Saturation is a term that is currently widely heard, because the level of oxygen in the blood is a significant diagnostic factor for coronavirus. However, doctors paid close attention to these numbers even before the pandemic.
Saturation is one of the important indicators of the body’s vital activity - along with body temperature, pressure, etc. It shows the level of oxygen saturation of capillary blood. It helps doctors understand how the respiratory system works. “Saturation is an indicator of oxygen saturation in the blood. It is measured as a percentage and allows us to determine whether our body receives the required amount of oxygen. Normally, in a healthy person it ranges from 95 to 100%. Figures of 94% and below indicate that a person has various types of respiratory failure,” says Elena Dolgikh, deputy chief physician for the medical department of the Khimki Regional Hospital, a doctor of the highest category .
What is saturation
Lung saturation is a term that is an indicator of the level of oxygen saturation in the blood.
Despite the constancy of the visible respiratory process, the intake of life-giving gas into the body can decrease and worsen the well-being and capabilities of the body.
What's important here is why exactly oxygen levels are being monitored. The substance is directly involved in obtaining about 90% of all energy generated by the body. Oxygen carries out the transfer of molecules that feed cells in order to obtain energy when processed during life. Therefore, when its level drops, the entire body suffers.
determination of saturation norm
Quantitative assessment of saturation - percentages, indicating the number of individual hemoglobin molecules compared to the total number of molecules interacting with O2 (the designation of oxygen in chemistry).
There are 2 methods of obtaining the indicator:
- in absolute value – SaO2 (analysis of a blood sample by laboratory method);
- non-invasively, without obtaining a sample - SpO2 (with a special device).
The latter method is used everywhere due to its speed and safety, as well as the absence of a time gap for research in the sometimes critical condition of the patient.
The non-invasive method (from the English invasion - immersion) involves the operation of a device called a “pulse oximeter”. It is attached to your finger and turned on - this takes just a few seconds due to its similarity to a clothespin. After collecting information and analyzing it, lasting no more than a minute, the result is shown on the screen.
pulse oximeter - measurement of blood saturation
The principle of operation is to capture the color spectrum when illuminating blood. With less oxygen content in it, the color will definitely change.
Ambulance teams must have this device in their kit. It takes up little space, weighs almost nothing and is inexpensive.
The essence of the measurements is the same for medical devices and popular electronic sports bracelets. The latter have much less accuracy, but they are also tuned to track hue.
In which organs is the blood saturated with oxygen?
To answer this question, you should first recall the school topic on anatomy “Circle of Blood Circulation.” After all, it is during this process that the body’s tissues are saturated with all the necessary substances and oxygen. And this happens in the following way: from the left ventricle, the heart muscle gradually flows through the arteries to all organs of the body. As a result of the large circle, a kind of gas exchange occurs in the capillaries. In other words, oxygen goes from the blood to the tissues, and carbon dioxide comes from the tissues to the blood. In this case, the red cells become venous and enter the right atrium through the vena cava, and then into the right ventricle.
Oxygen saturation of the blood occurs in the lungs.
Almost every schoolchild knows about this. By the way, this element is transferred to all internal organs and tissues not only with the help of our natural pump - the heart, but thanks to special carrier proteins contained in red cells or so-called erythrocytes. In medicine they are usually called hemoglobin. It shows the degree and level of oxygen saturation in the blood.
However, the next question immediately arises about what its norm is. It is worth noting that in the normal state, almost all hemoglobin is associated with oxygen. Moreover, the saturation rate itself varies from 96% to 99%. If this level decreases and becomes less than 95%, then the person experiences severe forms of diseases of the blood vessels, respiratory system and heart muscle. In addition, with severe anemia (that is, with a significant decrease in hemoglobin levels), the patient may notice other changes in the body (for example, weakness, deterioration in the condition of nails, skin, etc.).
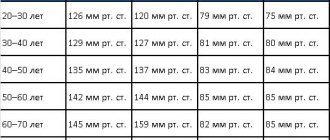
What is the norm of saturation in adults - table
What is the norm of saturation in adults - table
What does saturation 99 or 100 mean? In adults, the norm of saturation is in the range from 95 to 99%. There are no deviations in health, and there are no general therapeutic complaints. Individual characteristics of a person should also be taken into account:
- a healthy person without bad habits has an indicator of 95-99%;
- smoker – from 90 to 94% (and the longer the smoking experience, the worse);
- people with a chronic disease of the respiratory system – 90-95%.
