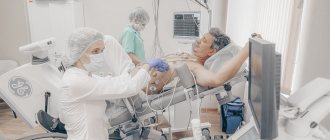
The Harvard step test is a simple and non-requiring technique used to determine the fitness of the heart muscle in healthy people who are professionally involved in sports or engaged in work (firefighters, rescuers, military personnel, etc.) that requires significant physical endurance. This method can be used starting from the age of 8; there is no upper age limit for the technique.
The Harvard Step Test was first proposed in 1942 by scientists from Harvard. To conduct it, experts used a bench 40-50 cm high, on which the subject had to climb, a stopwatch and a metronome that counted 120 beats in 1 minute. During the test, which takes 2-5 minutes, a person steps onto the platform first with one foot and then with the other. After this, he descends from the bench in the same way. Each step must correspond to the beat of the metronome. After this, the specialist calculates the pulse and uses a special formula to calculate an index that reflects fitness. Initially, this technique was used to assess the physical condition of Marine Corps conscripts.
The essence of the method
The essence of the test is as follows: the patient's pulse is measured, after which he performs a certain load, after some time after which the pulse is measured again and assessed to what extent it has returned to normal.
Normally, the pulse of an adult corresponds to 60-80 beats per minute. At this heart rate, the body receives a sufficient amount of blood to ensure the functioning of organs and skeletal muscles. During physical activity, the need for blood flow increases due to active muscle work, and the heart begins to contract more often.
In a well-trained person, after physical activity, the pulse returns to normal levels after a certain time, usually this happens within a few minutes or within half an hour. The heart rate stabilization interval depends on a person’s fitness, and Harvard scientists have created a formula for calculating an index that evaluates fitness.
Heart rate monitoring
When you first begin an aerobic program, it is very important to periodically monitor your heart rate during exercise. As your level of preparation improves, it will be enough to do this at the end of each lesson.
To help you calculate your target heart rate range for 10 seconds, you can use a table.
Table "Determining the target heart rate range in 10 seconds":
| Age heart rate heart rate \v | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 |
| 50 | 21-28 | 21-27 | 20-26 | 20-26 | 20-25 | 19-25 | 19-24 |
| 55 | 22-28 | 21-27 | 21-27 | 20-26 | 20-25 | 20-25 | 19-24 |
| 60 | 22-28 | 22-28 | 21-27 | 21-26 | 20-26 | 20-25 | 20-24 |
| 65 | 23-28 | 22-28 | 22-27 | 21-26 | 21-26 | 20-25 | 20-24 |
| 70 | 23-29 | 23-28 | 22-27 | 22-27 | 21-26 | 21-25 | 20-25 |
| 75 | 23-29 | 23-28 | 23-28 | 22-27 | 22-26 | 21-26 | 21-25 |
| 80 | 24-29 | 23-28 | 23-28 | 23-27 | 22-26 | 22-26 | 21-25 |
| 85 | 24-29 | 24-29 | 23-28 | 23-27 | 23-27 | 22-26 | 22-25 |
| 90 | 25-29 | 24-29 | 24-28 | 23-28 | 23-27 | 23-26 | 22-26 |
How to check your fitness test results:
Step 1: Find the column that matches your age.
Step 2: Find the line that corresponds to your resting heart rate.
Step 3. Move your finger down the age column and find the intersection of this column with the line that shows your heart rate.
The first number is the recommended lower limit of the heart rate range during exercise (50% heart rate reserve).
The second is the recommended upper limit for exercise with increased oxygen metabolism that affects the heart (75% heart rate reserve).
For example, if you are 25 years old and your resting heart rate is 80 beats per minute, then your heart rate during exercise should be between 23 and 28 beats per 10 seconds. As mentioned, this actually ranges from 138 (23 • 6) to 168 (28 • 6) heart beats per minute.
As your fitness improves, your heart rate will return to your resting level more quickly after vigorous exercise. You can use this to determine your fitness level. To do this, you need to develop the habit of monitoring the degree to which normal heart rhythm is restored some time after finishing exercise.
