Adolescence is a period of hormonal changes and active growth, and therefore teenagers cannot always sort out their feelings on their own. Because of this, you may miss symptoms that indicate the presence of serious diseases, including heart disease.
The best cardiologists in Rostov-on-Don do not recommend making diagnoses based solely on symptoms, but it is important to know what can signal a malfunction of the heart muscle in order to contact a specialist in time.
Heart diseases
All nosologies in pediatric cardiology are divided into several large groups:
- Congenital heart defects. These are anomalies in the development of the heart, its valves and great (main) vessels that occur in the 2-8th week of intrauterine development. These include defects of the interventricular, interatrial and/or aortopulmonary septa, open atrioventricular canal, ductus arteriosus, stenosis (narrowing) or insufficiency (incomplete closure of the leaflets) of valves, incorrect location of vessels or pathological collaterals between them (connections), absence of an atrium or ventricle, etc. .
- Valvular heart defects. These are acquired pathologies of the valve apparatus - stenosis (narrowing) or insufficiency.
- Diseases of the endocardium - the inner lining of the heart.
- Diseases of the myocardium - the middle (muscular) layer of the heart.
- Pathologies of the pericardium - the cardiac connective tissue sac.
- Pathologies of coronary circulation. This group includes myocardial infarction, Kawasaki disease (vasculitis of medium and small arteries) and anomalies of the origin and number of coronary arteries.
- Pulmonary hypertension. This is an overload of blood in the pulmonary arteries due to increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
- Heart damage due to hereditary diseases. They are the result of errors in the genetic code of the parents' germ cells; these mutations are passed on to the offspring. They can appear from birth or already in adulthood.
- Heart tumors.
- Vascular damage. Most often we are talking about arterial hypertension (increased blood pressure) or hypotension (lowered blood pressure).
- Heart rhythm disturbances are disturbances in the regularity and sequence of heart contractions. If the heart muscle is damaged, its course is distorted, which leads to an abnormal rhythm of heart contraction.
- Heart failure is a syndrome caused by decompensated dysfunction of the myocardium. That is, the heart is so affected that it is no longer able to provide the necessary blood output and supply blood to all organs.
It is important to clarify that heart disease rarely occurs in isolation. One pathology progresses and leads to another. Thus, aortic stenosis will lead to pulmonary hypertension, and infective endocarditis destroys the valves, resulting in defects. After myocardial infarction or inflammation (myocarditis), the conduction of impulses through the affected area is disrupted, and as a result, the normal rhythm of contractions is disrupted.
Causes of tingling in the heart area
Physiological factors
Tingling in the precordial area is possible with strong excitement during acute stress. In such cases, it appears suddenly, is mild and is localized mainly in the left half of the chest. The symptom is often accompanied by a feeling of freezing in the heart, hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet, dizziness, and trembling of the hands. After the unpleasant situation is resolved, the person’s well-being quickly returns to normal.
Neuroses
In most cases, tingling in the heart area is caused by neurological disorders. With cardioneurosis, the patient is bothered by periodic stabbing pain that is not associated with physical activity or time of day. Usually the symptom is provoked by mental overstrain, stress, or a conflict situation. The tingling sensation is moderate, but it seems to the person that it is a sign of severe heart disease.
Unlike organic cardiac diseases, with neurosis, patients tend to describe their sensations in detail: where exactly it stings, how often the symptoms occur, what they are accompanied by. Cardioneurosis is typically characterized by a combination of tingling in the heart area with other autonomic symptoms: sudden bradycardia or tachycardia, sweating, paleness or flushing of the skin.
Intercostal neuralgia
If the intercostal nerves are affected on the left side, many patients describe symptoms as tingling and heart pain. Discomfort increases when touching the ribs, and especially when feeling the intercostal spaces. Strong stabbing sensations appear when taking a deep breath, coughing and sneezing. To relieve symptoms, the person holds a stationary position, slightly bent over.
