- MagniuM
- Articles
- Magnesium norm
|
|
Date of publication: 06/28/2019
Magnesium is one of the most important microelements for maintaining normal functioning of the human body. Therefore, our body needs a daily supply of magnesium. Since every second person suffers from hypomagnesemia, the issue of eliminating it is more pressing than ever. We have combined the results of clinical studies, so from our article you will receive comprehensive information about magnesium, its level and the role it plays for health.
What functions does magnesium perform in the human body?
With a lack of Mg, disturbances in the functioning of most organs and systems are observed, because it is found in bone and muscle tissue, in the blood and brain cells. More than three hundred biochemical processes in the human body, including metabolism and the formation of enzymes, cannot occur without it. The mineral also participates in metabolic processes at the cellular level, promoting the breakdown of glucose.
It is indispensable during the period of active growth for children and adolescents, playing a major role in the structure of cells. After injuries, illnesses and surgical interventions, Mg participates in the restoration of the body, helping in the absorption of necessary vitamins, minerals and removing waste and toxins. These are B vitamins, calcium, potassium, ascorbic acid.
The work of the endocrine system cannot do without this useful substance. It affects the hormones that are responsible for the absorption of calcium and promotes the transport of calcium to organs and tissues. By interacting with each other, Ca and Mg qualitatively improve the structure of blood vessels and make them more elastic and strong. In addition, the microelement has a relaxing effect on muscle tissue, promoting the dilation of arteries and blood vessels. Because of this, blood circulates more actively between organs and systems, delivering useful substances to them.
In addition, the mineral performs many other functions.
- Accelerates tissue regeneration processes.
- Activates the process of muscle growth.
- Promotes the removal of cholesterol and bile.
- Prevents the formation of stones and sand in the gall bladder and kidneys.
- It has a calming effect on the nervous system.
- Normalizes intestinal function.
- Regulates blood sugar levels.
- Stimulates the functioning of the heart and cardiovascular system.
- Activates brain activity.
- Stabilizes blood pressure.
- Positively affects the respiratory system.
If a person does not have a deficiency of Mg, then he can tolerate physical activity and stressful situations much easier than people suffering from hypomagnesemia.
Mg has a significant effect on the nervous system, having a calming effect. Under its influence, nervousness and anxiety go away, sleep normalizes, migraines go away, concentration increases, and memory improves.
Interpretation:
- Dehydration, renal failure, adrenal insufficiency, Addison's disease, hypothyroidism, systemic lupus erythematosus, tissue trauma, multiple myeloma.
- Malabsorption syndrome, kwashiorkor, low-calorie diet with insufficient protein content, acute pancreatitis, hypoparathyroidism, chronic alcoholism, chronic glomerulonephritis, hypercalcemia of various etiologies, hyperaldosteronism, inadequate secretion of ADH, pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester, idiopathic hypomagnesemia.
Sample result (PDF)
Negative consequences of magnesium deficiency in the body
The lack of a substance affects the functioning of the entire body. If a person does not receive enough of the substance through food and water, then he begins to develop a pathology called hopomagnesemia.
Hypomagnesemia is a deficiency of Mg in the body. It can be primary (congenital) and secondary (acquired during life).
The disease can also develop due to poor absorption of the element. In pathology, the following clinical picture is observed:
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart and cardiovascular system - arrhythmia, heart attacks, heart pain, loss of elasticity of blood vessels, heart attack;
- blood pressure surges, high blood pressure, stroke, blood clots;
- development of urolithiasis and cholelithiasis;
- decreased immunity, poor antibody production;
- disorders of the digestive process;
- muscle spasms and cramps;
- disruptions in the endocrine system, changes in hormonal levels;
- brittle nails and hair, fragility of teeth and bones.
The nervous system reacts to Mg deficiency with a number of symptoms. This:
- migraine;
- insomnia;
- chronic fatigue;
- memory impairment;
- decreased concentration;
- depression;
- unreasonable fears, constant anxiety;
- irritability, nervousness.
