What is a panic attack
A panic attack is an attack of sudden fear and severe anxiety for no apparent reason.
The origins of panic disorder are not completely clear. However, it is believed that the disease has a genetic predisposition and more often affects the fair sex. Women are more prone to panic attacks and suffer from this disorder 2-3 times more often than men. Panic attacks cannot lead to death, despite the fact that this is the feeling that most often accompanies them. The more often attacks occur, the worse the quality of life becomes. People who have repeatedly experienced panic attacks become increasingly anxious and subconsciously try to avoid places or situations where and when they succumbed to fear. Those who have at least once experienced an attack at night subsequently experience sleep disorders.
The connection between dizziness and heart disease
Frequent episodes of dizziness within minutes of standing up may be a sign of health problems, according to a new study published in the journal Neurology.
When standing up, a sharp decrease in blood pressure can lead to dizziness, blurred vision, and often this is simply due to dehydration or a side effect of medications that the patient is taking.
However, if episodes of dizziness occur frequently, it may be an indicator of something more serious called orthostatic hypotension. These conclusions were made in a new study conducted by a group of scientists from Harvard Medical School (Massachusetts).
Orthostatic hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure caused by changes in body position. This condition may occur within 3 minutes of standing up, from a lying, or sitting position.
The research team examined the medical records of 165 people who underwent nervous system testing, a test that can determine how well a person's autonomic nervous system is functioning.
54% of people with mild OH developed severe OH over time
Of these individuals, 48 were diagnosed with mild orthostatic hypotension (DOH), 42 were diagnosed with severe OH—a more severe form of MOH—while 75 did not have orthostatic hypotension. The average age of the participants was 59 years.
During a 10-year follow-up, 54% of those with mild OH developed significant OH, while 31% gradually developed degenerative brain diseases such as Parkinson's disease or dementia with Lewy bodies, a disease caused by abnormal accumulation of brain cells. protein in the brain. Patients who also had diabetes at baseline were more likely to develop significant OH than those who did not have diabetes.
Mortality among study participants was 29% among those with mild OH and almost 64% among those with persistent OH. Among those who did not have orthostatic hypotension, the mortality rate was 9%.
In patients in whom minor OH transformed into severe OH, the mortality rate within 10 years was 50%.
Many patients with mild hypertension who did not develop severe hypertension took medications to stabilize their blood pressure.
Commenting on the findings, study author Dr. Christopher Gibbons, from Harvard Medical School, said:
“Our results show that more than half of people with mild OH go on to develop significant OH, which has more serious consequences for human health,” says the study author.
Our findings may help diagnose early and appropriately treat conditions and other underlying diseases that may contribute to early death."
The researchers say the study has certain limitations. For example, because this was a retrospective review of previously collected data and all participants underwent nervous system examination at a tertiary center, the results may not be applicable to the general population.
What to do in case of a panic attack
The most important thing to do during a panic attack is to switch your attention. Any method is suitable for distraction. If an attack occurs in a public place, you can clench and unclench your fists, rub your earlobes, or shift from foot to foot. If panic takes you by surprise at home, try turning on music and starting to do household chores: washing dishes, dusting. Any activity that involves muscle work and requires attention is suitable.
Since a panic attack is accompanied by a rapid heartbeat and a feeling of stuffiness, it would be a good idea to take a couple of sips of water and concentrate on breathing. It is best to master several techniques that will quickly relieve tension. In case of an attack, start by exhaling - slow it down, and the pulse will also slow down. The ratio of the length of inhalation and exhalation should be 1:2. You can experiment and choose the technique that will help you. A smartphone can also help you take your mind off panic. Games, social networks - all this will shift attention and distract from a panic attack.
Diagnosis of cutting pain in the heart
How to diagnose cutting pain in the heart? Make an appointment with a cardiologist at the KDS Clinic. Tell your doctor about the nature, frequency and intensity of pain. Thus, the specialist will determine the exact diagnosis. You will be sent for testing. It is worth undergoing examinations such as ultrasound diagnostics of the heart, electrocardiogram. Once a diagnosis is made, each patient is assigned effective and affordable treatment. If the situation is critical, call an ambulance and take painkillers.
In more advanced cases, the patient remains in the hospital, where KDS Clinic staff monitor the patient’s condition, indicators, improvement or deterioration. Most often, medication treatment is prescribed at home.
How is normal anxiety different from a panic attack?
The mechanism that triggers a panic attack is no different from what causes ordinary anxiety - both are psychophysical reactions to danger. The difference is that a panic attack is a reaction to danger in the absence of danger. However, a false alarm triggers the same cascade of reactions as a normal alarm - the sympathetic system is activated, and adrenaline is released.
A panic attack can occur due to excessive physical activity, fatigue and exhaustion, as well as due to the abuse of stimulants and alcohol. In addition, stress and unresolved conflict situations can trigger an attack. A lack of understanding of one's own experiences and feelings, a tendency to avoid and ignore negative emotions also increase vulnerability to panic disorder.
