Symptoms and first signs of stroke.
The main causes of death from stroke are: lack of prevention, unnoticed symptoms of the disease in time and, as a result, late seeking medical help.
According to statistics, only 15 percent of people go to the hospital on time when their health worsens. You cannot be indifferent to yourself and others, especially older people. At the first signs of a stroke, you should urgently call an ambulance. Caring for an elderly person lies not only with his relatives, but also with other people nearby. The main symptoms of a stroke are:
- Sudden weakness, numbness of the limbs, spasms;
- Drooping of the corner of the mouth, smoothing of the nasolabial fold,
- Disorientation in space, headache, dizziness;
- Speech problems, complete or partial hearing loss;
- Unsteadiness when walking, unsteadiness of gait.
- Facial asymmetry.
The need for prevention
Meanwhile, many dangerous diseases can be prevented. Analyzing the chain of events that led to a heart attack or brain stroke, doctors and their patients are often convinced that the cause of the disease is a simple reluctance to take care of oneself, listen to one’s condition and give up bad habits. Even bitter experience turns out to be powerless here: having recovered from myocardial infarction, many patients continue to indulge their weaknesses, regardless of the recommendations of doctors. As a result, a relapse of the disease occurs, and possibly death.
Simple measures for the primary prevention of heart attack and stroke in old age do their job well. Conventionally, they can be divided into four groups:
- use of preventive medications;
- changing your daily routine and diet;
- treatment of systemic diseases that increase the likelihood of developing damage to the cardiovascular system, including diabetes;
- regular monitoring of the state of the circulatory system and maintaining it in good shape.
Actions in the event of a stroke.
The first and most important thing to do at the slightest suspicion is to call an ambulance. It is important to do this as quickly as possible, because there are only a few hours from the onset of the disease to the onset of irreversible consequences in the brain. These hours can become vital in saving a person's life.
Older people are much weaker, so timely provision of first aid will increase the chances of a favorable outcome. After calling an ambulance you must:
- Place the patient on his side, with the head end raised.
- If the measurement reveals that blood pressure is elevated, it is worth giving the patient a drug to normalize it.
- You need to remember or write down the time the symptoms started, as well as how they manifested themselves. This will help doctors quickly determine further actions to provide medical care.
For older people, it is extremely necessary to prevent stroke (blood pressure control, timely intake of medications), and in cases of temporary or permanent incapacity of a person, relatives can use the services of a nurse and professional patronage assistance.
How to prevent a stroke?
05.08.2019
«
Companion
»
Scientist Dmitry Napalkov: seven rules help prevent stroke
Dmitry Napalkov, professor of the department of faculty therapy No. 1 of the medical faculty of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov, spoke to the Sobesednik publication about measures to prevent stroke
Every year, about 12 million cases of stroke are recorded worldwide. In Russia, someone has a stroke every minute and a half. This insidious disease can happen to anyone, regardless of age or genetics. When this happens to a loved one or an acquaintance, we grab our heads: well, surely everything could have been prevented? Can! Only for this you need to comply with several important conditions. One of my friends had a stroke while he was on a business trip. I worked all day long without rest. I had a sharp headache, my mind was so clouded that I couldn’t even speak two sentences. Colleagues did not immediately call an ambulance. They gave me some kind of pill: “Just lie down, everything will pass.” After a couple of hours, the situation worsened so much that only intensive care was able to pump out my friend.
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Faculty Therapy No. 1 of the Faculty of Medicine of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov Dmitry Napalkov to our question - how to prevent a stroke? – answered this:
– Everyone wants to prevent themselves from having a stroke, but few people do anything about it. Cardiovascular diseases depend mainly on lifestyle. Lack of physical activity, unhealthy diet, and bad habits are very serious risk factors. However, with serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, nutrition and exercise alone will not help. You must take medications as prescribed by your doctor. And be very careful! For example, a well-known anticoagulant (vitamin K antagonist), used to prevent stroke, imposes severe dietary restrictions: raspberries, green tea, green vegetables, cabbage, eggs and other foods rich in vitamin K are undesirable. However, science does not stand still, and a new generation of drugs has now been created - for example, based on direct thrombin inhibitors. They do not require dietary restrictions.
Do not neglect measures such as: reducing the amount of salt in the diet to 5 g per day (about half a teaspoon), avoiding foods high in cholesterol. Add fruits, vegetables, whole grains and low-fat dairy products to your daily diet, as well as one serving of fish two to three times a week. See a specialist regularly. It is important to consult not only a therapist, but also a neurologist. It is necessary to do an ultrasound of the neck vessels and receive a health card.
Monitor your blood pressure. Arterial hypertension increases the risk of stroke several times. Therefore, it is advisable to measure your blood pressure levels at least once a week. Even if you feel well and do not have symptoms of hypertension such as headaches, fatigue and sleep disturbances, an increase in resting pressure readings above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. – this is already a reason to see a doctor.
World practice shows that by controlling blood pressure alone, it is possible to reduce the risk of stroke by 50%.