Medical personnel consider levels below 94% to be health threatening. If the value is less than 90%, the person receives emergency medical care.
It is characteristic that this indicator is static: the body maintains it at approximately the same level. This was revealed on the basis of statistics and verified many times.
Signs of lack of oxygen
Of course, it is extremely important to understand that there is not enough oxygen as quickly as possible. After all, this will allow you to take action in time. Elena Dolgikh notes that manifestations of a decrease in saturation will be:
- shortness of breath (a person begins to breathe more quickly to compensate for insufficient oxygen levels);
- pale skin;
- tremor of the lower extremities;
- swelling.
All this, naturally, leads to the fact that the person’s condition is disturbed. And quite seriously.
Elena Dolgikh notes that it is important to monitor the numbers on the pulse oximeter. “If the saturation is below 95%, this is already a reason for alarm and a thorough examination by specialists. If there are problems with the lungs, doctors will begin examinations and prescribe the necessary treatment. Covid can also cause a decrease in saturation from the first days. If necessary, the patient will be hospitalized,” says Elena Dolgikh.
So you should pay close attention to yourself so as not to miss the body’s warning signals. Lack of oxygen becomes a serious complication, against the background of which a lack of energy, lethargy, and weakness develop. The longer oxygen starvation, the worse a person becomes. Doctors note that the body literally begins to age before our eyes, immunity deteriorates, the rate of cell renewal decreases, and all systems and organs wear out faster.
Saturation with coronavirus
The disease coronavirus infection (colloquially referred to as “coronavirus”) is characterized by powerful and comprehensive damage to the main respiratory organ – the lungs. The alveoli are primarily affected - single cells that perform gas exchange between the air entering the lungs and the blood that carries oxygen to the cells of the body.
The alveoli and their septa are blocked by the virus and become inflamed, as a result of which their useful work is reduced to zero in a short period of time. Inflammation spreads to neighboring alveoli, and the affected area increases. As a result, the volume of oxygen entering the body per unit of time continuously decreases.
The condition gradually or quite sharply (over 3-5 days) worsens, the state of health is subjectively assessed with the epithets “tired” or “exhausted”, and cold symptoms appear.
The important thing is that the victim does not know about the fact of infection until a state is discovered in which the body is already exhausted, and the volume of lesions in the lungs can lead to disaster.
Saturation during coronavirus is a criterion for the degree of damage to the body.
If the value is too low, immediate medical attention is required, including connection to a ventilator.
Symptoms of Covid-19
The content of the article:
- Symptoms and course of Covid 19 in adults
- ARVI and coronavirus
- Features of clinical manifestations of coronavirus in children and symptoms in pregnant women
- Saturation as an important indicator of coronavirus infection
Symptoms and course of Covid 19 in adults
Covid 19 is a disease that has caused one of the longest pandemics in the world. This term is usually understood as the name of the virus, however, this is not so. The pathogen itself is called SARS-CoV-2 and it is it that penetrates the human body, causing a dangerous disease.
Coronaviruses are a fairly well-known group of viruses that can cause an infectious process. The first serotypes were identified back in the 60s; over time they only mutated. However, one thing remained unchanged, the method of infection. The virus itself looks like a ball with teeth all over its entire area, hence its name “crown”. A viral particle invades a human cell, changes its mechanism of operation, and then reproduces many copies of itself. The immune system cannot recognize all of these mechanisms.
Of course, such a disease could not help but change, and today the following forms of coronavirus are distinguished: alpha (British), beta (South African), gamma (Brazilian) and delta (Indian). As scientists note, each new strain of the virus may be more aggressive than the previous one. Another important detail is that different strains have a greater impact on certain groups of people, for example, young people under 40 years of age are more likely to get sick with the betavirus, while pregnant women and young people are more susceptible to the gamma strain. With the latest delta strain, there is no official information yet on who is more susceptible to infection, but it is known that this type is spreading at an incredibly fast pace. According to the open Russian consortium for sequencing the genomes of SARS-CoV-2, it was the delta strain that caused the disease in more than 90% of those infected with Covid in July 2021. So far, all produced vaccines are effective against the identified strains.
What symptoms of coronavirus occur in a sick person and how to distinguish them from a regular ARVI, we will analyze in the article.
