Vascular diseases are widespread among middle-aged and elderly people. This is partly facilitated by an inactive lifestyle, monotonous work and poor nutrition, leading to increased cholesterol levels and the formation of plaques with the development of atherosclerosis. The circulatory system supplies blood and nutrients to all organs and tissues. But if there are obstacles in the arterial, venous, or lymphatic vessels, their functionality is impaired, and serious life-threatening complications arise.
Symptoms
The location of the disease directly affects its symptoms. When the limbs are affected, lameness develops, pain, sensory disturbances, and tingling appear. Without treatment, the disease develops into gangrene and ultimately leads to amputation.
If the vessels of the heart are affected, coronary artery disease, arrhythmia, angina pectoris, pain and shortness of breath become manifestations.
When cerebral vessels are damaged, the signs are as follows:
- Memory impairment.
- Headache.
- Poor blood circulation in the brain.
- Dizziness.
- Decreased attention, speech impairment.
- Mental changes, dementia.
- Motor impairment.
Get diagnosed with atherosclerosis at Clinic No. 1
- Neurologist appointment
- Doppler ultrasound
- Coronary angiography
For one-time payment for services - 20% discount
Call
What diseases does a vascular surgeon treat?
Basically, modern vascular surgeons specialize in performing minimally invasive surgical interventions (microsurgery). However, they are also involved in the full supervision of the patient - his rehabilitation and recovery, selection of conservative (in particular, preventive) treatment, correction of nutrition and lifestyle, dynamic monitoring of the state of the vascular system.
The angiosurgeon treats the following pathologies:
- Atherosclerosis in all forms and stages;
- Stroke and post-stroke disorders;
- Vascular malformations;
- Aortic aneurysm;
- Varicose veins;
- Myocardial infarction;
- IHD (coronary heart disease);
- Angina;
- Arterial or venous stenoses;
- Thrombosis (acute and chronic);
- Thrombophlebitis;
- Arteriovenous fistulas;
- Raynaud's syndrome;
- Buerger's disease (thromboangiitis obliterans);
- Angiopathy (including diabetic);
- Aortoarteritis;
- Arteritis and polyarteritis;
- Vasculitis;
- Endarteritis;
- Vascular hypertension (hypertension);
- Trophic ulcers;
- Lymphedema (lymphostasis).
Detection of symptomatic manifestations of one or more of these diseases should prompt you to seek professional medical help. Observation and treatment by competent vascular surgeons will significantly improve your quality of life.
Degree of disease development
The disease develops gradually. Main stages:
- Lipid spots.
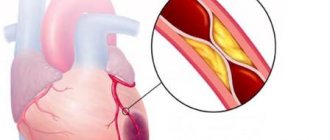
The easiest stage at which the artery walls begin to become saturated with lipid compounds. Localization is focal, in some areas. The changes look like yellowish spots, stripes spreading along the inner surface of the vessels. There are no symptoms. Plaques form faster in patients with excess weight, bad habits, diabetes, and high blood pressure. - Fibrous plaques.
This is the second stage of the disease, in which the previously formed lipid areas become inflamed. As a result, the immune system releases inflammatory mediators in the affected areas. The fats that have accumulated in the walls are destroyed, die, and sclerosis forms. The connective tissue grows, fibrous plaques form, protrusion occurs on the walls of blood vessels, stenosis develops, and blood flow is disrupted. - Complicated plaque.
This is the last stage in the development of the disease, during which complications appear and symptoms begin to appear. The protrusion hardens, calcifies, significantly narrows the lumen, and blood cannot circulate normally.
When is it necessary to contact an angiosurgeon?
An appeal to vascular surgeons should take place in the presence of subjective complaints and suspicions of relevant pathologies.
Persons over 45-50 years of age should undergo regular scheduled examinations with cardiologists, phlebologists and angiosurgeons to prevent and timely detect possible vascular pathologies. This age category of patients is automatically included in the risk group for various venous and arterial diseases. This is especially true for those who lead an unhealthy lifestyle with bad habits, irrational nutrition and physical inactivity, as well as those who have provoking chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, thrombophilia, etc.).
Contact your vascular surgeon if you notice the following symptoms:
- Severe swelling of the legs, especially in the evening or at night;
- Night cramps in the lower extremities;
- Feeling of heaviness, fullness, burning and itching in the calf muscles;
- Intermittent claudication;
- Fatigue of the legs with an objectively low load;
- The appearance of spider veins and protruding venous nodes on the legs;
- Regularly recurring headaches of unknown origin;
- Blood pressure disorders (hypo- or hypertension);
- Tendency to hypertensive crises;
- Changes in the shade and structure of the skin of the extremities (as well as ring pigmentation on the legs);
- Burning in the feet when walking long distances;
- Feeling of tingling, numbness and severe cooling of the extremities without objective reasons;
- Pulsation in the abdominal area;
- Spontaneous repeated fainting and syncope (short-term loss of consciousness);
- Transient paresis and paralysis;
- Loss of sensation in the upper or lower extremities;
- Constant dizziness and nausea;
- Visual disturbances (transient blindness, the appearance of floaters and light spots in the field of vision, peripheral vision disorder);
- Short-term disorders of speech functions;
- Unsteadiness of gait, frequent states of numbness;
- Blackening or blueness of fingers;
- Long-term non-healing wounds, fistulas and ulcers.