Often, patients with hypomagnesemia complain of excessive appetite, and the main dishes in their diet are sweets and baked goods. The reason for this is decreased sensitivity to insulin, which arose as a result of a serious deficiency of the mineral. Therefore, additional risks with pathology are the development of diabetes mellitus and excess weight gain.
Disturbances in the form of abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea are also possible in the gastrointestinal tract.
Panangin
In addition to magnesium, this drug also contains potassium, so Panangin is usually prescribed for heart problems, in particular for rhythm disturbances. This remedy is indicated for elderly people with arterial hypertension. The fact is that while taking blood pressure medications with a diuretic effect, potassium is “washed out” of the body. The medicine should be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor. The maximum daily dose of Panangin is three tablets three times a day, and the course of treatment is a month. In addition to tablets, Panangin is also available in the form of injections for treatment in a hospital. This magnesium and potassium supplement is well tolerated and is quite affordable. Contraindications include renal failure, elevated levels of magnesium and potassium in the blood, as well as severe atrioventricular block. Pregnant women, especially in the first trimester, need to take Panangin with caution to prevent excess potassium.
Panangin
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
As part of complex therapy for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias (mainly ventricular arrhythmias, as well as arrhythmias caused by an overdose of cardiac glycosides);
- to improve the tolerability of cardiac glycosides; — replenishment of potassium and magnesium deficiency when their content in the diet is reduced (for tablets). from 115
5.0 1 review
944
- Like
- Write a review
Magnesium Rich Foods
Photos from open sources
Excess magnesium, symptoms, causes
Less common, but no less dangerous, is hypermagnesemia. Despite all the positive properties of the element, its excess has serious health consequences.
Hypermagnesemia is an excess of Mg in the human body.
Pathology appears as a result of excessive consumption of vitamins and medications enriched with Mg. It can also occur under the influence of certain medications, such as laxatives or antacids.
Renal failure can also cause hypermagnesemia.
The pathology is manifested by dysfunction of the digestive and nervous systems and combines a number of symptoms:
- muscle weakness, sometimes reaching paralysis;
- drowsiness, lethargy, weakness;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite.
Experts call coma and cardiac arrest the most severe consequences of the disease.
Stay normal with Magnium! Find out more →
About preparing for testing
The amount of magnesium is determined using a method that uses a chemical reaction (resulting in the formation of a colored compound) or the atomic adsorption method. The second method is more sensitive and accurate.
It is very important to take a blood test correctly so that the result is correct. To do this, you need to fulfill a number of simple requirements:
- delivery is carried out in the morning, before this you cannot eat anything for at least 6-8 hours;
- a couple of days before the test, you should not drink drinks containing alcohol;
- It is advisable to stop smoking before taking blood, but it would be better if you do not smoke for a couple of days before taking the tests;
- the day before the test, increased physical activity is not recommended;
- a week before blood sampling, you should not eat fried foods or foods containing food additives;
- You should not take medications containing magnesium. If it is impossible to refuse them, be sure to inform the medical institution employee about this.
Blood magnesium tests are taken from a vein. A day later they are ready. If you follow the recommendations listed above, their results will be reliable and you will not have to repeat them.
Daily value of magnesium
The daily dose of magnesium is different for each person. The required amount of the substance varies depending on age, lifestyle, nutrition and other factors. On average, an adult needs 300-400 mg of microelement per day.
Daily value for children:
- up to 1 year – 50 mg;
- from 1 year to 3 years – 92-120 mg;
- from 4 to 8 years – 142-230 mg;
- from 9 to 12 years – 255-410 mg.
The second indicator of the norm indicates the upper limit, exceeding which can have dangerous consequences for the body. But it is also worth remembering that children during a period of intensive growth need an increased amount of the element, which is necessary for the formation and strengthening of muscles and bones.
Daily value for women:
- from 14 to 18 years – 350-650 mg;
- from 19 to 30 years – 320-620 mg;
- from 30 years – 330-600 mg.
As can be seen from the indicators, girls during growth and puberty also need more minerals.
