nipples of the mammary gland. May be multiple. Cellular polymorphism is often observed in the tumor. Hormone dependent. Treatment is surgical.
Angioleiomyoma from the trailing arteries
Clinically, a sharply painful tumor that can change size under external influences or emotions. The sizes are usually small, more often found in older people, on the limbs, near the joints. It is characterized by slow growth and a benign course.
Rhabdomyoma
A rare mature benign tumor based on striated muscle tissue. Affects the heart and soft tissues. It is a moderately dense node with clear boundaries, encapsulated. Metastases of rhabdomyoma have not been described. Relapses are extremely rare. Microscopically, 3 subtypes are distinguished - myxoid, fetal cell and adult. Rhabdomyoma of the female genitalia is also distinguished. The adult type mainly recurs.
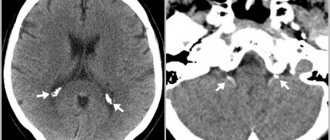
Diagnostics
The suspected diagnosis can be confirmed using special procedures. But initially the doctor must collect anamnesis and conduct a visual examination. He should also find out what symptoms are present. Based on this, it can be assumed that the patient has lymphangioma.
You can verify the presence and establish the main features of the pathology using the following methods:
- MRI;
- CT;
- Ultrasound;
- echography;
- lymphography.
Echography is most often used to examine children. This is an informative method that does not cause discomfort to the subjects.
To study the structure of neoplasia, puncture and histological examination are used. Based on its results, the main features of the tumor are revealed. This also makes it possible to detect the inflammatory process in lymphangioma.