Stages of the disease:
- From 1 to 3 days. A person feels the first signs of coronavirus, experiences muscle discomfort and weakness. Body temperature can reach subfebrile levels of 37-37.5 degrees. Possible nasal congestion. The general condition is similar to the onset of a common ARVI.
- From 3 to 5 days. During this period, the virus manifests itself as a mild cough. Many sick people lose their sense of smell, they stop feeling the taste of food, or it changes. More than half of the sick experience mild abdominal pain and diarrhea during this period. Body temperature continues to rise.
- From 5 to 10 days. During this period, patients whose immune system was able to cope with the virus begin to recover. The symptoms gradually disappear. Otherwise, especially against the background of chronic diseases, the symptoms not only do not go away, but also intensify. There is a strong barking cough, chest pain, runny nose, shortness of breath, tachycardia.
- From 10 to 13 days. During this period, the disease progresses greatly. Chest pain intensifies, breathing becomes rapid, the skin becomes pale. Blood oxygen levels can drop to critical levels, which is why it is so important to constantly measure them. Lung damage is diagnosed from 20 to 60%. The patient requires hospitalization.
- From 13 to 15 days. During this period of time, two options are possible: the further course of the disease is pneumonia, which requires artificial ventilation, or recovery with properly selected treatment.
- From 15 to 30 days. During the recovery process, even with significant improvement in the condition, shortness of breath continues to persist. Smell and taste may not return for a long time. The norm is taken to be from one month to six months.
Currently, various clinical variants of the course and manifestations of coronavirus in humans have been recorded, including the following:
- pneumonia with acute respiratory failure;
- pneumonia without respiratory failure;
- damage to the upper respiratory tract;
- septic shock;
- thrombosis, blood clotting disorder.
Symptoms of coronavirus can vary depending on the severity of the disease: mild, moderate, severe.
The mild form implies the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels;
- dry cough with almost no discharge;
- weakness in the body.
Less common, but also possible, are the following:
- loss of taste and smell;
- nasal congestion;
- sore throat;
- headache, migraine;
- conjunctivitis;
- diarrhea;
- skin rash.
The symptoms are similar to the onset of a standard respiratory illness, except for the loss of smell and taste.
Severe disease involves symptoms such as:
- dyspnea;
- severe cough with discharge, possibly blood;
- loss of appetite;
- severe chest pain;
- high temperature, 38 degrees or more;
- feverish state, loss of consciousness;
- a sharp drop in blood oxygen levels according to pulse oximetry.
Less common, but also possible:
- irritability, anxiety;
- convulsions;
- tachycardia;
- severe vitamin D deficiency.
In older people, the disease may have an atypical course, including various neurological disorders.
It should also be remembered that after infection with coronavirus, chronic diseases of the heart, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract often become more active, which means consequences such as stroke, ischemia, etc. are possible.
Attention! Symptoms may not fully manifest themselves; for example, cases of coronavirus without fever are not uncommon. Even more often, there are no symptoms at all, and the person experiences Covid in a very mild form, believing that he has a runny nose for 2-3 days.
ARVI and coronavirus
The coronavirus spread so quickly partly because it was impossible to diagnose it correctly right away. Covid, unlike ARVI, can lead to more serious complications, so you need to learn to distinguish between the symptoms of a common cold and coronavirus. For example, the sense of smell can disappear even with a cold.
Similar symptoms:
- cough;
- runny nose;
- a sore throat;
- elevated body temperature.
The difference between coronavirus and ARVI:
- long incubation period. ARVI develops rapidly, while Covid-19 enters the acute phase only after 2 weeks.
- low-grade fever that lasts up to a week. While with ARVI, the temperature rises to febrile levels already on the 2-3rd day.
- Cough with coronavirus is prolonged, often dry, barking, accompanied by pain in the sternum. With ARVI, the cough becomes productive with sputum discharge.
- During Covid, diarrhea and vomiting are often observed, while with ARVI such signs are absent, unless the respiratory disease is accompanied by poisoning.
What is the difference between coronavirus and flu
Common features of influenza and coronavirus:
- chills, body aches, general state of weakness;
- diarrhea;
- Influenza is also transmitted by contact and airborne droplets.
Main differences:
- unlike coronavirus, the flu develops rapidly, body temperature rises to 39-40 degrees;
- the patient feels a headache, pain in the eyes, and may experience light and sound sensitivity.
