What does the change in atmospheric pressure depend on?
A deviation of the barometer needle by 10 mm in one direction or another is sensitive to humans. And pressure drops occur for several reasons.
Seasonality
In summer, when the air warms up, the pressure on the mainland drops to its minimum values. In winter, due to heavy and cold air, the barometer needle reaches its maximum value.
Times of Day
In the morning and in the evenings, the pressure usually rises slightly, and in the afternoon and midnight it becomes lower.
Zoning
Atmospheric pressure also has a pronounced zonal character. The globe is divided into areas with a predominance of high and low pressure. This happens because the Earth's surface warms up unevenly.
At the equator, where the land is very hot, warm air rises and areas of low pressure are formed . Closer to the poles, cold, heavy air descends to the ground and presses on the surface. Accordingly, a high pressure zone is formed here.
How does atmospheric pressure affect our body?
Typically, atmospheric pressure changes during storms, atmospheric instability or strong winds. Climbing in height also takes its toll on the body. Mountain climbers are the people who suffer the most from these symptoms due to pressure changes when climbing mountains.
The most common symptoms are headache, gastrointestinal symptoms, weakness or fatigue, unsteadiness or dizziness, sleep disturbances , among others. The most effective measure against the onset of symptoms of altitude sickness is to descend to lower altitudes, even if they are only a few hundred meters.
Many climbers suffer from headaches when they climb too high.
How are atmospheric and blood pressure related?
This means that if you climb Mount Belukha (4,506 m), from the foot to the top, the temperature will drop by 30°C and the pressure will drop by 330 mm Hg. This is why high-altitude hypoxia, oxygen starvation, or miner's disease occurs in the mountains!
A person is designed in such a way that over time he gets used to new conditions. Stable weather has established itself - all body systems work without failures, the dependence of blood pressure on atmospheric pressure is minimal, the condition is normalized. And during periods of change of cyclones and anticyclones, the body fails to quickly switch to a new mode of operation, health worsens, blood pressure may change, and blood pressure may jump.
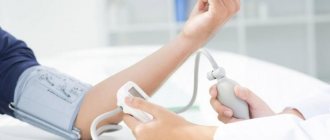
Arterial, or blood pressure, is the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels - veins, arteries, capillaries. It is responsible for the uninterrupted movement of blood through all vessels of the body, and directly depends on the atmospheric one.
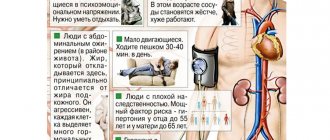
First of all, people with chronic heart and cardiovascular diseases suffer from horse racing (perhaps the most common disease is hypertension).
Also at risk are:
- Patients with neurological disorders and nervous exhaustion;
- Allergy sufferers and people with autoimmune diseases;
- Patients with mental disorders, obsessive fears and anxiety;
- People suffering from lesions of the articular apparatus.
What is prohibited for hypertensive patients?
When it comes to a person’s high blood pressure, all doctors agree that first of all you need to monitor your diet. It is also important to adjust your lifestyle and correctly distribute rest and work.techDirex.ndYaNew Porsche MacanApartments near Tsaritsyno metro station. Discounts! Project declaration on the advertised site
Prohibited for hypertensive patients:
- It is necessary to give up (or minimize) fatty foods, alcoholic beverages, coffee and strong tea, table salt, cigarettes, and sweet carbonated drinks.
- You should forget about heavy physical activity (bodybuilding and other strength training). In this case, it is better to perform gymnastic exercises that are included in the list of exercise therapy.
- If you have high blood pressure, you should avoid going to baths, steam rooms and saunas. Any increase in temperature will affect the heart and blood vessels.
Nutrition
A balanced diet is the main thing that every hypertensive patient should adhere to. It is important to carefully monitor your weight, as extra pounds put a strain on the heart and blood vessels.
What not to eat if you have high blood pressure:
- Limit the amount of table salt to a minimum. Consume no more than 3-4 grams, taking into account foods with sodium.
- Strong tea and coffee are prohibited. It is better to drink healthy herbal decoctions, chicory and infusion.
- Fatty meat should be excluded for the entire course of treatment.
- Avoid rich broths in your diet.
- Pies, buns, cakes and other baked goods can aggravate the disease. They are a combination of sugar and fat.
- Fish roe can occasionally be added to the diet, but in small quantities, as it contains a lot of salt.
