Ointments for the treatment of varicose veins have different effects on the body due to the components included in the composition. Let's take a closer look at what active ingredients are found in popular ointments and what benefits they bring to the body.
Heparin - affects blood clotting. Accelerates the dissolution of microthrombi in subcutaneous capillaries, thereby slowing down the process of blood clot formation. Inhibits the decomposition of hyaluronic acid in the body and helps connective tissue recover. Essential phospholipids reduce blood viscosity. Escin - increases the tone of veins, reduces capillary fragility, inhibits inflammation.
These three components are included in the composition of gels against varicose veins. Relieves pain, swelling, heaviness and fatigue in the legs. They should be used to get rid of the symptoms of the disease in the early stages or as an addition to treatment in the later stages.
Products containing extract from red grape leaves increase the elasticity of blood vessels. Do not allow plasma, proteins and water to penetrate from the vessel into the tissue. They help with swelling, fatigue and tension in the legs, and relieve pain. Recommended for relieving symptoms of varicose veins or for prevention.
Products containing an extract from the mucous membrane of the small intestine of animals reduce the level of a protein involved in the formation of blood clots. The drug thins the blood, reduces the risk of blood clots, and prevents swelling. Good results from use are achieved in combination with compression garments.
Horse chestnut seed extract increases vein tone, reduces inflammation and vascular permeability. Relieves swelling, a feeling of heaviness and fatigue in the legs, itching and pain.
“Magic” ointments and gels for varicose veins
Contact forms of therapeutic agents have appeared since time immemorial. Various ointment forms of medicinal substances appear in the works of all famous healers of antiquity. The commitment of many modern patients and doctors to the use of various ointments and gels is so strong that sometimes even common sense recedes. The modern pharmaceutical market presents a great variety of products for topical use: ointments and gels.
Patients with varicose veins rely on such ointments
Treatments for varicose veins are also very popular. In any city pharmacy you can find a whole stand with a good selection of various ointments and gels for varicose veins. The pharmacist will often provide detailed advice on which ointment is best for a specific form of varicose veins. Leading pharmaceutical companies, conducting a wide advertising campaign, use loud and encouraging statements. The hope of curing a serious pathology with a tube of ointment is fueled by “expert opinions” from advertising videos on the Internet and on television. After such information dumps, many patients do not even want to visit a doctor. And for what? If there is a remedy that is unique in its effectiveness and can relieve a long-troubling illness.
Which brand of ointment for varicose veins is better to choose?
Any pharmacy chain has analogues and identical medications, differing only in country, brand, and price. You can judge their quality and effectiveness in absentia by the reputation of the manufacturer. The best ointments for varicose veins, which were recognized by experts as leaders in 2021, were offered by the following pharmaceutical companies:
- Nizhpharm (Heparin ointment) is a Soviet pharmaceutical company in Russia that was created in Nizhny Novgorod back in 1919. Today it is one of the largest manufacturers of medicines. The product portfolio includes over 30 pharmacological groups, 100 names.
- CJSC "Green Dubrava" (Vishnevsky Ointment) is a full-cycle enterprise offering both substances and finished medicines. The company was officially registered in 2003, when it moved from Sergiev Posad to the city of Dmitrov. It is at the development stage and has 4 large workshops.
- Balkanpharma (Troxevasin) is a Bulgarian pharmaceutical company that was founded in 1999. Today it is part of the international holding Actavis. It uses the latest technologies according to European standards, producing medicines for the treatment of people and animals.
- Hemofarm (Gepatrombin) is an international pharmaceutical company that was founded in Serbia in 1960. Since 2006, it has been privatized by the German concern STADA AG. Today it is the largest exporter, as well as a leading player in the domestic pharmaceutical market.
- A. _ Menarini Manufacturing Logistics and Services (Lioton) is an Italian pharmaceutical company founded in 1915. Engaged in the development, production, processing, production of drugs for humans, as well as in veterinary medicine. Medicines from this brand are very popular on the Russian market.
- Sandoz (Venitan) is an international pharmaceutical company that was founded in Switzerland back in 1886. It deals with biosimilars and generics, that is, reproduction of the most popular medicines patented by other companies. This name is trusted by medical professionals today.
- Merckle GmbH (Dolobene) is a well-known German company that produces highly effective medicines. It was founded in 1881, first in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. It was moved to Germany in 1945. Her activities concern all areas of medicine.
- Elfa, Farmzavod, A.T. (Flucinar) is a group of companies that was founded in Poland about 20 years ago. Today it is the largest Polish manufacturer of ointments, as well as the main supplier of hormonal, cardiological, psychotropic and other groups of medicines. Production fully complies with GMP requirements.