The time between the end of classes and measuring the pulse is from 2 to 5 minutes. Your measured heart rate will fluctuate from activity to activity, but as a trend you will notice a decrease in changes in heart rate recovery, indicating an improvement in your fitness.
In addition to an objective assessment of the impact of the load on students, there is a subjective assessment, which is based on sensations and external signs. The main indicators here are complexion, sweat production, breathing, coordination of movements.
When you feel well, your complexion is pink, matte, with redness. If you feel unwell, the face becomes pale or there is severe redness, and spots appear on the face.
Sweating. When the exercisers are feeling well, they perspire; when they feel bad, they sweat profusely.
Breathing is rapid, deep, rhythmic, if the load is tolerated well. Breathing is shallow, arrhythmic through an open mouth with poor exercise tolerance.
Indications
The Harvard Step Test is more often recommended for athletes. In addition, it can be performed when starting training in fitness centers to determine a load program or when applying for a job that requires a sufficient level of physical fitness.
The Harvard Step Test is used for the following purposes:
- assessment of the athlete's preparedness;
- assessment of physical condition when an athlete returns to sports after a long break;
- selection of athletes for competitions;
- development of an individual training program;
- assessment of the effectiveness of physical activity;
- professional examination of emergency workers or military personnel.
What to do with test scores?
1. If you have an excellent or good level of fitness, your workouts can include a minimum of low-intensity cardio. And this also means that the doors to strength training, circuit training and interval cardio training are open for you. You will be able to withstand these methods quite easily, and they will bring you very noticeable results, since the intensity of the training can be quite high.
2. If your level of fitness is close to average, therefore, your training must be supplemented with low-intensity cardio training to increase the stroke volume of the heart. This means that three times a week you need to conduct at least half an hour of training in the aerobic zone, which can be determined using this calculator: calculation of individual load zones. A tangible result (measured by a step test) from these classes will be noticeable after 2 or more months.
Preparation before the test
No special preparation is needed to take the Harvard Step Test. The subject should know that 24 hours before the procedure he should not take drugs affecting the heart. Persons taking the test for the first time are introduced to the technique of performing it.
On the morning of the procedure, you can have breakfast, but remember that overeating can distort the results of the study. Before testing, you should wear comfortable clothing that does not restrict movement and breathing. Sports shoes are put on your feet.
Defining flexibility
This athletic quality is needed in many disciplines, even those that primarily require speed and agility, such as soccer. This sport is the most dangerous. Most often, football players suffer from legs: bones, joints and ligaments. Much of this damage could be avoided by developing flexibility.
A popular spinal flexibility test is “Reach to the Floor.” You need to stand up straight, bend over and touch the floor with your hands. It is useful to concentrate on the sensations in your body at this time. Discomfort indicates that your flexibility is poorly developed, and pain is a reason to consult a doctor.
We check the mobility of the shoulder joints. Stand up straight, then raise your right arm and throw it behind your back. Then lower your left hand, put it behind your back and try to reach your right hand.
We determine the condition of the thigh muscles. You need to lie on your back on a bench or separate bed. First, lie on the right side, pull your left knee towards your chest, and support it with your hands. Lower your right leg and try to rest it on the floor. Then repeat this exercise with the other leg.
Let's test the elasticity of the ligaments in the groin area. You need to sit up straight, feet on the floor. Then spread your knees to the side and bring your feet together. Then pull them towards your groin as close as possible. Remember how much space is left between your feet and your groin.
results
Test Score
Good Average Poor
“Reach to the floor” Palms on the floor Fingers touching the floor From fingers to floor > 10 cm
Shoulder joints Fingers connected Distance between fingers up to 5 cm Distance between fingers > 5 cm
Thigh muscles Heel almost reaches the floor Heel is much lower than the level of the bench Heel is at the level of the bench
Groin ligaments From groin to heels 5-10 cm From groin to heels 10-20 cm From groin to heels > 20 cm
How is the procedure performed?