- Delicacies such as honey, jam, compotes, jelly are limited, but it is not necessary to give them up completely.
- Since the body does not digest legumes well, they need to be included in the diet in minimal quantities.
- Alcohol, especially strong alcohol, is prohibited! It is also worth considering quitting smoking.
It is important to know at what stage the disease is. If the pathology has just begun to manifest itself, then you should not limit yourself in everything. If the disease is already progressing, then it is your diet that you need to monitor most carefully.
Prohibited sports
Professional sports strain the heart, which can cause blood pressure to rise. Often, athletes do not even suspect that they are beginning to develop hypertension. ADVERTISING
Hypertensive patients should not engage in bodybuilding, as numerous studies have confirmed that strength training significantly increases blood pressure levels. At the same time, even young beginner athletes are at risk.
Static exercises also negatively affect a person’s blood pressure, especially if performed for a long period of time. It is better to alternate them with aerobic exercise, which has a good effect on the heart and at the same time normalizes weight.
Climate and weather
Harsh climates and unpleasant weather can harm the body. Atmospheric pressure and human blood pressure are interconnected! In hypertensive patients, it usually immediately rises as soon as the atmospheric pressure begins to fall.
Rain, temperature, air humidity - all this affects the fluctuations in the patient’s cardiovascular parameters.
A sharp change in weather negatively affects the condition of a hypertensive patient! You need to choose places to relax with a stable temperature. Anapa with its resorts is well suited for this.
The northern part of Russia is an ideal place to live for those who suffer from heart and vascular diseases. Steppes, forests, mountains will be an ideal solution, since the air humidity there is not too high. The southern part of Russia has a very favorable mountain climate. There the air is quite clean and at the same time warm, and the weather practically does not change.
Psychological stress
More than half of patients with hypertension experience various psychological and emotional problems. Frequent depression, stress and overexertion appear.
This may be due to various factors:
- problems at work;
- financial difficulties;
- psychological trauma;
- loss of a loved one, etc.
In such conditions that depress the nervous system, the pressure usually increases by several tens of units. This can lead to dangerous complications. To restore and calm the nervous system, it is enough to take a drug with a sedative effect.
To ensure that the consequences of psychological conditions are not dangerous to health, the attending physician must prescribe complex therapy. In most cases, these are antidepressants that stabilize the patient’s nervous system and psyche.
Bad habits
Alcohol consumption is a serious risk factor for hypertension and its consequences. If the patient does not limit himself in drinking alcohol, this can lead to sad complications. Drunkenness always causes a hypertensive crisis, leading to brain hypoxia and heart attack.ADVERTISING
For hypertensive patients, the norm and limit per day is 40 grams of red wine!
Some believe that nicotine may be beneficial for high blood pressure. It relieves stress and other emotional states that are dangerous in hypertension. It is a myth! According to medical research, smokers have an increased risk of complications from cardiovascular diseases. Experts also say that in many cases this leads to disability or death.
Nicotine can constrict the walls of blood vessels after it enters the blood. In addition, it increases blood cholesterol levels.
How does a cyclone affect the human body?
A cyclone is an area with low atmospheric pressure. The thermometer drops to 738-742 mm. rt. Art. The amount of oxygen in the air decreases.
In addition, low atmospheric pressure is distinguished by the following symptoms:
- Increased humidity and air temperature,
- Cloudiness,
- Precipitation in the form of rain or snow.
People with diseases of the respiratory system, cardiovascular system and hypotension suffer from such weather changes. Under the influence of a cyclone, they experience weakness, lack of oxygen, difficulty breathing, and shortness of breath.
Some weather-sensitive people experience increased intracranial pressure, headaches, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Video: Atmospheric pressure and human well-being
We'll tell you what to do at low atmospheric pressure. Hypotonic patients need to monitor their blood pressure during a cyclone. It is believed that pressure from 130/90 mm Hg, increased for hypotensive patients, may be accompanied by symptoms of a hypertensive crisis.
Therefore, you need to drink more fluids and get enough sleep . In the morning you can drink a cup of strong coffee or 50 g of cognac. To prevent weather dependence, you need to harden the body, take vitamin complexes that strengthen the nervous system, tincture of ginseng or eleutherococcus.
How does an anticyclone affect the body?
When an anticyclone approaches, the barometer needles creep up to the level of 770-780 mm Hg. The weather changes: it becomes clear, sunny, and a light breeze blows. The amount of industrial pollutants harmful to health is increasing in the air.