- OJSC Akrikhin (Venolife) is a chemical and pharmaceutical plant in Russia, one of the leaders in the production of high-quality, affordable drugs. It is one of the five largest local pharmaceutical manufacturers in terms of production and sales volume.
- JSC Sopharma (Indomethacin) is a Bulgarian pharmaceutical company that was founded in 1993. Engaged in the development of medicinal, hygiene, and cosmetic products. Since 2007, she joined JSC “Bulgarian Rose-Sevtopolis” in order to expand its activities.
Why do ointments and gels not work for varicose veins?
In order to understand how effective local remedies are in the treatment of varicose veins, it is necessary to understand what “varicose veins” are. Varicose veins of the lower extremities are classified as surgical pathologies. Treatment of this group of diseases is always
carried out surgically. All conservative measures are used only as auxiliary and nothing more. Today there is no magic ointment that will cure varicose veins. This does not mean that local remedies are completely useless, but their effect should not be overestimated.
There are even such ointments for varicose veins!
Does rubbing the ointment with uniform, massaging movements contribute to a feeling of relief and comfort in the lower extremities? Absolutely yes. Does this treat varicose veins as such? Definitely not.
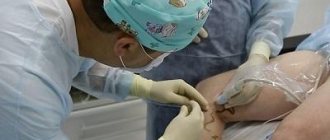
Surgery is not scary
For the treatment of varicose veins the following are used:
- phlebectomy - surgical removal of varicose veins, when they are pulled out through a small incision in the skin,
- laser and radiofrequency surgery are also surgical treatment methods that, unlike traditional surgery, do not require incisions, are performed under local anesthesia and have no physical limitations.
Surgical methods for treating varicose veins and spider veins are the most effective today. Laser and radiofrequency treatments are more often used. They are less traumatic and do not require a rehabilitation process. After the operation, the patient is recommended to take a half-hour walk.
Why you shouldn’t be afraid of treating varicose veins with surgical methods, read more in the article “Varicose veins: should you be afraid of surgery to remove veins?”
Why do phlebologists prescribe venotonic ointments and gels?
Why do many phlebologists at European-level urban phlebological centers continue to prescribe various ointments for varicose veins? In the complex treatment of venous pathology, good local remedies play a positive role, the condition of the surface layers of the skin improves, and there are certain effects on the smallest vessels (arterioles, venules, capillaries).
The use of ointments in the context of modern treatment is a good practice, but you should not expect miracles and replace the main component of the treatment of varicose veins, the removal of these same veins, with an ointment or gel.
Using ointment for spider veins on the legs
The use of ointments or tablets will not work on spider veins. To remove stars on the legs, sclerotherapy is used - a method in which a drug is injected into the vessel to glue the veins together, causing them to stop expanding. For varicose veins, this method also works and is used when it is impossible to use other types of surgical treatment.
Sclerotherapy is more like a cosmetic procedure. Traces after surgery completely disappear over time. The procedure is painless. Local anesthetic may be used individually at the request of the patient. After the operation, the patient goes home.
Questions from patients about the treatment of varicose veins with ointments and gels
Marina from Moscow asks: what ointment can cure varicose veins?
Dear Marina! The modern pharmacology industry offers a good selection of ointment and gel forms of drugs. Many of them have a good local cooling, soothing, anesthetic effect. But even the best ointment cannot cure varicose veins. The latter is a surgical disease and requires appropriate treatment.
Angelina from Moscow is interested in: what is the effective treatment for varicose veins with folk remedies, what ointments do you recommend?
Dear Angelina! Folk remedies include a balanced diet, proper exercise and rest. This will help to prevent varicose veins to some extent. There is not a single truly effective folk remedy, as well as ointment, for the treatment of varicose veins that have already appeared.
Lyudmila from Moscow asks: my mother has had varicose veins of the lower extremities for many years, she is regularly treated with ointment and good tablets. At the same time, the dark spot on the left leg increases. What tablets or ointments do you recommend for the treatment of varicose veins?
Dear Lyudmila! If your mother is diagnosed with varicose veins and clinically significant reflux is detected in the superficial venous system, then treatment with tablets and ointments will not help. It is necessary to contact a good phlebologist and follow his recommendations. Otherwise, the progression of venous insufficiency will lead not only to darkening of the skin, but also to the formation of a trophic ulcer.
Valentina from Moscow asks: I was diagnosed with varicose veins of the lower extremities, prescribed pills and a good ointment, judging by the reviews. I have been undergoing treatment for 2 months now, the skin on my legs has begun to peel off, is it possible to interrupt the treatment?
Dear Valentina! If you have been diagnosed with varicose veins of the lower extremities, then even a very good ointment and the best tablets, unfortunately, will not help. A completely different approach is needed here. The best option for you is to contact a good city phlebological center in Moscow, where, after a face-to-face consultation and professional ultrasound scanning, a specialist will answer your questions in more detail.
