Blood provides metabolism, nutrition and even respiration for all cells and tissues in the body. Doctors always closely monitor its indicators, using tests to determine the presence of certain diseases that destroy the body from the inside without visible symptoms. That is why blood tests are regularly taken: both for preventive purposes and to make a more accurate diagnosis.
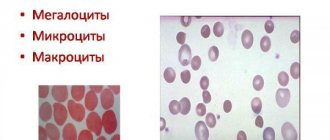
One of the most important components of blood are red blood cells or, as they are also called, red cells. They have a disc-shaped, doubly concave shape and perform one of the most important functions in the body - transporting oxygen to cells and carbon dioxide for its removal. Their size is not as important as their volume. In a healthy person, the volume of all red blood cells should be approximately the same, or with slight deviations from the norm; in the case of pathology, different cells appear. To identify such abnormalities, a blood test for RDW is performed.
The abbreviation RDW stands for Red Cells Indicies and translated means “red blood cell distribution width.” This indicator can be found in the results of a general blood test, since a separate study of red blood cells is not carried out. It has two markers:
- RDW-CV: shows how much cell size differs from the average (measured as a percentage)
- RDW-SD: Reflects the difference in size between the smallest and largest red blood cells (measured in femtoliters).
Indications for testing
Often, such an analysis is preventive and is taken on a regular basis (on average once a year) to identify diseases in the early stages, when they are much faster and easier to treat. It is prescribed to pregnant women to monitor their general condition and identify problems such as anemia, and for inpatient monitoring.
A general blood test is required during hospitalization to conduct a basic examination and obtain a more accurate picture of the disease, as well as before surgery to prevent possible complications. If the body is severely weakened, this may indicate that the person will not survive the operation; in such cases, it is necessary to undergo preliminary treatment for recovery.
The analysis is prescribed to identify and diagnose different types of anemia, as well as for possible diseases of the hematopoietic system. A general blood test helps track dynamics during monitoring of ongoing treatment, accurately determining the onset of improvements or deteriorations in the body’s condition, which helps to timely adjust treatment. It can be prescribed by a physician, general practitioner, surgeon, neurologist and hematologist.
More significant reasons
Even more significant reasons for changes in erythrocyte volume are:
- drinking untreated, low-quality or chlorinated water;
- defects in the functioning of the respiratory system or heart and blood vessels;
- period of growing up or approaching old age;
- genetic predisposition;
- the occurrence of iron deficiency anemia;
- various complications after ARVI, flu or colds;
- chronic infections;
- manifestation of symptoms of certain diseases (oncology, malignant tumors, etc.).
Blood levels
As mentioned above, the RDW indicator has two markers: RDW-CV and RDW-SD, each of which has its own units of measurement and content standards. Next we will look at each of them.
RDW-CV reflects the deviation of red blood cell size from the average, measured as a percentage and has different standards depending on the person’s age.
- Children under 6 months: from 14.9 to 18.7%
- Children over 6 months: from 11.6 to 14.8%
- Adults: 11.5 – 14.5%
RDW-SD shows deviations in the distribution of red blood cells by volume and is measured in femtoliters. The standard deviation is 37 – 54 femtoliters, regardless of age or gender.
Complete blood count with leukocyte count and ESR
Complete blood count is the most widely used laboratory method in clinical practice. It allows you to identify numerous pathological disorders in the body, often plays a key role in making a diagnosis, and may be an indication for prescribing other studies.
Prescribed in case of:
- Preventive examination;
- Planning hospitalization, invasive interventions, surgical operations;
- The presence of anemic symptoms (pallor of the skin, weakness, dizziness, tinnitus, tachycardia);
- Diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
It includes a large number of different parameters, each of which has its own value both individually and in a comprehensive study.