High blood pressure is not dangerous for hypotensive patients.
But if it increases, then allergy sufferers, asthmatics, and hypertensives experience negative manifestations:
- Headaches and heartaches,
- Decreased performance,
- Increased heart rate,
- Redness of the face and skin,
- Flickering of flies before the eyes,
- Increased blood pressure.
Also, the number of leukocytes in the blood decreases, which means a person becomes vulnerable to disease. With blood pressure 220/120 mmHg. there is a high risk of developing hypertensive crisis, thrombosis, embolism, coma.
Is it possible to reduce weather sensitivity?
It is possible to reduce weather dependence if you follow simple but effective recommendations from doctors.
- The advice is banal, follow a daily routine . Go to bed early, sleep at least 9 hours. This is especially true on days when the weather changes.
- Before bed, drink a glass of mint or chamomile tea . It's calming.
- Do a light warm-up in the morning, stretch, massage your feet.
- After gymnastics, take a contrast shower .
- Get in a positive mood . Remember that a person cannot influence the increase or decrease in atmospheric pressure, but it is within our power to help the body cope with its fluctuations.
Summary : weather dependence is typical for patients with pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, as well as for older people suffering from a bunch of diseases. People with allergies, asthmatics, and hypertension are at risk. The most dangerous for weather-sensitive people are sudden changes in atmospheric pressure. Hardening the body and a healthy lifestyle saves you from unpleasant sensations.
Atmosphere pressure
Since air has mass and weight, it exerts pressure on the surface in contact with it. It is calculated that a column of air with a height from sea level to the upper boundary of the atmosphere presses on a 1 cm area with the same force as a weight of 1 kg 33 g. Man and all other living organisms do not feel this pressure, since it is balanced by their internal air pressure. When climbing in the mountains, already at an altitude of 3000 m, a person begins to feel unwell: shortness of breath and dizziness appear. At an altitude of more than 4000 m, a nose may bleed, as blood vessels rupture, and sometimes a person even loses consciousness. All this happens because atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude, the air becomes rarefied, the amount of oxygen in it decreases, but a person’s internal pressure does not change. Therefore, in airplanes flying at high altitudes, the cabins are hermetically sealed, and they are artificially maintained at the same air pressure as at the surface of the Earth. Pressure is measured using a special device - a barometer - in mm of mercury.
It has been established that at sea level at parallel 45° with an air temperature of 0°C, atmospheric pressure is close to the pressure produced by a column of mercury 760 mm high. The air pressure under such conditions is called normal atmospheric pressure. If the pressure indicator is greater, then it is considered increased, if less, it is considered decreased. When climbing mountains, for every 10.5 m, the pressure decreases by approximately 1 mmHg. Knowing how pressure changes, you can use a barometer to calculate the altitude of a place.
Pressure changes not only with altitude. It depends on the air temperature and the influence of air masses. Cyclones lower atmospheric pressure, and anticyclones increase it.
Relationship between air density and altitude. Peculiarities
How does atmospheric pressure near the Earth's surface change with altitude? This question has already been answered by the picture above. The higher the altitude, the lower the air density. As long as we are close to the surface of the earth, the change in air density is imperceptible. Therefore, for each unit of height, the pressure decreases by approximately the same value. The two expressions we wrote down earlier should be perceived as correct only if we are located close to the Earth’s surface, no higher than 1-1.5 km.
How does altitude affect a person's well-being?
The main negative factor affecting the human body at altitude is the lack of oxygen. It is as a result of hypoxia that acute disorders of the heart and blood vessels, increased blood pressure, digestive disorders and a number of other pathologies develop.
Hypertensive patients and people prone to pressure surges should not climb high into the mountains and it is advisable not to take long flights. They will also have to forget about professional mountaineering and mountain tourism.
The severity of the changes occurring in the body made it possible to distinguish several altitude zones:
- Up to one and a half to two kilometers above sea level is a relatively safe zone in which no special changes are observed in the functioning of the body and the state of vital systems. Deterioration in well-being, decreased activity and endurance are observed very rarely.
- From two to four kilometers - the body tries to cope with the oxygen deficiency on its own, thanks to increased breathing and taking deep breaths. Heavy physical work, which requires the consumption of large amounts of oxygen, is difficult to perform, but light exercise is well tolerated for several hours.