Interesting on the topic: Loss of smell due to a cold
Features of clinical manifestations of coronavirus in children and symptoms in pregnant women
The total percentage of children infected with coronavirus in the world is about 10%; in Russia this figure is 6-7% of the total number of cases.
For the most part, children tolerate coronavirus much easier, often without even realizing they are infected, since there are no obvious symptoms. But there are often severe and moderate cases when babies need hospitalization.
More often, children become infected with Covid from sick adults.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease in children:
- fever;
- dry cough without discharge;
- nausea and vomiting;
- scratchy sore throat;
- diarrhea.
Children, just like adults, may lose their sense of smell and taste, but most often they do not attach any importance to this and do not experience severe discomfort.
A characteristic visual sign of coronavirus for children is blue-white fingers that appear to be frozen.
In children, as in adults, a practically asymptomatic course of coronavirus is possible, which means that any changes can only be observed on a computed tomogram (characteristic lung lesions are visible).
Symptoms of Covid in pregnant women
Pregnant women are at greater risk of contracting coronavirus because their immune system is less active while pregnant.
Their signs of infection are the same as for other people:
- headache, muscle pain;
- fatigue;
- loss of smell and taste;
- slight increase in temperature.
However, symptoms that are characteristic only of pregnant women and threaten the life and health of the mother and child may also occur:
- high blood pressure;
- severe swelling;
- abdominal pain;
- bleeding;
- a sharp drop in saturation.
Any of the above symptoms requires urgent hospitalization of the woman. When saturation drops and blood pressure rises, the woman needs to be connected to a ventilator, since both she and the child suffer from oxygen starvation. It is not uncommon to have an emergency caesarean section if the fetus has a slow heartbeat.
Pregnancy is a condition during which chronic diseases can worsen. Covid can worsen the negative consequences of the following diseases:
- diabetes;
- asthma or other lung diseases;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- kidney or liver diseases.
Saturation as an important indicator of coronavirus infection
Saturation is a term that has become firmly established in the everyday life of doctors and patients around the world, since this term refers to the level of oxygen in the blood, and as we know, during Covid this indicator decreases significantly.
In a normal state, a person’s lungs work in such a way that constant gas exchange occurs, as a result of which the blood and tissues are saturated with oxygen. With Covid, the alveoli become inflamed and dangerous conditions such as hypoxia and hypoxemia occur. In the first case, the tissues do not receive oxygen, in the second, blood.
Symptoms of low saturation:
- a feeling of lack of air, a person literally begins to suffocate during a conversation or intense movements;
- severe weakness and fatigue;
- dizziness;
- ringing or any other noise in the ears;
- cyanosis - blue discoloration of the lips, areas around the mouth, and fingers.
A severe form of hypoxia is also possible, in which a person experiences hallucinations, cannot navigate in space, and may faint.
The oxygenation rate is 98-99%. For smokers or people with lung diseases, this figure is lower - about 92-95%.
If the saturation rate is in the range of 80-90%, then this is a reason to use an oxygen mask. When the critical value is less than 80%, connection to artificial ventilation is required.
Uncharacteristic symptoms of Covid
According to the latest data, scientists believe that one of the characteristic signs of Covid may be a skin rash. There have been many cases where coronavirus infection causes damage to the walls of small blood vessels in the skin, resulting in erythema, exanthema and lichen, measles-like rash, and blisters of unknown etiology.
The symptoms of coronavirus are now quite well studied, so at the first signs of the disease you need to seek medical help. Treatment of coronavirus requires a systematic approach and, most often, constant monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Reasons for low saturation
Low oxygen saturation in the blood indicates some abnormal health condition. Most often this is:
- qualitative and quantitative change in the state of the blood (expressed in a change in the number and characteristics of red blood cells, etc.);
- disease of the respiratory system (from minor pneumonia to cancer);
- excess body weight (taking into account the constitution and standard weight for height);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (from transient infectious diseases to congenital heart defects).
Smoking is also cited as a cause.
How long does it take for saturation to recover?
With coronavirus, saturation is slightly reduced, but this is normal - the lung tissue needs time to restore the previous vital capacity of the respiratory organ. Breathing exercises (see Strelnikova’s set of breathing exercises) and walks in the fresh air with moderate physical activity are extremely useful.