If such symptoms are present, the therapist can make a pointless diagnosis, so if they are detected, it is advisable to contact a highly specialized specialist. In addition to a vascular surgeon, we recommend that you consult a neurologist and cardiologist.
Vascular surgeons deal with both congenital and acquired diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnostics
At the beginning of development, atherosclerosis does not manifest itself in any way. Later, as the disease progresses, several visible manifestations of atherosclerosis appear, which can be identified during a routine examination by a neurologist. This is weight loss, swelling, fatty tissue, and trophic disorders. The doctor will listen to the heart, measure blood pressure, and prescribe clinical tests. The following diagnostic measures are used:
- Ultrasound Dopplerography. Allows you to identify diseases at an early stage, assess the size of plaques and blood flow.
- Coronary angiography is used to assess the condition of the heart vessels.
Appointment with an angiosurgeon
A consultation with a vascular surgeon does not require any special preparation. Before going to the clinic, take a hygienic shower and put on clean underwear. Don't forget to bring a medical card with your medical history.
During the interview, the specialist may need the results of previously conducted examinations and tests, so if you have any on hand, take them with you. Tell the specialist your family history if your closest blood relatives have had acute or chronic diseases of the veins or arteries.
For a full diagnosis and final diagnosis, you may be prescribed the following studies:
- Laboratory blood tests (general, biochemical, lipid profile, prothrombin time, detailed coagulogram, etc.);
- Electrocardiogram;
- Echocardiogram;
- Ultrasound duplex scanning of blood vessels;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- Angiography (including cerebral and coronary);
- Ultrasound, CT, MRI;
- Endoscopy;
- Sonography.
The specialist conducts anthropometry directly during a face-to-face visit (the patient’s height and weight, body mass index, body fat density, constitutional body type and other indicators are assessed).
The angiosurgeon may require the opinion of related specialized specialists, to whom he will refer you if necessary.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the stage of the process. This may be a conservative approach or surgery. In the first case, the focus is on normalizing the patient's lifestyle. Nutrition is adjusted, a special diet is prescribed, and a weight loss program is developed, if necessary. As drug therapy, drugs are used that normalize blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, normalize blood counts, and replenish the supply of vitamins and microelements.
If the process has gone far enough and medications do not achieve the desired result, surgery is used. This can be open or modern endovascular intervention. A gentle method is angioplasty, during which the lumen of the vessel expands; if necessary, a stent can be installed to maintain the lumen of the vessel in the desired position. The operation is aimed at removing plaques that are blocking normal blood flow. In some cases, a severely damaged vessel may be replaced or a new blood flow path created.
Get diagnosed with atherosclerosis at Clinic No. 1
- Neurologist appointment
- Doppler ultrasound
- Coronary angiography
For one-time payment for services - 20% discount
Call
What does a specialist do?
A vascular surgeon works in the following areas:
- Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of vascular (arterial and venous) diseases;
- Timely detection of oncopathologies (when a malignant tumor is localized in close proximity to large vessels);
- Treatment of vascular lesions that occur due to severe injuries;
- Prosthetics of vessels damaged due to injury or surgery;
- Performing full and minor surgical interventions on veins and arteries;
- Removal of genetically determined vascular abnormalities (malformations, hemangiomas, etc.);
- Replantology (microsurgical intervention aimed at complete or partial reconstruction of limbs or their fragments after radical amputation);
- Prevention aimed at preventing the development of vascular diseases in patients at risk.
The prognosis of treatment directly depends on the degree of qualification of the specialist, his clinical experience, skills, as well as the timeliness of the patient’s contact with him.
Make an appointment with a neurologist
Clinic No. 1 in Moscow offers a consultation with a neurologist. Among the main advantages of a multidisciplinary medical center are experienced doctors, the latest equipment, comfortable conditions and safety for patients, as well as a convenient location of the clinic and a flexible system of discounts. You can make an appointment through the website or by phone.
Moscow, st. Krasnodarskaya, house. 52, bldg. 2
+7
We work on weekdays and weekends from 8.00 to 21.00
Treatment by a vascular surgeon
The decision regarding therapeutic tactics is made on the basis of the collected medical history, the results of additional studies, and the opinions of other specialists. The vascular surgeon evaluates the course of the disease, its form and causes (exogenous and endogenous). When choosing any treatment method, possible contraindications and limitations are taken into account.
Typically, vascular treatment becomes combined and combines conservative and surgical therapy.
After completing the main treatment, angiosurgeons begin preventive measures. In order to prevent relapses and complications, physiotherapy, physical therapy, and massages are used in clinical practice. The patient is prescribed the required degree of compression. The supervising specialist gives the patient recommendations regarding diet, limiting bad habits, and treatment of the main provoking disease.