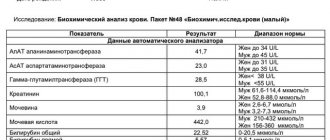
| № | Russian name | Reduction | Norm | Decrease in normal level | Increase in normal level | |
| Men | Women | |||||
| 1 | Red blood cells | RBC,Er, | 4.0-5.6*1012l | 3.4-5.0*1012l | Hemolytic, hemorrhagic, sideroblastic, iron deficiency anemia (IDA); Deficiency of vit B12, folic acid; Enteropathology; After intensive infusion, hypervolemia; Renal pathology associated with insufficient formation of erythropoietins - stimulators of red blood cell growth | Dehydration; Tumor hematopoiesis; Kidney neoplasms leading to hypersecretion of erythropoietin; Erythrocythemia, polycythemia; Chronic hypoxia, cardiopulmonary failure |
| 2 | Hemoglobin | HGB, Hb | 130-160g/l | 120-140g/l | ||
| 3 | Average HGB content in RBC | MCH | 27-31pg | |||
| 4 | Average Hb concentration in RBC | MCHC | 30-38g/dl | |||
| 5 | Color index | CPU | 0,84-1,0 | |||
| 6 | Hematocrit | HCT | 40-60% | 35-45% | ||
| 7 | Distribution width | RDW-CV | 11,4-14,8% | When going beyond any limits of reference values: Microcytosis or macrocytosis in a deficient anemic status; Metastases; Thalassemia; After blood transfusion | ||
| 8 | Heterogeneity index | RDW-SD | 35-60fl | |||
| 9 | Red blood cell volume | MCV | 80-100fl | IDA, intravascular hemolysis | Lack of vitamin B-12, folate, hepatopathology | |
| 10 | Absolute number of Er containing a nucleus | NRBC# | Normally absent | Used to diagnose thalassemia, sickle cell anemia; Oncohematology; Critical moments in resuscitation practice; Severe hypoxia; Widely used in neonatology and pediatrics. | ||
| 11 | Relative number of Er containing a nucleus | NRBC% | ||||
| 12 | Reticulocytes | RTC | 0,2-1,2% | Inhibition of hematopoiesis due to deficiency conditions or damage to the CMC | Posthemorrhagic, hypoxic status, the result of active treatment of anemia | |
| 13 | Platelets | PLT, Tr | 180-320*109l | Malignant destruction of red bone marrow, platelet germ, deficiency of vitamin B12, Fe and folic acid, viruses, hyperthyroidism | Myelofibrosis, autoimmune processes, tuberculosis, depression of megakaryocyte stem cells, collagenosis, liver cirrhosis, side effect of cytostatics | |
| 14 | Thrombocrit | PCT | 0,14-0,37% | |||
| 15 | Platelet volume | MPV | 7.5-12fl | Pregnancy; Multiple myeloma; Infections and inflammation; Oncohematology | After bleeding; Hereditary syndromes | |
| 16 | Large PLT Ratio (P-LCR) | P-LCR | 13-43% | |||
| 17 | Distribution width Tr | PDW | 15-17% | Exceeding the limits in any of the above situations, leading to quantitative and qualitative platelet changes | ||
| 18 | Leukocytes | WBC | 4-9.0*109l | Metastatic destruction of BMC, after chemotherapy, toxic effects, pneumonia, sepsis, immunodeficiency | The vast majority of infectious and inflammatory syndromes, trauma, surgical interventions, systemic immune hyperreactions | |
The leukocyte formula is used in the differential diagnosis of inflammatory aseptic, bacterial, viral, parasitic, and fungal diseases. Usually includes relative values of different types of leukocytes, however, if necessary (determined by the doctor), absolute numbers can be calculated:
- Basophils (BASO): above 1% occurs with allergies, hypothyroidism, chronic myeloid leukemia;
- Eosinophils (EO): 1-5%. Increased in allergic, parasitic, autoimmune conditions. Decrease in sepsis, abscesses, poisoning;
- Neutrophils (NEUT): band-nuclear up to 0-5%, growth in severe inflammatory-infectious pathology. Segmented up to 72%, less than 30% in case of anemia, damage to hematopoiesis due to intoxication, viral invasion, metastases, after chemotherapy;
- Lymphocytes (LYMPH) 19-37% . Lower in lymphogranulomatosis, AIDS, after cytostatic and glucocorticoid therapy. Higher in leukemia, toxicosis, drug overdose;
- Monocytes (MONO) 3-11%. Growth in bacterial invasion, rheumatoid arthritis. Fall due to immunodeficiency.