Control your weight. Neurologists agree that weight loss is one of the most effective measures in preventing stroke. Excess body weight contributes to the development of high blood pressure, diabetes and puts increased strain on the heart muscle.
It is clear that we cannot reduce our weight without a proper diet. It is worth giving up fatty and heavy foods to reduce blood sugar and cholesterol levels. To get results, you must stick to the diet for at least 3-4 months.
Be active. Physical inactivity, or too low a level of physical activity, is the scourge of our time. Therefore, it is important to do physical exercise for more than 30 minutes at least 5 times a week.
Aerobic exercise is the best way to prevent stroke—repetitive exercise that increases the supply of oxygen to the body. Your doctor will choose the best exercise for you, taking into account your age and existing diseases.
Well, these rules are available to everyone: use the stairs instead of the elevator, better get off one stop early and walk, find time to walk during your lunch break.
Treat diabetes. Those who suffer from diabetes have a significantly increased risk of stroke. Patients with diabetes suffer strokes much more severely than others. This is because due to atherosclerosis, many arteries are unable to move oxygen. And alas, the prognosis for stroke in diabetes mellitus in most cases will be much worse.
Drink less alcohol. Until recently, the relationship between alcohol consumption and stroke remained in question, but today there is no doubt: alcohol significantly increases the risk of stroke.
Stop smoking. Smoking people have a stroke 2-3 times more often than non-smokers. Conclusion: the more you smoke, the higher your risk of stroke! In addition, the age of the smoker is of great importance: in men and women who smoke under the age of 55, smoking is the main risk factor for stroke.
Atherosclerosis develops in the damaged vascular wall (thickening of the wall and reduction of the lumen), and this increases the risk of blood clot formation in the vessels of the brain. Smoking affects the properties of special blood cells called platelets, resulting in an increased risk of blood clots in the large arteries that carry blood to the brain and heart. Smoking also increases blood pressure, which is one of the most important risk factors for stroke.
By the way! A study of thousands of patients over 35 years (Nurses' Health Study) showed that a typical European diet, including large amounts of meat, eggs, fried and salty foods, refined bread, full-fat dairy products, sweet desserts and chips, increases the risk of stroke by 58% . While eating whole grains, fruits, vegetables and fish reduces this risk by 30%.
Link to publication: /sobesednik.ru
Who's at risk
Objectively, there are categories of people who have a high likelihood of developing a stroke. These include:
- people with diabetes, high blood pressure and cholesterol;
- people with a hereditary predisposition to this disease;
- people with blood pressure higher than normal (120 over 80);
- women over 55 years of age;
- all people over 65.
Read material on the topic: Features of the elderly
Kinds
The main classification of strokes (according to ICD-10) takes into account the cause and mechanism of stroke.
- An ischemic stroke is characterized by a cessation of blood flow to the brain tissue. The reason is a violation of blood flow, blockage of an artery with a blood clot and/or narrowing by an atherosclerotic plaque (atherothrombotic), vasospasm, and a decrease in pressure. Most often develops at the age of 50-69 years. The incidence is 64-75% among all types of stroke.
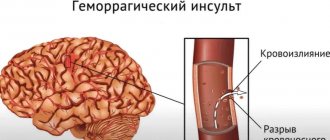
- Hemorrhagic stroke is a hemorrhage into the substance of the brain or under the arachnoid membrane due to rupture of a vessel as a result of high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, vasculitis, aneurysms, coagulation disorders. Patients aged 50-69 years are at high risk. At 39-49 years old it is less common. The incidence is 15-20% among all types of stroke.
There are classifications that distinguish types of stroke taking into account other signs.
1. By severity:
- minor, including microstroke (transient ischemic attack) - a passing disturbance of cerebral circulation with complete disappearance of neurological symptoms within 1 day to 3 weeks;
- moderate severity;
- severe, extensive stroke of the brain - damage to a large area with pronounced neurological symptoms and severe condition, sometimes with falling into a deep coma.
2. By location
- left or right hemisphere. Each side is responsible for different functions, so the symptoms will be different. For example, if the left half is affected, the movements of the right side of the body suffer, speech and memory are impaired. The person loses the ability to read and write.
When the right hemisphere is damaged, the movement of the left side of the body, the perception of oneself, one’s body, and the surrounding space are impaired, and mental disorders develop.
3. By quantity
- primary stroke (first) and repeated strokes (second, third, fourth). Repeated strokes are more severe because the lesion area increases each time.
4. By age
- in children, starting from the prenatal period, young, elderly. The severity of clinical manifestations and prognosis depend on the patient’s age, the cause of concomitant pathology, and the timeliness of diagnosis. The most difficult prognosis is for delayed detection of a stroke, a large lesion, a weakened body due to concomitant diseases, bad habits, and vitamin deficiency.
5. By localization
:
- in the vertebrobasilar basin with damage to the occipital lobe of the brain, cerebellum and brainstem - visual disturbances develop, gait changes;
- frontal lobes - speech and swallowing suffer;
- temporal lobes - memory, writing, speech deteriorate;
- parietal lobe - speech and speech understanding suffer.