Sudden feelings of fear and panic that appear for no apparent reason are the main symptoms of panic attacks. However, there are people who feel this feeling very often. Their condition is characterized not only by anxiety, but also by intermittent breathing and rapid heartbeat. Why is this happening?
Panic attack: causes, symptoms
This disease can occur due to a number of factors, such as:
- frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- taking narcotic substances;
- diseases of internal organs (heart, pancreas, thyroid);
- constantly being in stressful situations.
In addition, the disease can be transmitted genetically. People whose relatives have suffered from panic attacks have a 15-20% higher risk of developing this disease than others. Also, the likelihood of suddenly experiencing an uncontrollable attack of fear is higher among those who do not lead a healthy lifestyle.
In order to determine the occurrence of such a disease, you need to know its symptoms. The main signs of a panic attack are:
- goosebumps. The release of adrenaline causes blood to move quickly throughout the body. Due to this, people may experience goosebumps and tingling throughout the body, especially near the scalp;
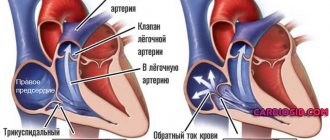
- rapid pulse. A strong heartbeat in an emergency situation is an indicator of a person’s self-preservation instinct, which is a protective function;
- increased sweating. Perspiration may appear on the forehead, above the lip, sweaty palms and armpits;
- frequent breathing. Despite the fact that the lungs are full of oxygen, during a panic attack a person feels as if he is not getting enough air. Therefore, he begins to breathe much more often;
- clouded mind. During an attack, a person loses control over his actions and has little understanding of what is happening around him.
The impact of stressful situations and nervous excitability on blood pressure
Increased blood pressure during stress is easily explained from a physiological point of view. The body perceives the situation as dangerous, and immediate action must be taken. During periods of anxiety and at times of strong feelings, hormonal levels change, nerve impulses in the brain indicate the need to speed up the work of the heart muscle in order to speed up blood flow. A sharp increase in hormonal activity increases heart rate, narrows the lumen of the arteries, and reduces the elasticity of their walls, which contributes to increased blood pressure.
When a person cannot control their nerves, the effects on the blood vessels and heart remain constant, further aggravating the situation. Provoking factors are smoking and drinking alcohol, constant lack of sleep, which increases the negative impact and stress.
The danger is that if a person is constantly in a state of stress, then the work of all organs is imposed on him, literally consuming them.
The nervous system cannot return to normal on its own, so medications are often required.
How to return the pressure to normal?
The main thing when a panic attack is approaching is not to panic. Various types of relaxation, physical exercises, breathing exercises, and yoga can help with this.
In addition, solving complex logical problems, reading poetry, and viewing colorful publications will help prevent pressure surges. It is also recommended to have a phone with the numbers of family and friends on hand, as this will help you feel more confident and relaxed in an unfamiliar environment, a stressful situation, or during a panic attack. To prevent pressure surges and panic attacks, contact an experienced doctor I.G. Gernet - the best psychotherapist in Moscow and beyond.
To the list of articles
Other articles
- Symptoms of a panic attack with VSD
- Is obsessive thought neurosis curable?
The difference between hypertension and a temporary increase in pressure
Hypertension is characterized by a gradual course of the disease. The first forms of the disease may be asymptomatic, and a person may not suspect the presence of problems for a long time and may not know that blood pressure is elevated. This stage is called “soft” and is characterized by a variation of 160/100.
A transient increase in pressure occurs sporadically, does not persist and decreases with the exclusion of provoking factors. It is easily corrected with medications; often, to normalize the condition, a person just needs to calm down and rest.
Persistent arterial hypertension has been observed for a long time.
After a stressful situation, there is a sharp increase in performance. If you take 3 measurements within 30 minutes that show no improvement and show that the situation is getting worse, you should take immediate action.
Complications that may occur
A sudden increase in pressure due to excessive stimulation can lead to a hypertensive crisis, which requires urgent hospitalization of the patient. A critical situation occurs when the pressure reaches 210/120. The danger of this situation is associated with the appearance of the following diseases in the body:
- swelling of the airways;
- blows;
- myocardial infarction;
- Cardiac muscle rhythm disturbances.
If symptoms are not relieved in a timely manner, a person may face death. Constant overload of the circulatory system is fraught with many diseases, including failure of the heart muscle, kidneys and liver, and the effect of pressure on the functioning of vital systems can be irreversible.
Prevention of nervous hypertension
Basic preventive measures should be aimed at eliminating the circumstances that provoke increased blood pressure and normalizing the activity of the nervous system. To solve the first problem, it is recommended to learn methods of emotional control and relaxation. After a hard day at work or stress, doctors recommend a mandatory bath, which will wash away all negative emotions from us.
