Non-menstrual bleeding from the genitals is a sign of uterine bleeding. This pathology is a dangerous symptom of gynecological diseases.
Appointment with a gynecologist - 1000 rubles. Comprehensive pelvic ultrasound - 1000 rubles. Appointment based on ultrasound or test results - 500 rubles (optional)
You cannot hope that the bleeding will stop on its own: due to blood loss, anemia will begin, and the cause of the discharge will become chronic. The result will be infertility, purulent inflammation, atrophy of the tissues of the uterus and adjacent organs, cancerous tumors and other dangerous pathologies.
Symptoms of uterine bleeding
The content of the article
Any discharge of blood from the vagina other than normal menstrual flow is considered bleeding.
In this case, two menstrual disorders are distinguished:
- Menorrhagia , which is heavy uterine bleeding that occurs at regular intervals (during menstruation);
- Metrorrhagia is irregular bleeding.
Pathological (disease-related) discharge can be distinguished from physiological discharge by several criteria. Characteristic symptoms of bleeding:
- Rich color due to blood admixture: blood red, scarlet, burgundy;
- Duration: bleeding begins outside the menstrual period (metrorrhagia) or menstruation lasts longer than normal - from 5 days (menorrhagia);
- Consistency: discharge may contain blood without impurities, blood with mucus impurities or inclusion of dark burgundy or burgundy-gray clots;
- Smell: not typical of menstrual discharge - during uterine bleeding, the discharge smells like blood, spoiled fish, meat, etc.
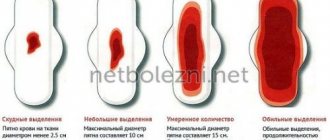
The volume of discharge in menorrhagia and metrorrhagia is also different:
- During menstruation (menorrhagia), the discharge is very heavy - about 80 ml per day (hygienic products have to be changed more often than after 2-3 hours);
- Outside of menstruation (metrorrhagia), the volume of excretion varies - blood smears (in common parlance - daub), drips or continuously flows.
- With persistent menopause, even a drop of blood is pathological.
Uterine bleeding is accompanied by symptoms of diseases associated with blood loss. The woman suffers from: dizziness, weakness, flickering spots in the eyes, ringing in the ears, shortness of breath, increased heartbeat. Gradually the symptoms intensify, fainting is possible. At the same time, pathology makes itself known - the cause of bleeding. Most often, abdominal pain begins, temperature rises, etc.
Treatment and reasons for choosing a therapy method
Treatment depends only on the underlying cause of the bleeding. Once identified, drug therapy (dysfunctional causes) or surgical intervention (malignant formations) may be required.
A woman should always choose the most appropriate treatment, including taking into account her age or her desire to have children. This allows you to increase patient adherence to therapy, as well as achieve maximum success.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Causes of menorrhagia and metrorrhagia
Uterine bleeding is a symptom of diseases of the uterus, ovaries and pregnancy pathologies.
Causes of bleeding outside of pregnancy:
- Injuries received during gynecological procedures - examinations, abortions, diagnostic curettages, removal of tumors, etc.;
- Cervical erosion, which is an ulcer at the entrance to the organ;
- Hormonal disorders resulting from the growth of polyps, endometrium - the mucous membrane of the uterus, etc.;
- Inflammation of the uterus, ovaries;
- Chronic STIs;
- Cancerous tumors of the uterus, fibroids, ovarian cysts.
Causes of bleeding during pregnancy and after childbirth
Bleeding during pregnancy, even a slight one, indicates the onset of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, frozen pregnancy, or premature birth.
The causes of such complications during pregnancy are pathologies of the uterus, cervix, hormonal disorders, fetal diseases (genetic, leading to miscarriage, or infectious).
After childbirth, bleeding is associated with postpartum complications - ruptures, injuries, uterine inversion.
Causes of bleeding during menopause
After the extinction of sexual function - during menopause - the hormonal background of a woman changes. On this basis, diseases associated with a lack of certain hormones develop. This includes various tumors, polyps, cysts, endometrial growths, uterine prolapse, etc. A symptom of all these pathologies is discharge mixed with blood.
Causes of sudden and severe bleeding
- Uterine trauma
. Such injuries can be caused by rough sex, especially rape, criminal surgical abortions (they are done through acquaintances in underground conditions, when gynecologists refuse to operate due to timing or contraindications), etc. - Miscarriage
. If a woman has lost her child and does not go to the clinic, severe uterine bleeding is possible. - Polyp torsion, cyst rupture, tube rupture during ectopic pregnancy. All these conditions are also accompanied by severe uterine bleeding.