- From four to five and a half kilometers - the state of health noticeably worsens, and it is difficult to perform physical work. Psycho-emotional disorders appear in the form of high spirits, euphoria, and inappropriate actions. When staying at such a height for a long time, headaches, a feeling of heaviness in the head, problems with concentration, and lethargy occur.
- From five and a half to eight kilometers - it is impossible to do physical work, the condition worsens sharply, and the percentage of loss of consciousness is high.
- Above eight kilometers - at this altitude a person is able to maintain consciousness for a maximum of several minutes, after which deep fainting and death follows.
For metabolic processes to occur in the body, oxygen is necessary, the deficiency of which at altitude leads to the development of altitude sickness. The main symptoms of the disorder are:
- Headache.
- Increased breathing, shortness of breath, lack of air.
- Nose bleed.
- Nausea, attacks of vomiting.
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Sleep disorders.
- Psycho-emotional disorders.
At high altitudes, the body begins to experience a lack of oxygen, as a result of which the functioning of the heart and blood vessels is disrupted, arterial and intracranial pressure increases, and vital internal organs fail. To successfully overcome hypoxia, you need to include nuts, bananas, chocolate, cereals, and fruit juices in your diet.
Acclimatization in the mountains
Features of traveling in high mountain areas
The first sensation of a person who has risen to a great height is a headache. There are also frequent cases of loss of sleep, appetite, stomach upset, vomiting, feeling of weakness, etc. This is due to the fact that due to low oxygen levels at altitude, swelling of the brain occurs, which in turn causes an increase in intracranial pressure. The fluid accumulated in the intercellular space puts pressure on the brain, causing the functioning of all other organs to deteriorate. It is very important to gain altitude gradually so that the body has time to acclimatize. Otherwise, as a result, the person will begin to lose balance, stop thinking soberly and appear drunk. If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to descend approximately 100 meters down as soon as possible, otherwise a person may die within 2-4 days.
Mountain sickness also occurs due to pulmonary edema. Due to low oxygen levels in the blood and physical activity, pressure increases in the blood vessels of the lungs. Blood pressure rises, which leads to blood vessels starting to leak.
This article describes the main aspects of traveling in high mountainous regions for those participants who travel with our club to the mountainous regions of Nepal, Tibet, Northern India, Altai, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Africa, etc. (altitude 3000-6000 meters above sea level) . This article can be called a brief educational program for all lovers of mountain hiking.
What causes poor health in high mountain areas?
Poor health at high altitude is due to several reasons. At low altitudes, atmospheric pressure is usually 1 atm. As altitude increases, pressure begins to decrease. At low atmospheric pressure, a person begins to feel a lack of oxygen, this is due to the fact that the distance between O2 molecules increases significantly, and oxygen simply becomes more difficult to extract from the air. At high altitudes, the concentration of O2 in the air remains the same as at sea level, but due to the lower pressure, oxygen takes up more volume and it is much more difficult for a person to get all the oxygen he needs. A person begins to breathe more often, but still there comes a moment when the lack of oxygen will be very noticeable. The altitude at which oxygen saturation decreases is different for each person (approximately 1800 meters above sea level). Oxygen starvation is stress for the body, and it is necessary for the body to get used to this mode of operation. That is why a prerequisite for staying in the highlands is acclimatization, which takes some time. Consult your doctor. There may be contraindications specifically for you.
What is altitude sickness? What are the signs of the beginning of acclimatization of the body in the highlands?
Mountain sickness is a deterioration in health associated with a lack of oxygen in the human body, physical exertion, dehydration, physical fatigue and other factors. Mountain sickness is a sudden and dangerous condition for human health; it leads to swelling of the lungs and brain. That is why it is very important to follow the rules of acclimatization. Also, you should not go to high mountain areas if you have contraindications to staying at high altitudes.
If, while in a high-mountainous area, you begin to feel lethargic, shortness of breath appears, and you begin to lag behind the rest of the group, then most likely you have developed swelling. A dry cough gradually begins to appear, which eventually becomes wet. To avoid these unpleasant moments, it is necessary for the body to undergo gradual acclimatization.
Acclimatization rules
For the acclimatization process to occur correctly it is necessary:
1) drink more fluids,
2) don't rush,
3) exclude alcohol, fatty foods and heavy physical activity during ascent
The first point says that you need to drink as much clean drinking water as possible (at least 4 liters per day). This is due to the fact that at high altitude the body loses a large amount of water, which is why it is necessary to restore the balance of water in the body. You need to drink hot water with lemon, hibiscus, ginger, rose hips or other tonic and sour foods.