A balanced diet with sufficient minerals and vitamins is essential to keep the body in good shape.
If there is not enough fresh fruit during the cold season, you should turn to vitamin complexes. Fatty, salty and smoked foods and foods with a large amount of preservatives should be excluded from the diet. You should limit your consumption of coffee, strong tea, and blood pressure monitors.
Walking in the fresh air is recommended for people with high blood pressure. Swimming and yoga are very effective. Any physical activity should be dosed and selected taking into account the severity of the disease and the patient’s condition.
How are neurosis, symptoms and signs of its main varieties classified?
The following types of neuroses are differentiated: • Anxiety disorders and phobias in the form of increased anxiety, panic attacks and unreasonable fears (phobias). In the clinic, this type of neurosis is divided into three stages. At the 1st stage, fear arises only in a truly dangerous situation, when the patient is afraid of something, at the 2nd stage - when thinking about the possibility of being in a similar situation again, at the 3rd stage - even when verbally mentioning phenomena, somehow associated with a phobia. The symptoms are dominated by various fears. This may be a fear of contracting some disease (for example, cancer, syphilophobia or speedophobia), which can ultimately lead to hypochondria. Phobias such as claustrophobia (fear of enclosed spaces), agoraphobia (fear of open spaces and crowds), etc. are quite common. • Obsessive-compulsive disorders, manifested in obsessive actions, thoughts, memories and aspirations, perceived by a person as unpleasant and alien. Patients are not able to cope with them on their own. Persons prone to suspiciousness, anxiety and introspection (reflection) are susceptible to this type of neurosis. Obsessive thoughts can manifest themselves in the form of counting steps, passing cars of a certain color, repeated attempts to answer meaningless questions, for example, why there are so many letters in one word, and more or less in another. Particularly difficult to perceive is the obsessive desire to do something shameful and unacceptable, for example, to undress naked in a public place, swear obscenely, or kill a loved one. Obsessive actions (compulsions) can reach the point of absurdity - washing hands up to 100 times a day, returning home multiple times to check that household appliances, gas, or doors are closed. There is also the performance of ritual actions before certain events (look in the mirror a certain number of times before leaving the house, jump or pull your ear, etc.). Only after such rituals can the patient leave home with confidence that nothing unpleasant or terrible will happen to him. • Hysterical reactions, otherwise conversion disorders, accompanied by changes in sensory sensations, disturbances in motor and autonomic reactions, memory loss, etc. Women are more susceptible to hysteria. The signs of neurosis in women are so diverse and changeable that they can resemble many bodily ailments. Hysteria is often called the great malingerer. The predisposition to it is more pronounced in individuals with an overly labile or immature infantile psyche. Hysterical disorder is manifested by such signs as a constant desire to be the center of attention, to play the main role in the team and family, and to dominate others. Hysterics are also characterized by hyper-emotionality, mood swings, a tendency to exaggerate their own role, demonstrative behavior, and elements of theatricality. Those around them often get the impression that a hysterical person revels in his illness, advertises it in every possible way and uses it to attract attention. The extreme manifestation of hysteria is a hysterical seizure, reminiscent of an epileptic one. • Somatoform disorder, otherwise somatic distress disorder, associated with the manifestation of symptoms of a physical disease without the presence of the disease itself. Signs of neurosis in this case most often resemble symptoms of a particular disease. A peculiarity of this type of neurosis is the particular torment and excessive focus of the patient’s attention on somatic manifestations, aggravated by contact with medical workers, which cannot be persuaded either by the results of clinical and laboratory examinations or by medical reasoning. The patient is confident that he has a disease, is deaf to any counterarguments and constantly initiates new examinations, which are practically useless and often expensive. Moreover, the symptoms differ in duration and progressive variability. For example, vegetative-vascular dystonia may be replaced by hypertension, tachycardia may be complicated by arrhythmia, stomach pain may be accompanied by intestinal spasms, etc. Moreover, only one symptom is rarely present; multiplicity is usually characteristic, for example, migrating pain throughout the body, neurosis with dizziness, headaches, high or low blood pressure, tachy- or bradycardia. Autonomic dysfunction of the cardiovascular, respiratory and gastrointestinal systems is often observed. All this significantly reduces the quality of life of the patient himself and his immediate environment. In therapeutic practice, almost every fourth patient has complaints that are not confirmed by a clinical diagnosis. • Neurasthenia – a state of increased intellectual fatigue, headaches with mental stress, inability to completely relax and sleep disturbances. This condition deserves more detailed discussion due to its relevance and impact on mental activity and intellectual abilities.