Bleeding during menopause
Menopause is a natural physiological process. You shouldn’t be overly emotional or wary about him. But at the same time, a woman during menopause needs to listen to her condition so as not to miss truly significant and alarming symptoms. One of them is bleeding.
Uterine bleeding during menopause may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the hormonal system, the occurrence of tumors in the body of the uterus or in the ovaries. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the disease using ultrasound and tests.
I would like to say a few words about bleeding during sexual intercourse. If this symptom appears, you should definitely consult a doctor. They may indicate cervical disease, be a manifestation of endometriosis, as well as vaginal pathology. In some cases, spotting during sexual intercourse may be associated with dryness of the vaginal mucosa, for example, during the postmenopausal period. In any case, to clarify the diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
First aid for uterine bleeding
It is impossible to cure the pathology on your own, as well as to identify the cause of this condition. Therefore, you need to contact a gynecologist and undergo a series of studies: tests and ultrasound.
In case of severe bleeding, when the blood flows without stopping, you need to call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, you need to provide first aid to the patient. It consists of the following actions, you can:
- Lay the patient on a flat surface, placing a pillow under her feet - they should be approximately 20 - 30 cm above body level;
- Apply a cold object (for example, a bottle of cold water) to the lower abdomen;
- The patient should be given sweet drinks.
If you are pregnant, you should call an ambulance in any case.
Common systemic causes
These are systemic pathologies that can affect several systems, which among the symptoms can also produce vaginal bleeding.
For example:
- bleeding disorders such as hemophilia A and B, von Willebrand disease, platelet function disorders;
- leukemia and lymphomas;
- liver failure;
- renal failure;
- severe dysthyroidism.
An important and fundamental classification for tracking the various causes of vaginal bleeding is the classification by age group.
Diagnosis of the causes of menorrhagia and metrorrhagia
The gynecologist determines the cause of bleeding based on test results and ultrasound.
- A gynecological examination in a chair will show whether there is prolapse of the genital organs, neoplasms or erosion on the cervix. During pregnancy, cervical insufficiency is clearly visible. Also, already at this stage, injuries from the spiral, after sexual intercourse, etc. are visible;
- Colposcopy. A gynecologist conducts an examination with a device equipped with magnifying glasses. Using a colposcope, internal pathologies of the cervix are identified, and the nature and stage of erosion is determined.
- An ultrasound of the uterus will determine whether there are injuries, neoplasms, or inflammation of the female internal organs.
- Smears for microflora and cytology show STI infections (STDs), precancerous conditions, and cancer.
- A blood test for hormones will determine whether there is a hormonal imbalance.
If this is not enough, you will have to undergo an MRI (tomography) to obtain images of the organs in 3D format at high magnification.
The main causes of vaginal pathological bleeding
There are many causes of vaginal bleeding, but they can generally be grouped into 5 broad categories:
Complications during pregnancy (sometimes undiagnosed, that is, which the woman does not yet know about) include:
- abortion (miscarriage);
- ectopic pregnancy;
- gestational trophoblastic disease.
Dysfunctional reasons:
- anovulatory cycles;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- less often metrorrhagia.
Benign organic pathologies:
- uterine fibroids;
- uterine polyps;
- adenomyosis;
- endometriosis;
- genital infections.
Malignant organic pathologies:
- endometrial cancer;
- cervical cancer;
- vaginal cancer;
- sarcomas.
Common systemic causes:
- blood clotting pathologies;
- leukemia;
- hypothyroidism;
- liver and kidney failure.
Spotting may occur during the first cycles of taking hormonal contraceptives (birth control pills) and after using the hormonal IUD.
Treatment of bleeding in menorrhagia and metrorrhagia
First of all, the gynecologist stops the bleeding. Pregnant women are prescribed drugs that relax the uterus and hormones that stop a miscarriage. The rest of the women are prescribed various hemostatic drugs, hemoglobin-supporting drips are placed, and in severe cases a blood transfusion is required.
At the same time, the disease itself is being treated. Depending on the cause, antibiotics and hormones may be taken. If neoplasms or erosion are detected, surgery is performed to remove polyps or fibroids, cauterize the erosion, curettage the uterus, etc. The list of possible measures is endless.
It is important to understand that only a timely visit to a gynecologist, high-quality diagnosis and effective treatment will help stop bleeding and get rid of the disease. Advanced pathologies accompanied by bleeding lead to removal of the uterus, infertility and severe purulent inflammation, since blood and lack of air in the uterus are an ideal environment for the development of putrefactive bacteria.
Treatment of bleeding during pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy is dangerous - it is a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, the onset of a miscarriage or early labor. If you notice discharge, especially accompanied by nagging pain (abdomen, lower back), you need to call an ambulance. You need to lie down until the ambulance arrives. You can take a No-shpa tablet, which relieves uterine spasms.