The second point says that you not only need to gradually gain altitude, but you also need to walk slowly, and in no case should you fuss. However, it is worth noting that, for example, when hiking in the highlands, physical exercise makes you sweat a lot, which in turn helps lower blood pressure.
The third point says that for good acclimatization in the highlands you need to adhere to prohibition. You should not drink black tea, smoke or eat fatty heavy foods.
Can medications be used to speed up the acclimatization process?
In order for acclimatization to take place correctly, you do not need to take any medications, you just need time. Over time, the body will get used to low atmospheric pressure and lack of oxygen. It is optimal if you gain altitude gradually: about 300-400 meters per day, rest should be arranged for every 3-4 days of ascent. If during the climb your head starts to hurt, then you should not torment your body and continue climbing. In this case, you just need to rest.
If you want to take any medicine, you can pay attention to homeopathy and the drug “Diamox”, which helps stimulate the brain, kidneys and speeds up breathing. Taking this drug should be started one day before the ascent and finished one day after the descent. The recommended daily dose is 500 mg, the drug should be taken twice a day.
To get rid of a headache you can take paracetamol, ibuprofen, spazgan. But the most important thing is not to rush while climbing. Medications can be taken to treat symptoms, but in no case to speed up the acclimatization process!!!
Contraindications for staying in high mountain areas
There is a whole list of medical contraindications for staying at high altitudes. Firstly, it is worth saying that a person can go to the mountains if he does not have any serious illnesses. People with chronic low blood pressure and problems with the cardiovascular system are strictly contraindicated from staying at an altitude of more than 3-3.5 thousand meters. Staying at high altitudes can cause negative consequences for teenagers and pregnant women. Most often, the physical fitness and age of the participants in the climb do not affect the acclimatization process.
How to make the acclimatization process easier?
1) Drink a hot drink from a thermos (not coffee or black tea) or plain acidified drinking water in small sips. A hot drink with honey, lemon and ginger is a great way to help with the acclimatization process.
2) Each individual first aid kit should contain moisturizing drops for the nose and eyes, hygienic lipstick with SPF factor and hand cream. These items will help you more easily cope with the dry air in the highlands.
3) While in the mountains, regularly take a complex of vitamins, and in the first 3-4 days in the mountains, the dosage of vitamins can be doubled. You can also take Microhydrin as a dietary supplement, which alleviates the symptoms of acclimatization.
4) Often during acclimatization, appetite decreases. But still, when going to the highlands, you need to take with you dried fruits, nuts, dark chocolate, cheese, lard and other high-calorie foods that will help you regain strength.
5) Don't forget to breathe deeply!
material prepared by Alexey Primanov
use of the article without the permission of the author is prohibited
Effect of altitude on blood pressure levels
When rising to a high altitude, a decrease in atmospheric pressure and thin air cause an increase in heart rate and an increase in blood pressure. However, with a further increase in altitude, blood pressure levels begin to decrease. A decrease in the oxygen content in the air to critical values causes depression of cardiac activity and a noticeable decrease in pressure in the arteries, while in the venous vessels the levels increase. As a result, a person develops arrhythmia and cyanosis.
Stability or anticyclone
When the air is colder and sinks, the barometric pressure increases because there is more air at the surface and therefore exerts more force. This causes atmospheric stability or also called an anticyclone. Anticyclone situation It is characterized by the fact that it is a zone of calm without winds, since the coldest and heaviest air slowly descends in a circle. The air rotates almost imperceptibly clockwise in the northern hemisphere and counterclockwise in the southern hemisphere.
Anticyclone on the atmospheric pressure map
Atmosphere pressure
Since air has mass and weight, it exerts pressure on the surface in contact with it. It is calculated that a column of air with a height from sea level to the upper boundary of the atmosphere presses on a 1 cm area with the same force as a weight of 1 kg 33 g. Man and all other living organisms do not feel this pressure, since it is balanced by their internal air pressure. When climbing in the mountains, already at an altitude of 3000 m, a person begins to feel unwell: shortness of breath and dizziness appear. At an altitude of more than 4000 m, a nose may bleed, as blood vessels rupture, and sometimes a person even loses consciousness. All this happens because atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude, the air becomes rarefied, the amount of oxygen in it decreases, but a person’s internal pressure does not change. Therefore, in airplanes flying at high altitudes, the cabins are hermetically sealed, and they are artificially maintained at the same air pressure as at the surface of the Earth. Pressure is measured using a special device - a barometer - in mm of mercury.