To prevent aggressive adhesions in the lungs in patients with fibrous changes evident on CT; usually with CT-4, CT-3, less often with CT-2 and very rarely with CT-1, antioxidant therapy for pulmonary fibrosis is prescribed, which includes a diet enriched with antioxidants, acetylcysteine, and vitamins E (if there are no allergies). To clarify the diagnosis and causes of reduced saturation after coronavirus, CT control is important.
What to do with low saturation
At critical levels, life-sustaining drugs and equipment should be used. This is done by the medical staff.
If it is low, it is recommended to do the following:
- breathe fresh and clean air, do breathing exercises;
- drink water in small sips and take blood thinning medications (as prescribed by your doctor);
- consume foods high in iron (buckwheat, meat, apples).
Regular breathing training, combined with physical exercise, will strengthen the body and make it easier to endure any disease due to the improved function of oxygen supply to all tissues in need.
Oxygen-helium therapy
The Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation has issued recommendations for the treatment of low saturation levels in COVID-19. Therapy with the addition of an oxygen-helium mixture has proven to be the most effective.
The mixture is introduced into the body through a device and heated to a temperature of 50-60 degrees Celsius. A warm oxygen-helium mixture is necessary for better penetration into the body and reduced breathing resistance. The mixture passes through hot water in a humidifier and is then supplied through a mask to the respiratory organs, in which case oxygen penetrates into the alveoli much faster, their O2 saturation increases, and saturation increases.
With such therapy, the disease progresses more easily, the body recovers at a rapid pace, and the rehabilitation period is shortened.
TECHNICAL SUPPORT FOR MONITORING VENOUS SATURATION
ScvO2 and SvO2 can be measured discretely by analyzing the gas composition of venous blood samples taken from a central venous catheter or the distal lumen of a Swan-Ganz catheter, respectively. However, for a number of reasons outlined above, continuous measurement of ScvO2/SvO2 may have a number of advantages, particularly in the face of rapid and difficult to predict changes in tissue blood flow and other determinants of oxygen delivery. Currently, there are several systems for continuous measurement of ScvO2/SvO2, operating on the principle of venous photometry (oximetry). The continuous measurement method is based on the use of a small-diameter catheter into which fiber-optic conductors are integrated, one of which emits light of a certain wavelength into the venous blood flow, and the second transmits the reflected signal to the optical sensor of the monitor (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Principle of continuous reflectance venous oximetry
1. CeVOX and PiCCO2 monitoring systems (Pulsion Medical Systems, Germany). The sensor for venous oximetry is installed through one of the lumens of the central venous catheter. Continuous ScvO2 measurements require CeVOX (PC3000) or PiCCO2 central units equipped with an optical module (PC3100) and a disposable fiber optic sensor (PV2022-XX, 2F (0.67 mm), 30–38 cm). Initial calibration of the monitor in vivo requires insertion of the sensor into the superior vena cava. After confirming a high-quality signal, a sample of venous blood is taken to determine its oxygen saturation and hemoglobin concentration. Entering these values into the monitor menu completes the calibration procedure. The convenience of the system is that repositioning, removing or replacing the oximetry sensor does not require repositioning or removing the central venous catheter. According to a recent study by Baulig W. et al.6 (2008), ScvO2 measured using the CeVOX system has acceptable sensitivity and specificity for predicting significant changes in the indicator. The PiCCO2 system allows continuous monitoring of DO2 and VO2 values.
2. The PreSepTM system (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, USA) includes a triple-lumen central venous catheter with a pre-integrated fiberoptic guidewire for continuous monitoring of ScvO2. The catheter can be connected to a number of Edwards Lifesciences systems, in particular Vigilance-I, Vigilance-II and VigileoTM. At 20 cm in length, the catheter diameter is 8.5F (2.8 mm). In vitro and in vivo calibration is required before installation. The quality of the ScvO2 signal can be impaired by pulsation in the area of the catheter tip, periodic contact with the vessel wall (catheter jamming), kinking and formation of a blood clot, and hemodilution. Updating the hemoglobin and hematocrit values in the monitor menu is necessary when these values change by 6% or more. Models with the “H” marker have the traditional antibacterial and heparin coating of AMC Thromboshield. Currently, PreSepTM catheters are protected from bacterial contamination by a patented OligonTM complex (a complex coating including silver, platinum and carbon atoms), the action of which is based on the release of active silver ions.
3. The CCOmbo system (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, USA) is a Swan–Ganz catheter with an integrated fiberoptic element. When connected to monitoring systems, Vigilance provides continuous measurement of SvO2, CO, as well as right ventricular end-diastolic volume and ejection fraction. The cost of the catheter is relatively high.