To conduct the Harvard Step Test you need:
- stopwatch;
- step bench 40 cm high for women and 50 cm for men;
- metronome (can be replaced by a “one-two” count for one second and “three-four” for the next second).
After the timing begins, the subject rises onto the bench with his left foot and places his right foot on the count of “one-two” or the first two beats of the metronome, descends from the platform with his right foot and places his left foot on the count of “three-four” or the next two beats of the metronome. In 1 minute a person performs 30 such ascents. During testing, movements must be performed according to a given rhythm, the leg is placed on the entire foot, the legs and body must be fully straightened after matching the two legs on the same plane.
After this, the subject is allowed to rest for 1 minute in a position convenient for him, and, starting from the 2nd minute, the pulse is counted for half a minute. After this, the actions and pulse measurements are repeated. During the entire test, three heart rate measurements are taken. These are written as f1, f2 and f3 and are used to calculate the index.
To calculate the Harvard Step Test index, two formulas can be used - basic and simplified. The second of them can be used when carrying out mass measurements.
The basic formula of the Harvard Step Test Index (IGST):
- add f1, f2 and f3;
- 100 divided by the sum of f1, f2 and f3;
- multiply the result obtained by 2 and the time for which the test was carried out (maximum 5 minutes).
The abbreviated IGST formula is used when performing one pulse measurement:
- 100 divided by f1;
- the result is multiplied by 5.5 and the time for which the test was carried out.
Anthropometric measurements
Rules and procedures for disinfecting premises against coronavirus
Physical development is one of the significant indicators of health. Methods for testing physical development include anthropometric measurements, which allow obtaining objective data on important morphofunctional parameters of the body - length, body weight, thickness of skin-fat folds, etc.
An important and quite accessible indicator of the level of physical fitness in practice is measuring the coverage dimensions using a centimeter tape. Based on changes in indicators, it is easy to trace the impact of health training on adjusting the body structure. The most indicative are the following measurements.
Chest girth (circumference) - measured during a pause, while inhaling and exhaling. The tape is applied along the lower corners of the shoulder blades and the upper edge of the fourth rib. The difference in values between inhalation and exhalation is called “chest excursion”.
Shoulder circumference - in a relaxed state, measured horizontally, exactly between the shoulder and elbow points. The hand is down.
Forearm circumference - a measuring tape is applied in the place of greatest development of the muscles of the forearm with the arm freely lowered.
Waist circumference - the tape wraps around the narrowest part of the waist.
Hip circumference - measurement is carried out in the horizontal plane. The maximum circumference of the thigh is determined under the gluteal fold, the minimum - in the lower third of the thigh 7-8 cm above the knee joint.
It should be noted that the ratio of waist circumference to hip circumference is an important informative indicator of excess weight and an increased risk of a number of diseases such as diabetes, diseases of the cardiovascular system, joints, and spinal column. The waist-to-hip ratio for men should not exceed 1.0; for women - 0.81.
results
The Harvard Step Test is recommended primarily for athletes.
The Harvard Step Test index is assessed using a developed table that takes into account calculation indicators and the type of sport:
| Result | Persons not involved in sports | Persons involved in cyclic sports (swimming, running, skiing, etc.) | Persons involved in acyclic sports (tennis, football, hockey, etc.) |
| Bad | Below 56 | Below 71 | Below 61 |
| Below the average | 56 – 65 | 71 – 80 | 61 – 70 |
| Average | 66 – 70 | 81 – 90 | 71 – 80 |
| Above average | 71 – 80 | 91 – 100 | 81 – 90 |
| Good | 81 – 90 | 101 – 110 | 91 — 100 |
| Great | Above 90 | Above 110 | Above 100 |
The Harvard step test allows you to evaluate not only the fitness of the heart muscle, but also evaluate the effectiveness of training by comparing the results obtained in different periods.
Video about how the Harvard step test is conducted:
How to choose the optimal route for travel?