It has been established that at sea level at parallel 45° with an air temperature of 0°C, atmospheric pressure is close to the pressure produced by a column of mercury 760 mm high. The air pressure under such conditions is called normal atmospheric pressure. If the pressure indicator is greater, then it is considered increased, if less, it is considered decreased. When climbing mountains, for every 10.5 m, the pressure decreases by approximately 1 mmHg. Knowing how pressure changes, you can use a barometer to calculate the altitude of a place.
Pressure changes not only with altitude. It depends on the air temperature and the influence of air masses. Cyclones lower atmospheric pressure, and anticyclones increase it.
Does pressure increase or decrease in the mountains?
Let's remember the geography course for high school. As you gain altitude, the air becomes thinner and the pressure decreases. Every twelve meters of ascent reduces the barometer reading by 1 mmHg. But at high altitudes the patterns are different.
See the table for how air temperature and pressure change with altitude.
| 0 | 15 | 760 |
| 500 | 11.8 | 716 |
| 1000 | 8.5 | 674 |
| 2000 | 2 | 596 |
| 3000 | -4.5 | 525 |
| 4000 | -11 | 462 |
| 5000 | -17.5 | 405 |
Atmosphere pressure
Since air has mass and weight, it exerts pressure on the surface in contact with it. It is calculated that a column of air with a height from sea level to the upper boundary of the atmosphere presses on a 1 cm area with the same force as a weight of 1 kg 33 g. Man and all other living organisms do not feel this pressure, since it is balanced by their internal air pressure. When climbing in the mountains, already at an altitude of 3000 m, a person begins to feel unwell: shortness of breath and dizziness appear. At an altitude of more than 4000 m, a nose may bleed, as blood vessels rupture, and sometimes a person even loses consciousness. All this happens because atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude, the air becomes rarefied, the amount of oxygen in it decreases, but a person’s internal pressure does not change. Therefore, in airplanes flying at high altitudes, the cabins are hermetically sealed, and they are artificially maintained at the same air pressure as at the surface of the Earth. Pressure is measured using a special device - a barometer - in mm of mercury.
It has been established that at sea level at parallel 45° with an air temperature of 0°C, atmospheric pressure is close to the pressure produced by a column of mercury 760 mm high. The air pressure under such conditions is called normal atmospheric pressure. If the pressure indicator is greater, then it is considered increased, if less, it is considered decreased. When climbing mountains, for every 10.5 m, the pressure decreases by approximately 1 mmHg. Knowing how pressure changes, you can use a barometer to calculate the altitude of a place.
Pressure changes not only with altitude. It depends on the air temperature and the influence of air masses. Cyclones lower atmospheric pressure, and anticyclones increase it.
Cyclones and anticyclones
There are two main types of pressure systems in the atmosphere: cyclones and anticyclones. Cyclones and anticyclones are wind systems that have opposite characteristics.
A cyclone is a collection of winds circulating in a low pressure system. It rotates counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. It is usually associated with wet and stormy weather.
An anticyclone is a type of wind that circulates in a high pressure system. It rotates clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. It is usually associated with dry and clear weather.
In order to better understand how these two phenomena differ, let's look at them in more detail.
A cyclone is an area of low pressure where air masses rise. This usually indicates bad weather, such as rain or clouds. Winds in cyclones blow counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere. In a cyclone, air near the ground is forced toward the low-pressure center of the cyclone and then rises, expanding and cooling as it moves. As the rising air cools, it becomes more humid, leading to cloudiness and high humidity inside the cyclone. The main effects of tropical cyclones include heavy rain, strong winds, severe storm surges close to shore, and tornadoes. Destruction from a tropical cyclone, such as a hurricane or tropical storm, mainly depends on its intensity, size and location.
There are two types of cyclones:
1. Tropical cyclones . These cyclones that form over warm tropical oceans are also called tropical storms or tropical depressions. They are relatively small in size. However, they are characterized by enormous, destructive wind power.
The main tropical cyclone basins include the North Atlantic (including the Caribbean), the eastern Pacific, the western Pacific, the northern Indian Ocean, the southwestern Indian Ocean, the southern Pacific and the Australian region. Typically, tropical cyclones develop between 5 and 30 degrees latitude, as they require ocean water at a temperature of 27°C or so to form.
