"We live because we breathe..."
...and iron plays a huge role in this, and at the cellular level. The adult body contains an average of 5 grams of iron. Most of it is found in hemoglobin, which transports oxygen to all organs and tissues, up to 10% is in myoglobin, the “oxygen cushion” for skeletal muscles and myocardium. Our body keeps approximately a quarter of the total amount of iron in reserve - in the liver, muscles, spleen, and bone marrow. And 1% of the mineral is contained in special enzymes that ensure the processes of cellular “respiration”. Iron's position is more than privileged. He even has his own personal “taxi” - the protein transferrin, which “carries” the metal directly to the places of use.
Prevention
Knowing that hemochromatia can occur due to prolonged blood transfusion, when carrying out this procedure, you should adhere to a diet that will reduce the entry of iron into the body. Reducing the amount of alcohol you drink also reduces the risk of excess iron in your body. If there is a risk of hemochromatia associated with heredity or certain circumstances, you should undergo preventive diagnostics by an endocrinologist approximately once every three months.
Causes of iron deficiency and increased need for it
- Heavy or prolonged periods. They lead to increased blood loss and depletion of iron reserves.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding. During pregnancy and childbirth, the need for iron increases on average by 2 times, and during lactation even more.
- Pathological chronic blood loss.
- Passion for vegetarianism, veganism or raw food eating. Non-heme iron from plant foods is less absorbed than heme iron from animals and requires the presence of vitamin C.
- Frequently eating fast food, which is poor in useful components, including minerals.
- Consumption of foods that bind iron and reduce its absorption in the intestines. For example, this is how salts of phytic acid act in unleavened dough made from whole grain flour and in cereals; oxalates of fresh vegetables, especially rhubarb, spinach, sorrel; phosphoproteins of eggs, polyphenolic compounds of coffee and tea, milk lactoferrin, EDTA preservative in carbonated drinks, seasonings, sauces and mayonnaise.
- Taking certain medications (for example, some antibiotics, antacids, proton pump blockers, H2 blockers).
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (celiac disease, peptic ulcer, inflammatory bowel disease, tumors, diverticulosis, parasitic infestations, etc.).
- Pathology of the urinary system (hemorrhagic cystitis, urolithiasis, glomerulonephritis).
- Overweight and obesity. In this condition, there is an increased production of pro-inflammatory substances that negatively affect the absorption and bioavailability of iron.
- Regular exercise. They significantly increase the need not only for proteins, but also for vitamins and minerals, including iron.
Iron chelate, 60 tablets, Evalar
375 ₽
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE
Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out on an empty stomach
Usually the study is carried out as planned. The patient comes for analysis in the morning on an empty stomach, after 8-14 hours of complete overnight fasting, and if this condition cannot be met, no earlier than 4 hours after the last meal. You can still drink clean water. 2-3 days before the study, it is not recommended to expose yourself to heavy physical activity, including sports training. You should get more rest, go to bed earlier, avoid stress, alcohol consumption and heavy smoking. You should also not smoke in the morning before the test.
For more accurate results, 7-10 days before the analysis, you should avoid taking iron-containing preparations and foods containing large amounts of iron (seaweed, dried and fresh mushrooms, legumes, hazelnuts, buckwheat, oatmeal, almonds, rose hips, prunes, dried apricots, cocoa). When taking medications that do not contain iron, but those that can lead to an increase in iron in the blood (antibiotics, cytostatics, contraceptives, etc.), you should discuss their discontinuation with your doctor.
If discontinuation of these drugs is not possible now, you should complete the course of therapy with these medications, and then conduct an analysis, or find an alternative to them, for example, replace oral contraceptives with barrier contraceptive methods (condoms, spermicides).
If it is necessary to determine the level of iron in the blood when acute intoxication with this metal is suspected, the above rules may not be followed. Such intoxication is an indication for emergency research and treatment.
Iron deficiency - symptoms in women
We often attribute rapid fatigue, lack of vital energy, irritability, mood swings, frequent dizziness and an increased tendency to colds, restless legs syndrome to constant stress, heavy workload, weather conditions... There are many reasons for deterioration in well-being, isn’t it? ? But when external changes add to the collection of problems - the skin becomes dry, cracks appear in the corners of the mouth, nails change their shape (take on a concave appearance) and become fragile, and the hair becomes dull, often breaks and falls out more than usual, then the question arises: what is it about? What is the body trying to tell us? These manifestations can occur due to a lack of iron.