What to do if you are getting ready to travel, but don’t know how to choose the optimal route for travel? If you have a family trip planned or there is a need for an urgent trip of a business or personal nature, but there is simply no time for a detailed analysis of the upcoming path?
In such cases, a professional service for calculating distances between cities will help out. Today, you just need to have an Internet connection to get detailed and accurate information about the intended route. In addition, you can find out in advance not only the names of all settlements on the future route, but also calculate the time that needs to be spent to cover a given distance, as well as calculate the average fuel consumption.
Such online services are gladly used by drivers of any qualifications - both professional truck drivers and ordinary car enthusiasts who want to travel in a personal car.
Agree that the best impressions and memories remain from a trip that was well planned and organized. Moreover, if we are talking about safety, because a long and unfamiliar path is always associated with special risk and unpredictability, therefore, studying the route in advance is one of the most important factors for a successful, efficient, and most importantly, safe trip.
Those drivers who, when setting off on a long journey, do not think through their route accordingly, more often than others have various troubles on the road (“winding up” extra distance, losing time and fuel, ending up off-road, becoming involved in various accidents). That is why it is extremely important to pre-calculate the distances between the cities you will be passing through, because you need to assess the complexity of the route and calculate how much fuel will be needed to overcome it.
Today there are many sites on the Internet that offer calculations of distances between cities, but, unfortunately, some of them are overloaded with unnecessary information that is not always necessary for the user.
Therefore, we invite you to use the services of our special free service, the main task of which is to professionally calculate distances between cities and calculate the most suitable route while simultaneously determining travel time and fuel consumption. If you are going on a long trip and do not have the necessary road atlas at hand, there are no modern road maps, and the vehicle is not equipped with a GPS satellite navigator, then you should not worry too much about this. The entire required route can be easily simulated by an online service for calculating distances between cities.
Working with our service is very simple - you should enter the point of departure in the “from” column, and the required destination in the “to” line. A special algorithm, which has in its database the names of most cities in the world, will helpfully tell you the name of the desired locality, including the country, region and district. All you have to do is click on the “show route” button to get a detailed calculation of the distances between cities. The pink line will indicate the shortest actual distance from point “A” to point “B”, and using the thick blue line you can determine the exact and most advantageous trajectory of movement to the object you need.
The service is constantly being improved and optimized so that regardless of the path you choose, the route we offer is always the fastest, most convenient and safest.
| Harvard step test | |
| Target | cardiac stress test |
Harvard Step Test
is a type of bicycle ergometry for the detection and diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. It is also a good indicator of a person's fitness and ability to recover from strenuous exercise by testing the rate of recovery. The test was developed by Lucien Broix and his associates in 1943.
Who should go
Since the pace of execution is quite intense, the test is performed only on healthy people. The second condition is sufficient physical preparation, since if the subject has not previously engaged in physical education, then he will not be able to achieve the recommended duration of the load.
The Harvard Step Test is used for the following purposes:
- determination of the athlete’s initial training,
- drawing up an individual training program,
- if the athlete returns to training after a break,
- when selecting for competitions,
- assessment of the effectiveness of physical activity,
- when undergoing a professional examination by specialists from the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
The age of the subjects can be from 8 years, girls and boys are allowed to participate, there is no upper age limit.
Audience for step testing
Based on the initial goals of developing an evaluation method, first of all, the test is practiced by professional athletes, skiers and other athletes. In addition, the use of this method is recommended for people starting active training to determine the level of readiness for stress, amateur athletes in order to develop a balanced training program, professional rescuers, firefighters, gas and smoke protection service workers.
For the latter category of people, the PWC170 test (a modification of the step test) is more often used. The abbreviation stands for Physical working capacit (translated from English - physical ability to work), the number indicates heart contractions at the maximum limit. Children from 8 years of age are allowed to take the test. There is no upper age limit. There are also no gender criteria.
How to take an ECG?
The study is not carried out if a person has chronic vascular and heart diseases or diagnosed pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Relative (temporary or relative) contraindications are:
- colds and viral infections;
- period of menstruation in women;
- hyperthermia (high temperature);
- muscle weakness, fatigue.