The terminology associated with tropical cyclones is quite confusing because people call these dangerous storms by different names in different parts of the world. In the North Atlantic and Caribbean, as well as the northeastern Pacific, they are commonly called "hurricanes." In the northwest Pacific, the most active tropical cyclone basin in the world, they are “typhoons,” while in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific they are simply “tropical cyclones” or “cyclones.” “Tornadoes”—much smaller and more localized than tropical cyclones, but capable of generating even higher wind speeds—are sometimes colloquially called “cyclones,” although they are completely different storms.
Particularly severe thunderstorms, which generate most of the world's most powerful tornadoes, form rotating updrafts called mesocyclones. In the United States, about 1,700 mesocyclones occur annually, with approximately 50 percent of them becoming tornadoes.
The birth of a huge tornado
Cyclones are among the most dangerous and destructive natural disasters that can occur. They have been responsible for 1.9 million deaths worldwide over the past two centuries. According to some estimates, up to 10,000 people die from these storms each year. Cyclones usually cause the greatest damage to coastal areas.
The consequences of Cyclone Idai - the deadliest tropical cyclone among the cyclones in the southwestern Indian Ocean that existed from March 4 to March 21, 2021. Wind gusts reached speeds of 280 km/h. The cyclone affected the states of Mozambique, Madagascar, Zimbabwe and Malawi, causing severe flooding in the affected areas, leading to numerous casualties. At least 1,297 people were killed, hundreds of thousands were left in need of assistance, and economic losses in these regions totaled more than $2 billion.
Consequences of tropical cyclone Kenneth in Mozambique. The cyclone hit northern Mozambique on April 25, 2021, with heavy rainfall and winds of up to 220 km/h. As a result of the disaster, more than 40 people died. In the Comoros Islands, the cyclone destroyed almost 80% of farms and more than 60% of crops, as well as over 3,800 houses. Previously, Mozambique was seriously affected by tropical cyclone Idai .
2. Extratropical or mid-latitude cyclones . They develop along frontal boundaries in mid-latitudes. These cyclones, which, unlike their tropical counterparts, develop where sharp temperature gradients exist between adjacent air masses, can be much larger than hurricanes, although their winds tend to be weaker. They reach several thousand kilometers in diameter.
3. Polar cyclones, also known as “Arctic hurricanes,” sometimes form over the Arctic and Antarctic seas, caused by the influence of cold air moving over slightly warmer ocean waters. In the Northern Hemisphere, meteorologists sometimes call polar cyclones “Arctic hurricanes” because their energy source is heat transfer from water to air and latent heat released by cloud condensation, and because their spiral cloud bands are somewhat similar to tropical cyclones. Polar cyclones often form quickly, sometimes in less than 24 hours, and are difficult to predict in advance.
An anticyclone is an area of high pressure where air masses descend towards the ground. This usually indicates good weather. Winds in an anticyclone blow clockwise in the northern hemisphere and counterclockwise in the southern hemisphere. Air masses in the center of the anticyclone move downwards, being replaced by a downward flow of air from high altitudes. As it moves down, the air compresses and heats up, which reduces its humidity and leads to a decrease in the number of clouds inside the anticyclone, dry and cloudless weather.
As you know, winds blow from a high pressure system to a low pressure system. In the case of an anticyclone, the wind blows and diverges from the center of the high pressure system. However, it does not flow straight out. Due to the Earth's rotation, air tends to move in a spiral. In the Northern Hemisphere, air currents in areas of high pressure move clockwise, and in the Southern Hemisphere, they move counterclockwise. This pattern ensures that winds to the east of an anticyclone in the Northern Hemisphere will bring cold air from the north, while winds to the west will bring warm air from the south. In the Southern Hemisphere this picture is reversed.
An anticyclone brings stable weather conditions corresponding to the time of year. In summer the weather is windless and hot, in winter it is frosty. It is characterized by few or no clouds.
Anticyclones form in certain areas. For example, they are most often found over large bodies of ice: in Antarctica, Greenland and the Arctic. They also sometimes appear in the tropics.
Anticyclones also carry danger and unpleasant consequences. They can contribute to fires and prolonged drought. With a long absence of wind in large cities, harmful substances and gases accumulate, which is especially important for people with respiratory diseases.
Smog in China. In some cities, it is almost impossible to go outside without a mask. The smog is even visible from space. Scientists have calculated that walking the streets without a mask is equivalent to smoking a pack of cigarettes.