Daily value for men:
- from 14 to 20 years – 400-700 mg;
- from 20 to 30 years – 380-680 mg;
- from 30 to 50 years – 450-750 mg;
- from 50 years – 450-750 mg.
Due to the fact that men have a faster metabolism, they need to receive more micronutrients during the day.
Women during pregnancy and lactation need an increase in the daily dose of Mg, because during this period they provide vitamins and vital elements not only to themselves, but also to their child. Thus, pregnant women need to receive from 420 to 700 mg of the substance throughout the day. Depending on the age of the expectant mother, this figure may change slightly. Young girls under 30 years of age need 30-40 mg less Mg per day than women over 40 years of age.
Girls and women need to receive approximately the same amount of the substance during breastfeeding. As in the previous case, the indicator will vary slightly depending on the age of the nursing mother. On average, a woman during lactation needs from 420 to 650 mg Mg.
Mg is very important for a pregnant woman. If a gynecologist detects a lack of it, then you should not neglect his recommendations to increase the level of the useful substance in the body.
Scientists have proven that the trace element helps in the transfer of genetic material from mother to child. It is also involved in the formation of the DNA molecule. Therefore, a doctor can prescribe a woman to take the mineral even before conception.
After conception, the action of Mg is aimed at ensuring the normal functioning of the placenta, through which it transfers the necessary elements from the mother’s body throughout the entire period of gestation. During this period, the placenta and uterus contain the greatest amount of Mg compared to other organs.
Hypomagnesemia for pregnant women is several times more dangerous, since not only the health of the expectant mother is at risk, but also the life of her unborn child. In the early stages of pregnancy, pathology is dangerous due to improper formation of the musculoskeletal system and heart. Lack of Mg can cause miscarriage.
In later stages, more than 30 weeks, deficiency of the element can cause gestosis.
Preeclampsia is a pathology that occurs in late pregnancy and is manifested by symptoms such as increased blood pressure, edema, cramps, and loss of protein during urination.
In addition, with hypomagnesemia, the body tries in every possible way to compensate for the lack of substance. It begins to take it from the organs where Mg is concentrated in the greatest quantity. As a result, a woman’s bones and teeth become fragile and vulnerable. Quite often, expectant mothers and nursing women experience teeth crumbling, hair falling out, and nails breaking.
Also, Mg deficiency can cause complications during labor, as it negatively affects the muscles. They become less elastic and contract poorly, so the risk of injury during childbirth increases for both the woman and the baby.
During the process of bearing a child, the substance plays a significant role in the body of the expectant mother. It takes part in the formation of the placenta and is indispensable for the structure of protein structures in the baby’s body and the creation of its nervous system. Mg increases the woman’s resistance to stress and takes part in the regulation of uterine tone.
The consequences of hypomagnesemia can be premature maturation of the placenta, gestational diabetes mellitus, disturbances during childbirth, the threat of miscarriage and premature birth.
Supplements or food?
All the experts we interviewed were unanimous on this issue. Why take magnesium supplements at all if you are not deficient when there are so many delicious foods around that are rich in this micronutrient? Here are some examples.
- Dark Chocolate: Approximately 64 mg of magnesium per slice (16% DV).
- Avocado: One medium-sized fruit contains 58 mg of magnesium (15% of the daily requirement).
- Cashews: A 28g handful of cashews provides 82mg of magnesium (20% of the daily requirement).
- Brazil nuts: 100 g (approximately 12-15 pieces) cover the daily requirement for magnesium by 100%.
- Beans: A cup of cooked black beans provides 120 mg of magnesium (30% of the daily requirement).
- Banana: one piece contains 37 mg of magnesium (9% of the daily requirement).
- Salmon: Half fillet weighing 178 g contains 53 mg of magnesium (13% daily requirement).
The benefits of normal food do not end with the fact that it is tastier and more nutritious. There are two more important points.
Compatibility.
Dietary supplements with magnesium cannot be taken together with antibiotics (tetracyclines and quinolones), because magnesium forms poorly soluble compounds with them. Real food has no such restrictions.
Side effects.