Timely treatment of blood vessels is an important step towards achieving health and longevity. It should only be trusted to professionals.
What symptoms should you be wary of?
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels do not immediately make themselves felt. The first alarming symptoms can be expressed as follows:
- obvious shortness of breath with little physical exertion, climbing stairs;
- fast fatiguability;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- rapid pulse;
- slight increase in blood pressure;
- arising and passing pain in the heart area;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating.
Further, these symptoms intensify and occur more often. The most serious complications are heart attacks and strokes.
Common symptoms and pathologies in cardiology:
- Chest pain
- Heart disease in adults
- Pericarditis
- Angina pectoris
- Endocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Tachycardia
- Cardiac dyspnea
- Aortic aneurysm
- Arrhythmia
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Feeling short of air
- Interruptions in heart function
- Swelling in the legs
- Dyspnea
- Burning behind the sternum
Which doctor interprets MRI of the brain?
A radiologist is responsible for describing the images.
The study takes 15-30 minutes (depending on the need for contrast injection). After the session, a radiologist examines the images and analyzes what he saw. The doctor records all deviations from the norm: an increase or decrease in the size of the objects in question, foci of demyelination (white spots on tomograms, characteristic of multiple sclerosis and many other pathologies), and interprets the images. The result is a description of the study. The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, symptoms of the disease, laboratory and instrumental data. A competent synthesis of information can only be carried out by the attending physician.
To perform a study of the brain and other organs at the Magnit diagnostic center, call +7 (812) 407-32-31! Our specialist will give detailed recommendations.
Possible complications after the procedure
Like any other surgical intervention and violation of the integrity of the vessel, coronary angiography can have a number of complications, even if it is performed by an experienced specialist. Possible complications include:
- heart attack;
- rupture of an artery or heart;
- heart attack or stroke due to a blood clot breaking off from the wall of a vessel;
- arrhythmia;
- bleeding;
- allergies.
Of course, complications do not always arise and are often limited to small hematomas or swelling at the puncture site. However, the possibility of serious consequences cannot be excluded, so before the procedure you need to carefully study the contraindications to it.
Contraindications for the study
Contraindications for cardiac vascular examination with contrast are:
- various respiratory diseases that are accompanied by elevated body temperature;
- anemia;
- open bleeding of various locations;
- low potassium levels in the blood;
- poor blood clotting;
- diabetes;
- obesity or underweight;
- renal, heart failure;
- lung damage.
Why is an MRI of the brain done?
MRI of the brain reveals:
- aneurysms (changes in the vessel wall in the form of protrusion);
- multiple sclerosis;
- inflammatory diseases;
- tumors and cysts;
- infections;
- strokes due to vessel thrombosis and hemorrhage;
- consequences of head injury.
Recently, the technique has been used to diagnose an increasingly wide range of diseases. Increased signal has been found in the white matter of the cortex and cerebellum in a mental illness called bipolar disorder. Symptoms of this condition include extreme mood swings: mania or depression.
There are interesting developments in early magnetic resonance diagnostics of autism (a condition manifested by severe communication deficits) in children at risk.
MRI scanning of the brain has also found use in COVID-19. An increase in the signal from the olfactory bulbs and the direct gyrus of the right hemisphere, responsible for receiving and processing odor data, was detected.
One of the types of brain research is functional magnetic resonance imaging, which allows us to identify areas that are responsible for speech, movement, vision, and hearing. fMRI is used in planning neurosurgical operations and diagnosing diseases that are not anatomical, but functional in nature (epilepsy, etc.).
Conditions when an MRI of the brain is prescribed are:
- high blood pressure, poorly controlled by antihypertensive drugs;
- development of disorders in behavior, memory, thinking;
- partial or complete loss of vision, double vision;
- convulsive seizures, episodes of loss of consciousness;
- frequent, unexplained headaches.
Which doctor prescribes an MRI of the brain?
The study is prescribed by a neurologist
There are several ways to go through the procedure:
- receive a referral for research at the clinic at your place of residence;
- contact a neurologist at a medical center;
- take the test yourself at a diagnostic clinic.
The doctor can give a referral for a free examination as part of compulsory health insurance. There must be strong indications for such a prescription (suspicion of a tumor, etc.). The procedure may take some time.
When a patient contacts a neurologist at a private medical center, the doctor assumes responsibility for the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. The doctor explains why and why an MRI test is needed, directs you to the study and gives explanations and recommendations on the results. In this case, you will have to pay for consultations and procedures.
If you go to a diagnostic center on your own, you need to find out if they do an MRI of the head. Focusing only on the price of the test, you can get uninformative images if the institution uses a device with low resolution. Based on the results of the study, a radiologist's report will be issued, but to make a diagnosis you need to contact a specialized specialist. Only a doctor can understand why and when to do an MRI of the brain. Most often this is a neurologist, but it can also be any other specialist, such as an ophthalmologist or endocrinologist.