ESR (ESR): for men – up to 10 mm/hour, for women – up to 15 mm/hour. One of the markers of acute inflammatory process. It increases with increasing concentrations of immunoglobulins, C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, which is observed during inflammation, intoxication, and progression of malignant tumors.
To correctly interpret the results obtained, it is not enough to know the reference numbers; you need clinical thinking and the ability to comprehensively assess the current medical situation, which only an experienced specialist can help with.
Deviations from the norm (what they talk about)
Before talking about the possible reasons for deviations in this indicator, it is worth noting that it is not specific and cannot serve to accurately determine a particular disease. RDW is analyzed only in conjunction with other data from a general and biochemical blood test. So, if there is a slight deviation from the norm, but other indicators do not cause concern, then, most likely, this simply indicates the characteristics of the body, but to make a more accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a doctor.
An increase in RDW is normal only for newborns under 6 months of age. There is also a slight increase as a result of recent nervous stress and after a blood transfusion, but in all other cases, elevated results indicate the presence of the disease. They may indicate various types of anemia:
- Anemia of megaloblastic, myelodysplastic and siderablastic types
- Anemia with heterogeneity in red blood cell size (most often due to diet)
- Anemia due to impaired myelopoiesis
- Anemia due to chronic diseases
- Anemia due to acute blood loss (may indicate internal bleeding)
- Aplastic anemia
Also, elevated RDW levels may indicate the following diseases:
- Some homozygous hemoglobinopathies and homozygous thalassemias
- Increased reticulocyte count
- Hyperglycemia
- Congenital genetic diseases
Reduced indicators do not indicate the presence of any abnormality or disease, therefore such values are not taken into account during the examination. Most likely, this is a variant of the norm.
Why does the size of red blood cells change?
If RDW is elevated in a blood test, what does this mean? This is a common question. The simplest source of the problem of changes in blood cells is considered to be an unbalanced human diet. With a non-critical transformation of blood quality, the issue most likely lies in the deficiency of certain microelements, mainly such as B9, A, B12, folic acid, iron. If the reason lies in poor nutrition, then it is often enough to simply change the situation by adjusting it, that is, eating foods that contain the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities.
If this indicator significantly exceeds the norm, then the person has reason to worry and immediately consult a doctor for a thorough examination.
How the research works
In modern medicine, equipment plays an important role in treatment. the same can be said about a blood test. On an empty stomach, blood is drawn either from a vein in the elbow or from a finger (this method is especially often practiced in the case of children), and then all the work is transferred to a modern analyzer, which conducts research quickly and with high quality, giving an accurate result .
It counts the number of red blood cells of different sizes per microliter of blood, calculates the average cell size and determines the degree of deviation from the norm of this indicator. The largest and smallest cells are also measured and the difference between this spread and the possible norm is analyzed. This indicator is recorded in femtoliters.
Of course, the equipment may not always be accurate; maximum accuracy of results can only be obtained by manual counting, but this is a very long and labor-intensive process, which is practically not used in modern medicine.
If deviations in this indicator occur, the blood test is performed again to obtain a reliable result, because the diagnosis cannot be made as a result of a single blood sample.
Kinds
There are two varieties of this indicator:
- RDW CV, that is, the relative value of the width of the red blood cell distribution by volume, demonstrating the coefficient of heterogeneity in the size of red blood cells. This indicator in the analysis is required to establish the nature of the differences between blood cells.
- RDW SD. Determines deviations from the standard norm, which reveal differences in the distance between the maximum and minimum volume of red blood cells.
So, RDW in the blood test is increased. The reasons for this are presented below.