Tingling in the chest with intercostal neuralgia is observed constantly for several days, its occurrence does not depend on the time of day. Some patients try to relieve pain with nitroglycerin, but the drug does not have any effect. Paresthesia and numbness in the affected area of the chest are also possible. Increased pain is sometimes accompanied by sweating and redness of the skin.
Arrhythmias
Extrasystole is often clinically manifested by tingling in the cardiac region. This type of arrhythmia is characterized by a combination of stabbing sensations with periodic cardiac arrest. The difference from coronary cardiovascular diseases is the absence of irradiation of pain to other parts of the body. Tingling due to rhythm disturbances, as a rule, occurs without a visible provoking factor and does not last long.
Myocarditis
With this disease, tingling usually develops several weeks after a viral or bacterial infection. Discomfort in the heart area appears against the background of deteriorating health - the person complains of weakness, shortness of breath, and increased body temperature. The stabbing sensations with myocarditis are not intense, long-lasting, and do not radiate to the arm or shoulder blade.
Cardiac ischemia
With stable angina, precordial tingling can be felt during the interictal period or at the very beginning of an anginal attack. In IHD, stabbing pains have a clear connection with physical activity (fast walking, climbing stairs) or with a psychologically traumatic situation. The pain lasts about 5-10 minutes and radiates to the arm and left shoulder blade. A pathognomonic sign is relief of the condition after the use of nitrovasodilators.
Joint damage
Unpleasant sensations in the heart area can be caused by arthrosis of the costosternal joints and osteochondrosis. Tingling is provoked by physical activity, sudden turns or bending of the body. When a person sits or lies quietly, the intensity of the symptom decreases. Tingling pain occurs not only in the heart area, but also in the center of the sternum, on the side of the chest.
In addition to tingling, there is numbness and a feeling of “pins and needles in the chest.” Symptoms intensify with deep inhalations and exhalations. Sometimes with osteochondrosis, the above symptoms are combined with pain in the upper abdomen. Patients also complain of difficulty raising their arms, impaired fine motor skills of the fingers, and decreased skin sensitivity.
Rare causes
- Acute coronary syndrome:
unstable angina, myocardial infarction. - Cardiomyopathy:
hypertrophic, restrictive, dilated. - Inflammatory processes
: pericarditis, endocarditis. - Congenital and acquired heart defects.
Etiology
The causes of heart problems in children are conventionally divided into large subgroups. Let's look at each one separately.
Mother's side
If during pregnancy a woman has suffered from rubella, systemic lupus erythematosus, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, if she has diabetes mellitus or other chronic diseases, then all this is reflected in the fetus.
The list of approved drugs for pregnant women is strictly limited; most antibiotics, warfarin and other drugs (they are called teratogenic) are too toxic for the fetus. Taking them increases the risk of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) or various abnormalities in the development of the child.
Drinking alcohol, smoking and using drugs during pregnancy also leads to congenital pathologies in children.
Genetic disorders
Most often these are chromosomal abnormalities. But genetic predisposition and mutations are not considered the only cause of cardiac pathologies. In 90% of cases, the cause of heart problems is multifactorial.
Bad habits
We have already talked about how the state of the mother’s body affects children. But the risk factors for developing heart problems in children are similar to those in adults:
- Smoking;
- Alcohol;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Narcotic substances;
- Stress;
- Infections;
- High cholesterol levels.
This list is more relevant for teenagers 14-17 years old than for kids. However, we must understand that nicotine and ethanol metabolism products destroy the myocardium and vascular wall in a child in the same way as in an adult. “Pampering” behind garages can result in a heart attack at age 30.
Statistics show that over the last decade the percentage of children with excess body weight has increased, which also negatively affects the heart. Myocardial infarction, due to obesity and other risk factors, has become “younger” and is already occurring in girls and boys aged 20-30 years, which was considered casuistry back in the 2000s.