Treatment for bleeding during pregnancy depends on the cause:
- Ectopic pregnancy .
Pregnancy outside the uterus is a common occurrence, and only an obstetrician-gynecologist can distinguish it from normal. Severe bleeding with an ectopic is a sign of rupture of the organ where the fetus has taken root. In this case, an urgent operation is performed. - Miscarriage or premature birth
. At first a slight spotting appears, after a while the discharge intensifies. This occurs when the cervix opens and the fetus comes out.
With timely treatment, pregnancy can be saved. The gynecologist will prescribe hormonal medications and vitamins that relax the uterus. If a miscarriage occurs, the uterus is curetted. If this is not done, the remaining placenta will fester, resulting in blood poisoning.
Treatment of bleeding after childbirth or surgery
Discharge after pregnancy should last no longer than 2 weeks. Symptoms such as abdominal pain and an unpleasant smell of discharge indicate that inflammation of the uterus has begun. If you have such symptoms, contact your gynecologist. The doctor will take swabs for infections and perform an ultrasound of the pelvis.
Pathological uterine bleeding after childbirth is a sign of inflammation, non-healing wounds, incomplete passage of the placenta and other complications after pregnancy. Treatment in this case also depends on the cause. Strong antibiotics are often needed. Therapeutic curettage may be required. With timely help, problems go away and the body recovers. Advanced pathology guarantees peritonitis - purulent inflammation of the uterus and peritoneum.
Treatment of bleeding during menopause
The first stage of menopause lasts up to 2 years. During this period, scanty discharge, similar to menstruation, is not dangerous. Heavy bleeding or blood after the onset of persistent menopause is a consequence of tumors, prolapse of internal organs and other processes associated with the aging of the body.
The gynecologist will prescribe blood tests for coagulation and tumor markers (indicating cancer), and conduct an ultrasound of the pelvis. If tumors are found, a biopsy will be required.
To treat bleeding during menopause, a modern technique is often used - hormone therapy, and tumors are removed. If everything is really bad, the uterus is removed. After menopause, it is quite possible to live without this organ.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on observation of symptoms and the general clinical picture associated with the use of instrumental studies.
Gynecologist assesses bleeding characteristics:
- duration;
- intensity;
- associated symptoms;
- main pathologies.
If the bleeding is quite cyclical and regular, it is likely due to benign organic lesions or anovulation. If bleeding is irregular, the possibility of malignancy should also be considered.
Blood tests are performed to assess whether the patient has anemia, which in severe cases requires supportive care, including blood transfusion.
Blood tests
From an instrumental point of view, the gold standard for diagnosing vaginal bleeding is transvaginal ultrasound, which can identify both benign and malignant organic lesions, evaluate the characteristics of the endometrial mucosa and any changes in the ovaries.
The ultrasound results may then require other methods such as
- CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis;
- Nuclear magnetic resonance;
- In case of organic lesions - hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy.
But first of all, the possibility of pregnancy is always excluded using an hCG test.
Is it possible to cure uterine bleeding with folk remedies?
Uterine bleeding is a symptom of a huge variety of diseases and requires especially careful attention due to the likelihood of serious consequences for life and health. Any discharge of blood from the vagina that is not associated with normal menstruation should be taken as a reason for an urgent visit to a gynecologist.
Having noticed signs of uterine bleeding, many women try to treat themselves, resorting to traditional medicine, which can lead to tragic consequences. Folk remedies against uterine bleeding, such as infusions of nettle, viburnum, horsetail and shepherd's purse, do demonstrate some effectiveness, but are used only as an addition to the main therapy after consultation with the attending physician.
Malignant organic pathologies
They most often occur in the perimenopausal period and consist of malignant tumors of the genital organs. Most common:
- cervical cancer (the most important risk factor is human papillomavirus infection);
- endometrial cancer;
- ovarian cancer;
- cancer of the vagina and vulva.
Ovarian cancer
These are pathologies with a very poor prognosis if they are not recognized in time and treated.
About the disease
Gastrointestinal bleeding is an extremely dangerous sign. We are talking about the leakage of blood that comes out of damaged vessels and enters the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Bleeding is considered a complication of inflammatory and chronic diseases. It is often caused by alcohol and drug intoxication of the body.
The sources of hemorrhage are the stomach, intestines, and esophagus. The disease is as common as appendicitis. Often this phenomenon occurs as a complication of duodenal ulcers, chronic gastritis, and the appearance of neoplasms.
We recommend diagnosing gastrointestinal bleeding at the medical institution “KDS Clinic”. All examinations are carried out using modern technical equipment and innovative techniques. The disease will be diagnosed even at an early stage.