Interesting fact A woman can be “craving for salty foods” not only during pregnancy, but also, for example, due to iron deficiency. Its signs also include unusual changes in taste (the desire to “feast” on sand, chalk, clay, tooth powder, raw minced meat, etc.), and smell (the smells of gasoline, acetone, varnish, and paint seem attractive).
And iron deficiency in a child can manifest itself as a decrease in learning ability, increased fatigue, lethargy, tearfulness, and a tendency to frequent colds and intestinal infections. If you have the above symptoms, there is a reason to go for a check-up. However, it doesn’t hurt to get checked even in the absence of obvious symptoms of iron deficiency, in order to exclude its hidden deficiency.
First harbingers
Lack of iron in the body can lead to various diseases. It is a mistake to believe that a low level of iron in the blood is already anemia. The first signs of element deficiency appear long before anemia occurs. Among them:
- Dyspnea.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Noise in ears.
- Floaters before the eyes.
- Clear signs.
If you do not attach importance to these symptoms, then in the future, with insufficient iron intake in the body, serious consequences will develop.
- Iron-deficiency anemia. This disease can occur in different ways. The mild form is treated by adjusting the diet. For moderate anemia, you need to take special medications under the supervision of a doctor and constantly monitor your blood tests. For very low hemoglobin, hospital treatment is indicated.
- Decrease in the body's defenses. The immune system guards the entire body. Failure in its operation leads not only to frequent colds, but also to allergic reactions and inflammatory processes.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system. The consequence of severe iron deficiency with concomitant anemia may be the development of heart failure. If there were heart problems (for example, hypertension) before the development of anemia, the risk of developing heart failure increases, as well as the development of other pathologies (heart attack, stroke).
- Chronic headaches. This is not just a symptom, a malfunction of the vascular system, it is a serious problem that affects the quality of life. Headaches can often be accompanied by pressure surges and the development of neurological symptoms.
- Depression. The functioning of brain neurotransmitters is impaired due to iron deficiency. The balance of amino acids, adrenaline, dopamine, serotonin and other mediators responsible for important functions changes. The consequence is the gradual development of depression. This is not just a bad mood in rainy weather, it is a clinically confirmed diagnosis with characteristic symptoms.
- Developmental defects in a child. They occur when iron levels are very low in children. During intrauterine development, the child receives iron from the mother. If the baby was born on time, then the supply of the element should be normal. If the birth is premature, there may be problems, since the fetus receives a considerable amount of iron in the last week before birth. If the mother has an iron deficiency during pregnancy, the child will not receive enough iron, and autism and mental retardation may develop.
According to the above, it can be argued that the lack of iron is due to the fault of the person himself. Therefore it is important:
- Eat a balanced diet.
- When playing sports, you need to understand the importance of nutrition for the body to fully recover after exercise.
- During pregnancy, you need to pay special attention to your health, regularly get tested and visit a doctor to prevent all sorts of risks for mother and child.
- Caring for children includes providing them with nutritious, healthy food, especially during critical age periods; all this is in the hands of parents, their responsibility.
- A timely medical examination will allow you to identify many diseases in the early stages.
It all comes down to one thing - vigilance in relation to health. It is better to prevent a problem than to eliminate its serious consequences.
Laboratory check: not just hemoglobin!
The hemoglobin level, of course, is a very important indicator, but it must be remembered that its norm does not exclude the presence of the latent (hidden) iron deficiency we have already mentioned - a condition in which the metal reserves in the body are already depleted. That is why today, for a more accurate diagnosis of an iron deficiency state, in addition to hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells, a whole range of laboratory indicators is used: ferritin and serum iron levels, iron-binding capacity of serum, transferrin saturation with iron, morphological assessment of red blood cells, etc. A full check will help the specialist dot the i's. . If there is a severe lack of iron and anemia, it is necessary to conduct an urgent comprehensive examination to identify possible health problems that are causing it.
Readily Available Iron 18 mg, 60 Capsules, Nature's Bounty
925 ₽
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE
Why and how much?
Iron acts as a catalyst (accelerator) for many metabolic processes. Without it, full breathing is impossible. Not only the lungs participate in respiration; every cell “breathes” as long as it is endowed with oxygen.
But iron is not synthesized independently; its source is certain foods.
Approximately 15 mg of the element is needed per day for women (the dosage is doubled for pregnant and lactating women), 10 mg for men, and for children from 5 to 15 mg.
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, iron deficiency is observed in a large part of the world's population (more than 50%).
Which iron is best to take?