Symptoms
A child who has heart problems may complain of:
- Chest pain (in the area of the heart, possibly radiating to the arm, hypochondrium, or armpit);
- Shortness of breath;
- Rapid heartbeat or noticeable pauses;
- Interruptions in heart function;
- Dizziness;
- Darkening of the eyes and fainting;
- Paleness or cyanosis (bluish coloration of the skin and mucous membranes);
- Acceleration of the pulse or its difference in the hands;
- Poor appetite and short stature;
- Frequent respiratory infections;
- Swelling and pulsation of neck vessels;
- High or low blood pressure;
- Chest deformation, etc.
Symptoms usually begin or worsen after exercise. At first, the child usually does not attach any importance to this, then his endurance begins to suffer, and his condition worsens, which becomes the reason for contacting a cardiologist.
Heart disease in children: what parents should be wary of.
1. In 2021, 211 children died in physical education lessons. If you subtract vacations, holidays and weekends from 273 school days, it turns out that every day a child died in one of the Russian schools. From a medical point of view, sudden death in children can be caused by various reasons - both cardiological with the development of acute heart failure, and diseases of the central nervous system. Parents may not even know that their child has such a problem. However, everything can be diagnosed with a timely visit to a pediatric cardiologist.
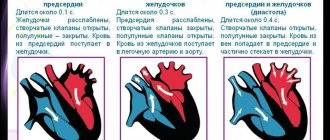
2. According to the medical examination plan, at 1 year, then at 3 years (before kindergarten) and 6–7 years (before school), children must undergo a medical commission, which includes a cardiologist, who is obliged to refer the child for standard studies - EchoCG and ECG. EchoCG (or ultrasound of the heart) allows you to evaluate the functioning of the heart, its anatomical structure, the contractility of the ventricles, and measure the pressure in the cavities, which is necessary to exclude congenital and acquired anomalies of the heart and lungs. An ECG analyzes the functioning of the conduction system of the heart and identifies its disorders, including life-threatening ones. If a child is suspected of having an arrhythmia, the doctor will refer him for further examination - daily ECG monitoring and consultation with a pediatric arrhythmologist.
3. With some undiagnosed heart defects, tragedy can occur even with average physical exertion. But it’s even more dangerous when under-examined children, trying to earn points before admission, decide to pass the GTO standards, which require absolute health and serious preparedness. Therefore, doctors insist that before passing the GTO standards and competitions, children undergo a full cardiac examination (echocardiography, stress ECG, daily ECG monitoring) to exclude life-threatening disorders in the heart.
4. Often, after suffering from viral diseases, myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) and inflammation of the blood vessels of the heart (aortitis, coronaritis) develop. This leads to a decrease in the contractility of the myocardium, disruption of its blood supply (including the conduction system of the heart), to the development of heart failure and life-threatening arrhythmias. Therefore, after recovering from a viral infection (especially a severe one), the child should be released from physical education for two weeks and must undergo an ECG.
5. The causes of fainting can be associated with both cardiac dysfunction (cardiac arrest, vegetative-vascular dystonia), and with pathology of the central nervous system (tumors, epilepsy), diseases of the endocrine system (hypoglycemia, diabetes mellitus), abnormal development of the spine (Kimmerle anomaly) etc.
6. The cardiovascular system of a rapidly growing child's body is extremely vulnerable. In adolescence, many children develop vegetative-vascular dystonia of the vagotonic type - a condition in which there is a tendency to hypotension. A sharp drop in blood pressure can lead to fainting, in which unsuccessful falls can cause fatal brain damage. Therefore, if a child complains of dizziness, headache, or periodically loses consciousness, be sure to consult a specialist and undergo the necessary examination.
7. Another problem is the special nutrition system that teenagers who are concerned about their figure choose. They eliminate fats from the diet and replace meals with protein shakes. However, the exclusion of one food component provokes the early and rapid development of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, leading to myocardial ischemia, the development of acute heart failure and sudden cardiac arrest.