When the condition has stabilized, the step test is allowed.
Methodology for conducting the Harvard step test
The test requires a platform or step of a calculated height (from 35 to 50 cm) depending on gender and age. The duration is from 2 to 5 minutes. Since the pace of the test is very important for standardizing the result, it is recommended to use a metronome.
Before starting, you need to give the patient time to master the technique, then begin testing. The load consists of entering the step platform with one foot and descending with the other. The free leg is placed next to the working leg. Each step takes one metronome beat. He is set at a frequency of 120 beats per minute. For example, the test goes like this:
- Climb up the step with your right foot.
- Place the left one.
- Go down left.
- Place the right one.
During the test, you can change your working leg. The arms move arbitrarily; be sure to straighten completely after walking. In 5 minutes it is required to complete 150 such cycles. If the subject has lost his rhythm and cannot maintain the given pace, then conducting the test further is inappropriate. The time that the patient was able to complete is taken into account to calculate the result.
Methodology for conducting the Harvard step test
After completing the test, the patient sits on a chair, and the doctor measures his pulse after 1 minute. 3 measurements will be received in the following time periods (in seconds):
- from 60 to 90,
- from 120 to 150,
- from 180 to 210.
European Physical Fitness Test
Emergency medical care is... definition, purpose, composition of teams, work rules, compliance with regulations and orders of the Ministry of Health
Table 45
| Magnitude | Factor (ability) | Test | The order of application of tests |
| General muscle endurance | General (aerobic, respiratory capacity) endurance | Ergometric running - Rover test (PWC170) | 9 |
| Force | Static force | Hand dynamometry | 5 |
| Dynamic (explosive) force | Standing long jump | 4 | |
Muscle endurance | "Functional strength" | Hanging on bent arms | 7 |
| Core strength | “Lie down and sit down” in 30 s | 6 | |
| Rapidity | Agility running | Shuttle run 10×5 m | 8 |
| Speed of hand movements | Touching circles (tapping test) | 2 | |
| Flexibility | Flexibility | Bend forward in a sitting position | 3 |
| Equilibrium | Whole Body Balance | Maintaining balance on one leg | 1 |
| Anthropometric (body) measurements | Body length (cm), body weight (kg), subcutaneous fat thickness (at the level of the biceps and triceps muscles, on the waist, under the shoulder blade, on the side of the body and on the lower leg) | ||
| Data | Age (years, months) | ||
| Floor |
Equipment: table with adjustable height; 2 rubber mugs (each 20 cm in diameter) attached to the table; a plate measuring 10x20 cm (size between circles), stopwatch.
Testing procedure. The subject stands in front of the table at a short distance (80 cm from the middle of the circles). The palm of the less dexterous hand is placed on the plate. The palm of the more dexterous hand is lowered crosswise onto the lying less dexterous hand. At the signal, the subject must, as quickly as possible, alternately, touch (touch) one and the other circle with a more dexterous hand. He must touch each circle 25 times, for a total of 50.
The result is the time that the subject will spend touching each circle 25 times (with an accuracy of 0.1 s). In this case, the displayed time, for example, 10.2 s gives a result of 102 points. Of the two attempts, the best result is taken into account.
Shuttle run 10x5 m.
Equipment: stopwatch, measuring tape, chalk, 4 rubber cones at a distance of 120 cm from each other, two installed on each of the boundary lines, 500 cm apart from each other.
Testing procedure. The subject on the command “March!” runs as quickly as possible from one line to another, crossing them with his feet, and so on 10 times.
The result is the task execution time with an accuracy of 0.1 s. This time, however, must be multiplied by 10. For example, 24.5 s gives a result of 245 points.
How to calculate the index
The endurance rating is determined by the index. It reflects how quickly the heart restores its normal rhythm after exercise. The shorter this time, the better the index, and therefore the fitness level. Calculation method:
- Add up all 3 heart rate measurements obtained.
- Divide 100 by the resulting amount.