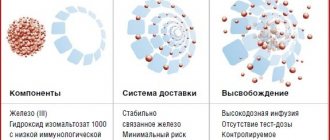
As an additional source of iron, a specialist may choose tablets or capsules of readily available iron. For example, iron in amino acid chelate form - easily digestible and as natural as possible for our body. Hemoglobin and other iron-containing proteins are clear confirmation of this! Another important advantage of chelated iron is the absence of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract. In case of hidden microelement deficiency, iron can also come to the rescue in combination with vitamins and minerals that increase its bioavailability: for example, vitamins C, B12, folic acid, zinc, copper, manganese.
Chlorella tablets, 100 g, polezzno
889 ₽
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE
Interesting fact Copper is a great friend of iron! It promotes its inclusion in hemoglobin during the formation of new red blood cells. When there is too little copper in the body, red blood cells do not mature fully and this can lead to anemia.
Spirulina, chlorella, quinoa, lentils, buckwheat, pumpkin seeds and other superfoods can provide good support for iron deficiency.
Iron deficiency anemia: causes, prevention and treatment
Chronic fatigue, pale skin and dizziness can be associated with overwork.
However, symptoms that seem harmless at first glance may turn out to be a signal of serious problems in the body. According to the World Health Organization, about 20% of women worldwide suffer from iron deficiency anemia (hereinafter referred to as IDA). It is important to know that latent (hidden) iron deficiency is widespread among the population, the frequency of which ranges from 20 to 30%. The daily iron requirement for men is 10 mg, for women – 15 mg (20–25 mg for pregnant and lactating women), and for children – 5-15 mg, depending on age.
Iron deficiency anemia is indicated by a low hemoglobin level, but a latent state is when the hemoglobin level is still normal, but the body’s iron reserves are already depleted.
There are three stages of iron deficiency in the body:
1. Prelatent iron deficiency is a hidden iron deficiency when the body accumulates iron with the help of ferritin, an iron-containing protein. If the ferritin level in the biochemical blood test is low, this indicates pre-latent iron deficiency.
2. Latent iron deficiency - at this stage, along with ferritin, tissue reserves of iron are depleted with optimal hemoglobin levels, clinical symptoms of iron deficiency are not observed, a compensatory increase in iron absorption occurs in the intestine, and the activity of iron-containing enzymes gradually decreases.
3. Obvious iron deficiency is characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells and a decrease in the level of hemoglobin, which is part of red blood cells and is a substance that transports oxygen to the body tissues from the lungs, the development of dystrophic changes in organs and tissues, as well as an increased amount of protoporphyrin in red blood cells.
Redox processes and the supply of oxygen to cells depend on the concentration of iron in the blood. Despite the fact that people of different sexes and ages can encounter the problem of iron deficiency anemia, anemia is considered a “female” pathology, more precisely a disease of women aged 15–45 years. About 50 to 86% of women in various populations have risk factors for anemia. The reason for this is pathological menstruation (long or heavy), pregnancy and lactation. During pregnancy, iron consumption increases sharply for the needs of the fetus and placenta, blood loss during childbirth and lactation. The iron balance during this period is on the verge of deficiency, and various factors that reduce iron intake or increase iron consumption can lead to the development of IDA.
Causes of anemia
IDA often develops with gastrointestinal (hemorrhoids, peptic ulcer) and uterine (uterine fibroids) bleeding or is associated with chronic diseases: inflammation of the pancreas or duodenum, bronchitis, kidney disease. Impaired absorption of this microelement is another reason why it is not used by the body for its intended purpose. In this case, the problem can be provoked, for example, by chronic gastritis.
Plant-based or fermented milk diets also contribute to the development of anemia. The fact is that iron is better absorbed from foods of animal origin - meat, fish, seafood, and dairy foods are rich in calcium, which interferes with the absorption of iron.
Dry skin, cracks in the corners of the mouth (angular stomatitis), brittle hair and nails, shortness of breath, dizziness, decreased performance, as well as the desire to taste chalk and deeply inhale the smell of fresh paint or gasoline are symptoms indicating a lack of iron in the body. However, these symptoms are not enough to make a diagnosis. To confirm IDA, you need to take general and biochemical blood tests. Hemoglobin is responsible for the circulation of oxygen in the blood. In case of iron deficiency, its level is usually reduced - less than 115–120 g/l (in women). However, in the early stages of the disease, hemoglobin may be normal. Laboratory determination of the level of serum iron, as well as transferrin and ferritin - proteins responsible for transporting iron to organs and tissues and creating a reserve of the microelement in the body - allows you to avoid mistakes in making a diagnosis. These indicators are markers of anemia at the initial stage and their low level indicates a problem.
To find out the cause of the disease, you will need to undergo additional examination - first of all, check the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (using gastroscopy, x-ray of the stomach, colonoscopy) and the organs of the reproductive system.