8. There are many children who have had heart surgery at an early age. But they lead a normal life. They participate in sports clubs, as they say, without fanaticism, for their health. But to practice, they, like other children, need to get a certificate from a cardiologist.
9. What parents should be wary of:
- Blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle and the area around the eyes is a sign of deterioration of venous outflow and insufficient blood oxygen saturation.
- Pain in the heart, shoulder blade, left arm.
- Persistent hypothermia is a low body temperature.
- Shortness of breath, which occurs due to blood stagnation and oxygen starvation.
- Cold palms and feet.
- Fatigue after physical activity - the child sits down, sighs, and complains of palpitations.
- Fainting.
10. It must be remembered that hypertension is rarely asymptomatic. Children complain of headaches, dizziness, weakness, fatigue, blurred vision or spots before their eyes. Children with hypertension often have sharply reduced vision. It is very important not to attribute these complaints to overwork, but to consult a doctor in time. The initial forms of childhood hypertension are corrected without medication. Results can be achieved if you normalize the child’s weight, daily routine (the student needs to get enough sleep, he should not get tired or overexcited) and nutrition. It is very important to choose suitable physical activity. The best results are achieved by cardio training (fast walking - 30-40 minutes daily, swimming, cross-country skiing, cycling).
11. But strength training for children with hypertension is absolutely contraindicated. If these measures do not produce results, medications are prescribed, the doses of which are selected individually and can only be discontinued by a doctor.
12. Most often, increased blood pressure worries children in adolescence (13–16 years). Blood pressure standards in children vary depending on age, weight (overweight children have higher blood pressure), height (short children have lower blood pressure) and gender (boys have higher blood pressure than girls). In children under 14 years of age, the average pressure should not exceed 120/80 mm Hg. Art., for older ones – 135/85 mm Hg. Art. Make an appointment with the cardiologist of the Children's Department, Anna Yuryevna Kozhina, by phone. 43-03-03 and 41-03-03 or
Complications
If you have cardiac problems, medical supervision is always necessary. In the youngest patients, the pathology may disappear on its own, but this is a rare occurrence. Teenagers during puberty are often worried about arrhythmia or tachycardia (increased heart rate) - this is the price to pay for hormonal changes; in most cases, everything returns to normal on its own.
Despite the presence of happy outcomes, if a child has heart complaints, you should urgently consult a cardiologist.
Otherwise, complications may arise:
- Secondary arterial hypertension (in the systemic and/or pulmonary circulation);
- Destruction of valves and adaptive changes of the heart (dilatation or hypertrophy;
- Poor circulation (other organs suffer, ischemia occurs - insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues);
- Heart attack;
- Pneumonia;
- Heart failure.
Death is a common result of heart pathologies, especially with congenital defects.
Online consultation with a pediatrician
consultation cost: 500 rubles
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
A common disease is cardiac arrhythmia in a child.
Heart rhythm disturbances in children account for a quarter of all diseases in children under 3 years of age. Also, manifestations become more active at the age of 11–13 years, when the child is actively growing. It is extremely important to constantly visit a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov, who will listen to the rhythm during the appointment and, if necessary, prescribe an ECG or ultrasound of the heart. If heart rhythm disturbances in a child are not treated in time, it will develop into arrhythmia, which is becoming more and more difficult to overcome every year.
In second place in the number of patients with childhood heart disease are congenital disorders.
Some childhood heart diseases, such as mitral valve prolapse or myocarditis, may appear 2-4 weeks after viral infections such as:
- measles;
- diphtheria;
- herpes;
- flu;
- angina
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections with complications.
After the active stage of the disease and during the recovery period, it is necessary to visit a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov, who will prescribe the necessary tests and examinations, as well as formulate comprehensive heart prevention to minimize the risk of developing disorders. Children's heart disease in the form of extraneous noise against the background of neoplasms can be triggered by rheumatism, which manifests itself after a sore throat.