Causes of sharp pain in the heart area
The occurrence of severe pain is influenced by many factors. It is by paying attention to the symptoms that an accurate diagnosis can be made and effective treatment can be prescribed.
- Pain syndrome, which is localized in the chest, indicates pathologies of the cardiovascular system. There are several associated symptoms. Among them, increased heart rate is tachycardia.
- Hypertension and hypotension. With hypertension, a person feels dizzy, feels a sharp stabbing pain in the heart and head, and has migraines for a long time. Pain syndromes are nagging, aching. With hypotension, the patient becomes dizzy, has a feeling of general weakness, fainting, and loss of appetite. It is not life-threatening when taking medications that normalize blood pressure.
- Angina pectoris. Acute pain in the heart area may be a sign of angina. Associated symptoms are headache and tinnitus. Not dangerous to human life if treated correctly.
- Myocarditis and endocarditis.
- Myocardial infarction. When a person breaks into a cold sweat, becomes dizzy and experiences sharp pain in the heart, then we are talking about myocardial infarction. You should call an ambulance immediately.
- Cardiac aneurysm.
- Cardialgia. It causes intense nagging pain, panic and anxiety in the patient.
Non-cardiac causes also influence the patient’s poor health. They are responsible for the condition of other internal organs. Among them:
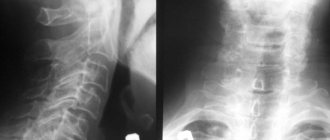
- Osteochondrosis. With osteochondrosis, a person feels severe pain not only in the spine. The severity also affects the cardiovascular system.
- Tuberculosis and pneumonia. If the respiratory tract is impaired, pain occurs when moving, breathing and laughing.
- Ulcer. Inflammation of the duodenum leads to acute pain in the stomach and heart.
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders. If there is a gastrointestinal tract disorder, the patient's condition may be accompanied by acute pain in the heart area.
- Mastopathy and other pathologies. In women, heart pain is often caused by breast problems. One of them is called mastopathy.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Musculoskeletal disorders. Inflammatory processes in the musculoskeletal system are caused not only by pain in the joints and muscles, but also by a pulling sensation in the heart area. Such diagnoses include fractures of ribs, joints, cracks, and pits.
- Nervous system disorders. The nervous system is closely connected with the heart, so frequent stress and emotional stress cause pain in the heart area.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. The main symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are migraine and heart pain.
- Pancreatitis. With the inflammatory process of the pancreas, acute pain in the heart and stomach is observed.
- Toxic poisoning. In case of toxic poisoning with drugs or alcohol, the patient begins to experience tachycardia, increased blood pressure and severe pain in the heart.
- Cholecystitis. When the walls of the gallbladder are inflamed, pain in the heart is observed. The pain is dull.
It is noteworthy that heart pathology develops when the patient feels severe pain in the center of the organ. She is observed behind the sternum. Cardiovascular system disorders are characterized by other symptoms. The patient's condition worsens after stress and emotional stress.
If the pain is associated with other organs, then it intensifies when turning, walking and talking. Sharp pain syndromes appear in the case of angina pectoris, myocardial infarction and stroke. In such cases, you should urgently call an ambulance. With a cardiac aneurysm, the patient cannot tolerate severe attacks and suffers from dizziness and general weakness. The pain also spreads to neighboring organs. Continues for several hours. With pneumothorax, the discomfort increases with every second, especially when breathing. The stabbing pain intensifies with walking and movement.
How to treat panic attacks and when to see a specialist
It is necessary to contact a specialist if you have recurring panic attacks. Therapy is selected individually and, as a rule, includes psychotherapeutic work and drug therapy. Psychotherapy involves various techniques aimed at recognizing and understanding the causes of problems, teaching ways to deal with the symptoms of the disease, and relaxation methods. Psychotherapy can take place in the form of individual meetings with a psychotherapist or in the form of group sessions with other patients. Drug therapy for panic disorder is carried out with various drugs that help reduce the level of anxiety and fear. Prescription, dosage adjustment and discontinuation of treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Modern neurotechnologies can also help in the treatment of panic attacks. Methods of neurofeedback training have been developed for patients with panic disorder. During the trainings, patients learn to manage their emotional state, they form new neural connections, and their anxiety level decreases. In addition to professional help, lifestyle plays a significant role in the treatment and prevention of panic attacks. Try not to abuse alcohol and caffeine, get more rest, go in for sports, preferably yoga.
Source: https://www.wmj.ru/krasota/telo/golovokruzhenie-zhar-i-dazhe-udushe-simptomy-panicheskikh-atak-i-kak-s-nimi-borotsya-razbiraem-s-vrachom.htm
Back to list