Experts agree: a balanced diet, including foods high in iron, is the best prevention of iron deficiency. Among the record holders for the amount of valuable microelements are meat (beef, lamb), fish and seafood, buckwheat, sesame seeds, pumpkin seeds and apples. It should be remembered that iron cannot be absorbed normally if there is a deficiency of vitamin C and folic acid. Iron absorption is also inhibited by polyphenols and phytates found in tea, coffee, whole grains and dairy products. It is also important to take into account the fact that the longer the product is subjected to heat treatment, the less iron remains in it. According to recent data, the bioavailability of iron from the normal adult diet is no more than 10%, and in developing countries this figure is below 5%.
Therefore, if iron deficiency anemia has already occurred, then it is impossible to cope with it with diet alone. To prevent IDA, doctors also recommend that women of fertile age not only eat right, but also take additional medications containing iron.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia, although simple, is quite lengthy. The principle of treatment is extremely simple: eliminating the cause of iron deficiency and taking iron supplements. The main mistake encountered in practice is prescribing iron supplements for a short period of time. Even a slight iron deficiency can be replenished within at least two months. For severe iron deficiency, treatment may last six months or more. In the vast majority of cases, iron supplements are prescribed in the form of oral preparations (capsules or tablets).
Medicine FERROFOL in capsules
– a combined antianemic agent based on iron in combination with folic acid.
Ferrofol contains: elemental iron – 50.00 mg (in the form of iron II sulfate), folic acid – 0.50 mg.
Important advantages of Ferrofol:
- Available in the form of extended-release capsules
- The iron content in the preparation is in the daily preventive doses recommended by WHO
- the active ingredients are contained in pellets (microgranules), which ensure their absorption mainly in the upper part of the small intestine
- the absence of local irritation on the gastric mucosa contributes to good gastrointestinal tolerability of the drug
Who do we recommend and how to take Ferrofol?
Adults over 18 years of age take Ferrofol before or during meals. Capsules must be swallowed whole.
For mild iron deficiency anemia and hidden (latent) iron deficiency with folic acid deficiency or for the prevention of iron deficiency and folic acid deficiency: 1 capsule per day.
For severe iron and folic acid deficiency (not in pregnant women): 1 capsule 2-3 times a day.
During pregnancy for the prevention and elimination of iron deficiency and folic acid deficiency: maximum dose of 2 capsules per day.
Ferrofol is a ferrous iron preparation, has good bioavailability, and can significantly increase hemoglobin levels within 2–4 weeks after starting administration.
It must be remembered that many foods and medications (for example, antacids) impair iron absorption. Taking this into account, Ferrofol should be taken one hour before meals or two hours after meals. If you are taking other medications, the interval between them should be at least two hours before or four hours after taking them. Ferrofol should be taken with water, or with apple or orange juice.
The main side effects when taking iron supplements are related to the gastrointestinal tract: constipation, diarrhea, nausea, metallic taste in the mouth. If such side effects are observed while taking Ferrofol, you do not need to stop taking the medications, but should consult your doctor; you will probably be advised to reduce the dose of the drug for a single dose, which will avoid negative effects. It is important to know that iron supplements can turn stool black; this is not a sign of gastrointestinal bleeding, but a normal reaction of intestinal contents to interaction with iron.
Iron salts are taken under the supervision of a doctor. The dose and duration of treatment are individual and depend on the degree of iron and folic acid deficiency.
BEFORE USING THE MEDICINE, READ THE INSTRUCTIONS. There are medical contraindications and side effects.
26 Oct 2020
Previous News Feed Next
Iron absorption
In order for iron to be well absorbed by the body, vitamin C and folic acid are needed. Vitamin C is found in large quantities in citrus fruits, kiwi, green vegetables, herbs and berries. To absorb iron, it is useful to drink orange or grapefruit juice with meals. Folic acid is found in green leafy vegetables that add flavor to any meal.
Calcium and iron are antagonistic enemies in our body. Foods rich in calcium, such as milk, interfere with the absorption of iron. So, if you eat buckwheat porridge with milk, then neither the iron from the buckwheat nor the calcium from the milk will be absorbed. It is better to separate such products: some in the morning, and some in the evening. Tea, coffee, Coca-Cola and chocolate also reduce the absorption of iron.
And remember that any excessive heat treatment can kill most of the beneficial substances contained in the product.
Who's at risk
- Women of childbearing age (lose iron with regular bleeding)
- Children (increased need in a growing body)
- Elderly people (undernourished and poorly nourished)
- Athletes (increased need due to regular increased loads)