When taking supplements, an overdose is possible, which is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms such as nausea, abdominal cramps and diarrhea. And this, in turn, can cause dehydration and loss of magnesium. There is no risk of overdosing on nuts, pumpkin seeds and salmon. Also because in this case a “smart” algorithm works. The body itself regulates the level of absorption: it increases from an average 30-40% to a maximum of 80% if there is little magnesium in foods, and reduces to 25% if there is too much.
Methods for obtaining magnesium
As we have already said, you can get magnesium only through food, drink and taking mineral complexes. This is not a substance whose deficiency can be replenished without doing anything, like, for example, vitamin D, for which you just need to be in the sun.
Water with magnesium
The quality of the water that enters our houses and apartments through a centralized water supply is quite questionable. Not only is it chlorinated. It reaches us through old pipes, the surface of which has been covered with rust and plaque for years and is a fertile environment for the growth of dangerous bacteria. Therefore, talking about tap water as a way to replenish micronutrient deficiencies is pointless.
All mineral waters contain magnesium in a certain amount, but its concentration in them is insignificant, so they can only be called auxiliary actions for saturating the body with this element.
But more recently, Russian scientists have developed innovative mineral water, the action of which is aimed specifically at replenishing Mg deficiency. Healthy water "Magnium" contains the mineral in the most digestible form - magnesium citrate. It is quite difficult to place a citrate molecule in water; the substance is most often found in this form in medications. But as a result of long research and clinical trials, the developers of this water managed to transfer magnesium citrate into water, where it does not disintegrate until it enters the human body. After entering the body and assimilation of the substance, the molecule breaks down into water and carbon dioxide.
The functional drink “Magnium” has no contraindications with the exception of hypermagnesemia, that is, excess content of the element in question in the body.
To obtain a daily dosage of Mg, an adult needs to consume 2-3 cans of water per day. For a pregnant woman, the need increases to 4 cans of Magnium. But it is worth remembering that pregnant women are not recommended to drink more than 1.5 liters of water per day, as this can cause edema. Therefore, drinking Magnium water during pregnancy should be combined with eating foods enriched with the mineral.
Children should limit themselves to drinking one can of Magnium water throughout the day. They need to get the rest of the element from food, since in addition to Mg they also contain a lot of other useful substances necessary for the full growth and development of the child.
other methods
We can also get Mg from food products of plant origin. The greatest amount is found in nuts and peanuts, sunflower and pumpkin seeds, red caviar, oatmeal and buckwheat. The list of products is very wide, so even the most picky gourmet will find something to suit his taste.
In addition, modern pharmaceuticals offer a wide selection of vitamin and mineral complexes containing magnesium in all types and various quantities.
Where to buy MagniuM
About normal indicators
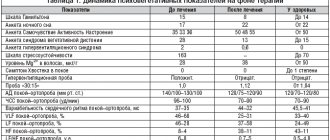
When determining the level of magnesium in the blood, its norm depends on the age of the person. The following table contains microelement indicators that correspond to the norm for a child and an adult:
| Age | Norm mmol/l |
| 0-1 month | 0,66-0,95 |
| 1-12 months | 0,7-1,2 |
| 1-12 years | 0,7-1,2 |
| 12-20 years | 0,7-0,91 |
| 20-60 years | 0,66-1,07 |
| 60-90 years | 0,66-0,99 |
| Over 90 years old | 0,7-0,95 |
For children, the normal level of magnesium in the blood must correspond to the element, since it greatly affects the formation of bones, which is important for the developing organism.
The following table shows the level of magnesium in the blood of women.
| MOTHER AND FATHER | mg/dl | mEq/l | mmol/l |
| Not pregnant | 1,5-2,3 | 1,25-1,9 | 0,63-0,95 |
| Pregnancy 1st trimester | 1,6-2,2 | 1,33-1,83 | 0,67-0,92 |
| Pregnant women 2 trimesters | 1,5-2,2 | 1,25-1,83 | 0,63-0,92 |
| Pregnant 3 trimesters | 1,1-2,2 | 0,92-1,83 | 0,46-0,92 |