Preparation for the procedure
Since taking blood for a general analysis does not imply anything unusual, and the study itself is carried out regularly for almost all people, preparation does not require a person to take any special measures, but no one has canceled the standard recommendations before taking tests so that the results are reliable and correctly reflect the clinical picture:
- The RDW test is taken in the morning and on an empty stomach. Dinner in the evening of the previous day before donating blood should be light and at least 8 hours should pass between the last meal and the test, and preferably 12
- It is highly not recommended to drink alcohol 2 days before the test, as it can significantly distort the results
- It is advisable to give up fatty and fried foods, which have a negative effect on the body, 2 days in advance.
- You should not take a blood test after physiological and x-ray procedures
- It is recommended to refrain from smoking one hour before blood collection.
- It is advisable to exclude any physical and emotional stress; before the analysis, a 15-minute break and complete calm are required.
- Particular attention must be paid to the medications you are taking. Almost any medicine can distort the results of a blood test, so before donating blood you need to consult with a specialist: you may have to stop taking the medicine for a while to get an accurate clinical picture, or simply take the drug after the test.
If a repeat blood test is prescribed, it must be taken at the same time (since the composition of the blood may depend on the body’s circadian rhythms) and in the same laboratory. This is due to the fact that units and methods of measurement may vary between laboratories. Only if all recommended measures are followed will the result of the study be correct.
Signs
In the event that deviations in the activity of the circulatory system become more than minor changes, the human body gives certain alarm signals.
In any case, adjusting your diet or starting to treat the pathological process at an early stage is easier than bringing the matter to a critical stage.
The following symptoms may indicate an increase in RDW in the body:
- a strong increase in temperature of a systematic nature;
- excessive sweating;
- decreased activity, general fatigue, drowsiness;
- sudden changes in mood for no apparent reason;
- in some cases, the skin acquires a yellow tint.
If the symptoms listed above are noted, then there is no need to self-medicate or think that everything will go away on its own. It’s not worth much effort to see a doctor and get tested at the nearest laboratory or clinic. It is impossible to allow the occurrence of such consequences that can manifest themselves with the development of anisocytosis to the second, third and fourth degrees.
It is very important to understand the significance of a general blood test. RDW is often elevated, but only a qualified specialist is able to make the correct diagnosis based on the information received. In this case, it will also help to add possible additional signs that may worry the patient. Naturally, it is much easier to prevent a disease or eliminate it at an early stage.
Analysis for RDW in MedArt
The medical laboratory is equipped with modern high-precision equipment, high-quality reagents, all necessary consumables and qualified personnel. Our clients can rest assured of the reliability: if all preparation recommendations are followed, the results obtained will be 100% accurate. rdw in the blood test is reduced
Our team performs the work quickly, efficiently and with due understanding. Since there are people who are catastrophically afraid of any medical intervention, including blood sampling, we try to provide all our clients with the most comfortable and calm atmosphere, while performing all hematological studies at the highest level and providing accurate results.
With us, you can take a general blood test in a calm and comfortable environment and get a reliable result in the shortest possible time at an affordable price, without waiting in line for long hours, and then endlessly visiting doctors in an attempt to find out the result. We care about each of our clients and strive to do our work with the highest quality possible.
Detailed Definition
Red blood cells are disc-shaped, biconcave red cells that color the blood accordingly. In addition, they are its basis and transport oxygen to organs and tissues. In a healthy person, red blood cells do not differ in shape, color or volume. The proper functioning of red blood cells is determined not by their diameter, but directly by their volume. Its average is designated as MCV.
The coefficient is significant only when the RDW CV readings are fully identified. This value in a healthy person can fluctuate only slightly. This range in medicine is called the heterogeneity of erythrocytes, or the width of their distribution over the total volume. Most often, red cells decrease in volume as a person ages, that is, differences appear between them. This may also be caused by malignant tumors or anemia. If red blood cells of different volumes appear in the blood, this is called anisocytosis. To detect changes, the specialist must refer the patient to determine the RDW. It is often elevated in blood tests.