- The result of the 2nd action is multiplied by 2, and then by the time that was sustained by the subject (5 minutes - maximum).
For screening tests or the need for a quick sample, pulse rate can be measured once.
In this case, one result is taken for calculation, and instead of the coefficient “2” the number is multiplied by 5.5. The remaining stages remain unchanged.
Watch the video about the Harvard Step Test Index:
CLAIM
1. A set of step platforms of different heights for conducting functional load tests, containing at least two step platforms, characterized in that each of the subsequent step platforms has geometric dimensions smaller than the previous one, and each of the step platforms set is made in the form of a hollow thin-walled truncated quadrangular pyramid, the angles of inclination of the side surfaces to the base of which are made acute with maximum approximation to right angles, and the values of the above angles are selected from the condition of ensuring the possibility of removing the platforms from the injection mold and the possibility of inserting one platform to the maximum depth to the other, while on the outside, the upper working surface of each platform is made to resist sliding, on the inside, each platform contains longitudinal and transverse stiffeners, and the two oppositely located sides of each platform are equipped with protrusions extruded along its entire height, forming grooves between them and having a trapezoidal cross-section, the dimensions of the protrusions and the width of the grooves are selected from the condition of the possibility, when docking platforms, of placing the protrusions of one step platform in the grooves of another, the kit also additionally contains a mat made of elastomeric material with a high coefficient of friction, on the outer surface of which the joining elements are located, made with the possibility of placement in the internal cavities of the trapezoidal protrusions of the platforms during docking.
2. The set according to claim 1, characterized in that the step platforms are made of polypropylene.
3. The set according to claim 1, characterized in that the step platforms are made of colored polypropylene - red, orange, yellow, green, blue, light blue.
4. The set according to claim 1, characterized in that in the middle part of the side surface there is a recess, which is a rectangular recess with wedge-shaped sides expanding towards the base.
5. The set according to claim 4, characterized in that on the highest platform in the lower part of the wedge-shaped expanding recess there is a handle in the form of a segment of a U-shaped profile connecting the sides of the recess.
6. The set according to claims 1-5, characterized in that the width of the mat is selected from the conditions for its diagonal insertion into the assembled set of step platforms.
7. The kit according to claims 1-5, characterized in that the working surface of each of the platforms of the kit is equipped with recesses for installing nameplates with logos and/or technical characteristics of the platforms.
8. A method for manufacturing a set of uneven-high platforms for conducting functional load tests according to claims 1-7, including the manufacture of a mold containing a matrix and a punch with a geometry that provides a given shape of the step platform, subsequent thermopress casting of molten polymer into the mold and obtaining a finished platform, and step platforms of a smaller geometric size are obtained by cutting from step platforms of a larger size.
9. The method according to claim 8, characterized in that to eliminate shrinkage deformations during cooling of the step platforms, spacers of a responsive shape corresponding to the internal geometry of the step platform are inserted into the latter during the period of their cooling.
Decoding the result
The resulting figure is analyzed using a special table. Its value is reflected by qualitative characteristics. For example, 55 units is a bad result, 65 - 79 is an average result. For professional level athletes it can be about 170 units. Marathon runners and skiers have especially high results.
Values from 80 are considered good, and values above 90 are considered excellent. It should be borne in mind that the Harvard test will not always accurately reflect athletic achievements, but if the test is repeated on the same athlete, endurance can be reliably assessed.
Harvard Step Test Index
Push ups
With their help you can test your muscle strength. This is a great way to determine your fitness level. It's simple - the number of exercises performed will tell you about your strength. When doing this, it is advisable not to arch your back. Women are allowed to perform push-ups from some kind of support, such as a bench.
Women
Value Age
18-30 30-40 40+
Good 15 and more 12 and more 10 and more
Average 10-15 8-14 6-12
Poor less than 10 less than 8 less than 6
Men
Value Age
18-32 32-40 40+
Good 32 and more 25 and more 21 and more
Average 18-30 14-25 12-22
Poor less than 17 less than 14 less than 12