What to do to be less nervous
Doctors recommend increasing the level of stress resistance in hypersensitive people who are prone to constant unreasonable anxiety. This can be done through special training or consultation with specialists such as a neurologist or psychotherapist. Such people are well influenced by pharmacotherapy and physiotherapy, which help normalize the functioning of the nervous system.
People prone to nervous excitability can resort to the following recommendations.
- You should not plan several important things for one day;
- Learn to focus on what is important and not worry about the little things;
- Plan your day in advance, leaving enough time for unforeseen situations;
- Learn to prioritize, take your time, and understand that 10 minutes won't solve anything in most cases.
In order not to get nervous, it is important to learn to calm down and keep your emotions under control. Such techniques are obtained through relaxation and hypnosis sessions. The latter help to reveal the true causes of human anxiety, which are often hidden deep in the human mind.
Features of the course in men
Neurosis occurs differently in all people. In women, the hysterical variety is more often found. Characterized by unstable behavior, dramatization of situations, tears and screams. Symptoms when treating neurosis in men who require treatment are somewhat different. They are less likely to encounter a diagnosis, but more often progress the condition to its extreme stages. In representatives of the stronger sex, the diagnosis is often associated with overexertion and workaholism. Common features include:
- Aggression. Reactions to familiar things become acute. A man responds to everyday events with anger.
- Low self-esteem. A person does not believe in himself and is afraid to start a new business.
- Strong self-criticism. They place high and sometimes unattainable demands on themselves.
- Inability to adapt to the situation. Even a small failure unsettles a man with neurosis.
Of particular importance for representatives of the stronger sex is such a manifestation as decreased libido. Sexual life is becoming less and less attractive. In addition, there is a complete or partial absence of erection. This leads to the progression of a nervous disorder and forces one to completely withdraw into oneself. It is important that the male half of society has always been distinguished by hushing up its own problems. Hiding the facts and the lack of measures taken also provokes the development of HP in a man.
Outpatient program and remission
In the absence of an aggravating factor, therapy can be carried out on an outpatient basis. Treatment includes identical points:
- Attending psychotherapeutic sessions in accordance with the approved schedule;
- Taking medications according to indications as needed;
- Treatment of the underlying provoking disease, if present;
- Searching for some kind of “outlet” in hobbies and creativity;
- Gradual return to society.
Neurosis is highly treatable, under the supervision of the attending physician, and quickly fades into the background. Relapses are observed in rare cases, but as part of psychotherapy, the patient is taught to independently cope with anxious thoughts and panic. If you follow all the recommendations, peace and joy will forever take away nervous tension.
Treatment methods
Today there are many methods that can be used to treat and normalize blood pressure. Pharmacological treatment plays an important role; methods of traditional medicine and physiotherapy are used as a supplement. The list of drugs on the pharmacological market is represented by a large assortment, but they cannot be prescribed independently. The course of therapy should be determined by the attending physician based on the results of medical examinations.
Medicines
The doctor gives recommendations on the use of drugs and their dosage. In the first stages of treatment, antihypertensive drugs are not prescribed; recommendations are limited to strengthening the immune and nervous systems, getting more rest and sleep. In the second stage of pathological changes, the use of beta-blockers is indicated.
At the third stage, a complex of antihypertensive drugs may be prescribed. In most cases a combination is used:
- beta-blockers and diuretics;
- ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists.
If the increase in blood pressure is one-time and caused by stress, taking medications with antihypertensive effects requires a careful approach. Taking the drug can cause a sharp drop in blood pressure, fainting, and hypotensive crisis.
Therapy
The difficulty of therapy is that it is often difficult to determine how a person’s emotional state affects blood pressure. Patients often associate deterioration in well-being with excessive fatigue and poor quality of sleep, meaning already advanced forms of arterial hypertension. To exclude difficult situations, doctors recommend constant monitoring of blood pressure readings.
Traditional therapy has the following goals:
- stopping the process of destruction of blood vessels, preventing possible complications;
- normalization of mental state;
- stabilization of blood pressure.
A good therapeutic effect in combination with medications is shown by physical procedures such as massage and acupuncture, which are used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Folk remedies
In order to normalize the mental state, traditional healers recommend taking herbal infusions and tinctures. A good calming effect can be observed when using sedatives such as thyme, peony, and valerian root.
A good effect of lowering blood pressure is observed when taking chokeberry. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to eat 15 berries per day. For treatment, you need to drink blueberry juice for 15 days.
The harm of self-medication
Many people try to get treatment based on advice taken from a dubious website. Following such recommendations and taking measures on your own is extremely dangerous. The following situations may occur in response to improper treatment:
- Progression of neurosis;
- Development of a persistent irreversible disorder;
- The appearance of other chronic diseases;
- Suicidal thoughts;
- Drug poisoning;
- Problems in society;
- Damaged relationships with loved ones and colleagues.