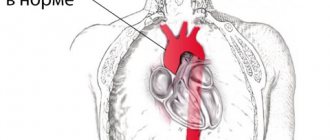
How are the veins in the legs arranged?
The legs have two groups of venous vessels: superficial and deep or deep. The first are located in the subcutaneous tissue, that is, on the surface of the leg. The latter are located deeper, in the thickness of the muscles, next to the arteries and tendons. The deep and superficial vessels are connected by perforating or perforating veins. Their wall consists of collagen and elastin fibers, with weak and few smooth muscles. The venous wall has a three-layer structure:
- At the top is the adventitia, which is composed of loose connective fibers, smooth muscle cells elongated along the walls, surrounded by small capillaries and nerves responsible for the trophism of the vessel.
- In the middle is the media, consisting of circular smooth muscle fibers.
- The intima is located on the inside. The basis of the intima is the endothelium; between its cells there are longitudinal fibers of smooth muscles. The inner shell is folded, the thickenings are opposite each other and resemble swallows' nests or patch pockets. They are called valves and are responsible for the correct direction of blood flow.
Venous valves direct blood from the peripheral parts to the heart, as well as from the superficial to the deep veins. They prevent reverse outflow and increase venous pressure. In addition to the valves, smooth muscles, tendons and muscles of the leg take part in maintaining normal tone. When any of the layers (usually the median and internal layers) are damaged, the veins lose their tone and expand, and varicose veins occur.
- There are several superficial veins:
- The great saphenous vein is located on the inside of the leg; its walls are equipped with several valves; blood from the anterior femoral surface is collected into this vein through a series of smaller vessels.
- The small saphenous vein is located on the outside of the leg, equipped with valves, and collects blood from the veins on the front and back of the leg.
Communication between the large and small veins occurs through connecting vessels.
- The deep veins are the posterior and anterior tibial veins, the popliteal vein, and the femoral vein. Varicose veins develop in them at advanced stages, when the disease is not treated for a long time.
How can varicose veins be complicated?
- Thrombosis due to blood stagnation.
- Vascular thromboembolism as a result of blood clot detachment.
- Thrombophlebitis or inflammation of the venous wall.
- PE (pulmonary embolism). In this case, blood flow in the pulmonary circulation is sharply disrupted, which leads to death. Small blood clots can lodge in the small pulmonary arteries and cause a heart attack or pulmonary edema.
- Trophic ulcers, eczema on the skin of the legs due to tissue malnutrition. With poor blood circulation, little oxygen and nutrients enter the tissues, which impairs regeneration or causes massive cell necrosis.
- Edema syndrome. As a result of impaired blood outflow and stagnation, fluid leaks through the walls of blood vessels into the intercellular space. The swelling is soft in consistency, elastic, and most often appears near the affected vein, regardless of the time of day.
- Dermatitis. The inflammatory process in the skin develops due to impaired blood flow and tissue nutrition.
- Hyperpigmentation, cyanosis of the affected areas of the skin.
- Consolidation of subcutaneous fat due to swelling and hemorrhage.
When are venotonics prescribed?
Venotonics should be taken from the first signs of vascular problems. Under favorable conditions, that is, when varicose veins are at the zero stage, but unpleasant symptoms such as swelling and heaviness already appear, venoprotectors can prevent the severe consequences of varicose veins and minimize consequences such as thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, and trophic changes.
The earliest stage is the case when it is important to take a comprehensive approach to treatment and “hear” your body.
At later stages, it is recommended to coordinate medications and especially the dosage with your doctor.
Chronic venous insufficiency - symptoms and treatment
There are many ways to treat CVI. In specialized clinics, the main focus is on minimally invasive treatment methods, that is, surgical interventions with minimal damage to the skin.
Endovasal laser coagulation (EVLC)
In developed countries, up to 40% of patients suffering from this disease receive assistance using laser technology. With early diagnosis, treatment takes little time and leaves no traces. Many clinics use a phlebological water laser with a wavelength of up to 1500 nm, supporting radial light guides. This technology allows you to close veins of any diameter through a small puncture of the skin.
Sclerotherapy
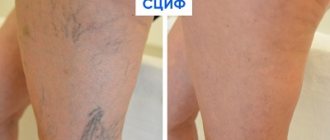
The sclerotherapy method is based on the introduction of a sclerosant into the lumen of the affected vessel. Thanks to this substance, the vein becomes overgrown and subsequently disappears completely. For deeper location of varicose veins, the echo sclerotherapy technique is used. For more accurate intravenous administration of the drug, the procedure is performed under ultrasound control. With this technique, replacement occurs with connective tissue, which disappears within a few months. Sclerotherapy is also used to eliminate the external cosmetic manifestations of varicose veins.