Oxygen measuring device
Oxygen saturation is measured using a medical instrument called a pulse oximeter. It is shaped like a clothespin. This device is equipped with a sensor and 2 diodes that emit light rays of different wavelengths and interact with a photocell. The blood is then scanned by absorbing light emitted by an oximeter placed on a finger or earlobe.
A pulse oximeter is a simple, small-sized device. To use it, it is usually enough to place your finger inside and nothing more. Pulse oximeter models are similar to each other. Of course, the most common is the finger device, but there are also wrist versions that are designed to determine the parameter in question during sleep. Such models must be securely attached to the user’s hand.
The pulse oximeter allows you to accurately determine SpO2 levels and heart rate. The data is displayed on the LED screen both in the form of stripes and as a numerical expression. They consume little power, mainly because they are designed to go into standby mode or turn off when not in use.
Pulse oximetry can tell you whether blood oxygenation levels are normal or below normal. The results make it clear whether there is respiratory failure and to what extent, and whether oxygen therapy should be prescribed.
How to saturate the blood with oxygen if the lungs are not working
The main methods of treating distress syndrome are artificial ventilation (ALV) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
A ventilator is essentially a compressor that, one might say, forces oxygen into the patient’s lungs. To do this, doctors insert an endotracheal tube into the trachea. A special humidifier heats the air from the ventilator to body temperature and humidifies it. The device also removes exhaust air - carbon dioxide.
Patients are given medications that relax the diaphragm and other muscles—effectively immobilizing them—to allow the machine to fully regulate breathing.
There is also non-invasive ventilation, when the patient is put on a mask with a tube over the mouth and nose, but the tube is not inserted into the respiratory tract.
An ECMO machine is like an artificial heart and lung for the patient. To connect the device to the body, special long devices, called cannulas, are inserted into the patient’s large blood vessels. Through them, the blood enters the oxygenator - a device with a special membrane, with the help of which oxygen is added to the blood, and carbon dioxide (exhaust air) is removed.
The oxygenated blood is then warmed and returned to the patient's body. To comply with physiological mechanisms, blood sampling and infusion occurs as close to the heart as possible.
New ventilator in Barnaul Clinical Hospital No. 11.
Anna Zaikova.
Does it make sense to buy a pulse oximeter?
It's a difficult question. The recommendations of medical societies do not advise everyone to buy pulse oximeters. However, for some patients who have heart failure or chronic lung disease and use oxygen at home, doctors recommend having a pulse oximeter at home. This is necessary for a person to determine whether he needs to breathe oxygen and generally control his condition. Some doctors, however, recommend pulse oximeters for people without such indications. The arguments in this case are as follows:
- So as not to panic again
. A feeling of “stuffiness” in the chest and shortness of breath are not necessarily associated with severe lung damage. In some cases, fever, cough, and anxiety can lead to the same sensations. If pulse oximetry readings are 94-96%, there is no need to worry: most likely, urgent hospitalization is not required. - To control changes in your condition
. With an acute respiratory viral infection that proceeds as usual, using a pulse oximeter you can notice a deterioration in the condition early enough and inform your doctor about it. We are talking about a constant saturation below 92-93% in the waking state (during sleep it can normally be lower). - To help the doctor
. If you tell the doctor about your complaints, temperature, pulse and blood oxygen saturation, it will be easier for him to determine further treatment tactics, even with a remote consultation.
The arguments against are obvious: constant measurements can increase someone's anxiety, and random low readings even more so. In any case, it is important to understand that the general condition should be assessed comprehensively, and not just according to the readings of the device. If you want to buy a pulse oximeter, it is best to discuss this with your doctor.
How much do pulse oximeters cost?
The device looks something like this, although there may be variations
Sadly, their prices have increased significantly since the start of the coronavirus pandemic. This is not to say that they cost exorbitant amounts of money, but a few months ago they could be bought 2-3 times cheaper. A quick study of the offers showed that today the cost in Russia varies from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles and they are in stock . But you can be smarter and order a pulse oximeter on AliExpress, it will be much cheaper. There pricing policy is from 500 to 1000 rubles.
This pulse oximeter costs 1,000 rubles
If you are concerned about any of the above, but don’t want to take risks and visit hospitals during this difficult time, it may make sense to explore several options for home pulse oximeters.