Diagnostics
At each appointment, the pediatrician conducts auscultation (listening with a phonendoscope) and examination of the chest to check the functioning of the child’s heart, even if the patient came in for ARVI. Pathological murmur is easily auscultated by a cardiologist. It indicates heart problems, even if the patient is not worried about anything or does not attach importance to some symptoms (in addition, children are sometimes afraid to report their problems and worries).
Basic diagnostic methods in cardiology:
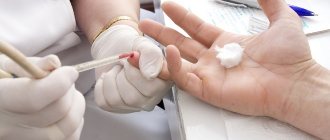
- ECG (assessment of the conduction of electrical impulses through the heart muscle);
- Daily ECG monitoring;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- Echo-CG (study of the morphology and functional state of the heart);
- Doppler echo-CG (study of blood flow in the chambers of the heart and great vessels);
- Plain radiography of the chest (determining the size and location of the cardiac shadow);
- Coronary angiography (study of coronary vessels);
- CT;
- MRI.
It is important to identify the disease in time: the earlier treatment is started, the better the effect. However, most violations can only be detected using special equipment. In addition, the baby is not able to voice complaints, so instrumental diagnostics in pediatrics cannot be avoided.
What may indicate childhood heart disease?
First of all, it is painful sensations in the sternum, as well as in the back in the area between the shoulder blades. Sometimes the pain is so severe that it may be symptoms of coronary artery disease. As a rule, pain appears after active activities or sports, and can sometimes become more active at night when the body is in an uncomfortable position. Among the additional symptoms that indicate that you urgently need to visit a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov are:
- persistent cough;
- frequent fever;
- dyspnea;
- the child complains of headaches;
- severe motion sickness in transport;
- increased fatigue.
During your appointment, an experienced cardiologist will carefully listen to the heart’s function to determine whether the child has a heart rhythm disorder. Heredity is taken into account, as well as:
- how the pregnancy progressed;
- were there any complications during childbirth;
- whether there have been previous infections.
Self-diagnosis
To independently diagnose the state of the cardiovascular system, functional tests are carried out: Martinet-Kushelevsky, Kotov-Deshin, Rufier, with a 15-second run at the fastest pace, and others. You can familiarize yourself with the sampling methodology in the relevant articles on the Internet.
These are simple tests to roughly assess the adaptation of the heart and blood vessels to stress. In schools and universities, they are carried out in special medical physical education groups to monitor the well-being and fitness of students.
Treatment
Therapy depends entirely on the specific nosology. Infectious endocarditis and pericarditis are treated with drugs, but tumors or defects require surgical intervention, otherwise the child will grow, and with it pathological holes (or neoplasms) in the organ, which will lead to death.
Conservative treatment
Non-drug methods are recommended for all patients with a predisposition to or presence of cardiac problems. They include:
- normalization of work and rest regimes;
- 8 hours sleep;
- regular moderate physical activity;
- control of salt intake;
- weight loss (if you are overweight);
- avoiding alcohol and smoking;
- changing your diet towards proper nutrition.
Specific drug therapy depends on the cause of cardiac dysfunction. Main groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics (for bacterial etiology);
- Antihypertensives (Beta blockers, diuretics, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers dilate blood vessels to lower blood pressure);
- Cardiac glycosides (to restore cardiac conduction and contractility);
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (suppress inflammation);
- Immunosuppressors (for autoimmune processes), etc.
Surgery
The surgeon restores the heart rhythm by implanting a pacemaker. The batteries for it are changed every 5-7 years during repeated surgery.
All affected valves are replaced with artificial ones. In severe cases, a heart transplant is required.
Pediatric heart disease at birth
The most common condition of heart development, which is diagnosed by a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov at a very early age: patent foramen ovale. As a rule, it closes by 12 months, but it is possible at a later date (up to 5 years). This condition requires examination to exclude congenital heart disease - atrial septal defect, since in this case surgical treatment is required. The operation is simple, and the recovery period after this procedure does not take more than a month. Many childhood heart diseases can be treated and corrected, and you can give your child a normal, full life.