The technique of diode fluorescent sclerotherapy consists of illuminating telangiectasia (up to 0.4 mm) or reticular veins (up to 2 mm) with a fluorescent lamp, into the lumen of which a special solution is injected.
A promising direction in aesthetic phlebology is the combined use of diode laser and sclerotherapy - laser cryotherapy (ClaCS). This method allows you to eliminate reticular veins and telangiectasias without any particular discomfort.
Conservative therapy for CVI consists of:
- taking phlebotonic drugs, which improve the rheological properties of the blood and maintain the tone of the veins;
- eliminating factors for the occurrence of CVI (reducing the body weight of patients, increasing physical activity, etc.);
- wearing compression stockings.[4][6]
The patient should not worry about choosing a treatment method, since the phlebologist will select an individual treatment option depending on the patient’s age and type of activity, the form of his disease and the presence of pathologies. Usually, when visiting large phlebology centers, specialists simultaneously use many methods to treat one patient. For example, for the most effective and efficient treatment of CVI, laser surgery is performed in combination with injection methods for treating veins.[4]
Classification and stages
Like any disease, VV has several stages, differing from each other in the degree of spread of the pathology and symptoms. Among them, the following stages are distinguished:
- Initial (or compensation).
- Second (or subcompensation).
- Third (or decompensation).
A detailed description of each stage can be found here.
It is worth noting that complications can occur at any of the above stages, but their greatest likelihood is inherent in the last two. VV can serve as an impetus for the development of diseases such as:
- Thrombophlebitis.
- Erysipelas.
- Deep vein thrombosis.
- Trophic eczema.
A visit to a specialist, made at the first signs of the disease, will help reduce the risks of worsening the situation and begin removing varicose veins. You should not ignore even minor symptoms, because this can lead to undesirable and extremely negative consequences.
For what reasons does varicose veins appear, and who is at risk of getting sick?
It is difficult to say why people get varicose veins at the moment. Only a number of risk factors have been identified, due to which the valves weaken and the elasticity and tone of the walls of the superficial and perforating veins decrease.
Here are the factors that lead to the development of the disease:
- Heredity. The structure of the walls of blood vessels is determined genetically; with some changes in the genes, they weaken and the valves do not close well. As a result, with the slightest increase in pressure in the veins, a reverse outflow of blood occurs, the vessels overflow and expand.
- Hormonal changes in the body in women. This situation is typical for pregnant women or for the second half of the cycle, when the amount of progesterone increases and the level of estrogen decreases. As a result, blood rheology changes (coagulability increases), vascular tone decreases, elastin and collagen fibers are destroyed, and the risk of blood clots increases.
- Obesity. People who are overweight move little, which slows down blood flow throughout the body. Excess subcutaneous fat on the abdomen leads to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity and compression of the main veins. This leads to stagnation of blood in the vessels of the legs, and further to varicose veins.
- Diabetes. Sugar, the level of which increases in this disease, damages the vascular endothelium, which increases the risk of blood clots.
- Alcoholism. When drinking large doses of alcohol, dehydration occurs, the blood thickens, clots form, clogging small blood vessels and causing congestion.
- Static occupational loads, such as lifting heavy loads, standing or sitting work. In such a situation, muscle tone drops, blood moves worse from the lower extremities to the heart, stagnation occurs, and the veins in the legs dilate because of this.
- Congenital pathologies of blood clotting. Hypercoagulation, in which too many factors are produced that are responsible for the formation of clots in the blood, provokes thrombosis and impedes the movement of blood through the vessels.
- Wrong diet. A diet deficient in a number of vitamins (C, E, PP) and plant fiber leads to disturbances in the structure of the endothelium and other structural elements of the vascular walls.
- Tight underwear. When wearing tight underwear, some of the veins are pinched, which causes obstructed blood flow from the lower half of the body.
- Frequent constipation. People suffering from this problem have to constantly push, this increases the pressure inside the abdomen, as a result, the outflow of blood becomes difficult.
- High heel. Overstraining the calf muscles and insufficient contraction causes blood to stagnate in the veins.
- Hot climate. In summer, during the heat, the body becomes dehydrated. If you do not compensate for the problem by drinking a sufficient volume of fluid, the risk of blood clots in the vessels will increase.
- Pathologies of the heart and kidneys. These may be congenital or acquired heart defects, renal failure.
- Exceeding doses of medications that affect coagulation. In this case, the blood vessels may become clogged with blood clots.
- Operation. The risk of thrombosis in this case increases due to blood loss and compression of veins during the intervention.