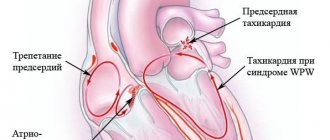
Palpitation, or sinus tachycardia, is the body’s very first and most common reaction to excitement, anxiety, and fear.
That is why almost all people with anxiety disorders, as well as those who have been diagnosed with the non-existent disease vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), have complaints about this physical ailment in their arsenal.
Content:
- Etiology and risk factors.
- Main symptoms and forms of alcoholic neurosis: 2.1. Neurasthenia. 2.2. Hysterical alcoholic neurosis. 2.3. Obsessive-phobic alcoholic neurosis.
- Treatment and preventive measures.
Alcohol addiction always requires a comprehensive approach. The belief that to get rid of the painful craving for alcohol, drug coding and, at most, a course of hepatoprotectors is enough - nothing more than a myth. The fact is that systematic drunkenness not only has an extremely negative impact on a person’s physical condition, pathological changes also affect the psycho-emotional sphere. Alcoholic neurosis usually occurs at the stage of giving up alcohol. And if previously, to resolve all difficulties, it was enough to simply drink, at a certain stage of treatment the patient realizes that now he needs to take responsibility for his actions, which often becomes the cause of increasing internal discomfort and anxiety. Such a condition necessarily requires at least a consultation with a psychotherapist, who, if necessary, will select a course of drug therapy. Otherwise, such a neurotic disorder may cause a relapse.
Etiology and risk factors
Unlike most other mental and psychoemotional disorders, the main cause of neurosis is the influence of various traumatic external factors. When it comes to alcoholic neurosis, the main cause of the disease is obvious - the systematic abuse of strong drinks.
Ethanol not only has a direct damaging effect on nerve cells. Systematic drinking very quickly leads to the depletion of physiological reserves of endorphins and other neurotransmitters (which, in fact, determines the development of addiction). As a result, without such “external supply” the central nervous system cannot fully function.
When a person gives up alcohol, the production of neurotransmitters and their interaction with target cells is gradually restored, but this requires a minimum of 6-12 months. Naturally, a deficiency of serotonin and other endorphins cannot but affect the patient’s emotional state.
In addition, the following contribute to increased anxiety levels:
- uncertainty regarding future employment;
- problems in relationships with relatives, children, spouse;
- financial difficulties;
- a radical change in your social circle;
- uncertainty about the further success of treatment;
- periodically appearing compulsive desire to drink;
- confidence in one's own inferiority;
- fear for one’s health, fears that many diseases that arise from systematic alcohol abuse are incurable, etc.
Why does it appear?
Due to a busy daily routine, problems at school or work, and stress, every third person has encountered neurosis. And such a disease as neurosis of the stomach and intestines has its own causes. Among them are:
- poor nutrition. This is the root cause of all diseases, in particular neurosis. Frequent consumption of fast food and processed foods instead of natural food, as well as untimely nutrition can lead to stomach problems;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, ulcers, tumors and gastritis;
- mental disorders and stress. They are the cause of many neuroses and lead not only to problems with the nervous system, but also to problems with the body as a whole;
- diseases of the digestive organs: pancreatitis, cholecystitis, colic. Because of them, a reflex reaction of the stomach occurs;
- external influence on the stomach. This includes poisoning from spoiled food, as well as exposure to chemicals that enter the body through the respiratory tract. Most often, gastric neurosis occurs in people over 35 years of age.
Main symptoms and forms of alcoholic neurosis
There are several variants of the course of the disease:
- neurasthenia;
- hysterical neurotic disorder;
- obsessional neurosis (obsessive-phobic).
But a number of symptoms can be identified that are common to all forms of the disease. This:
- impatience, inability to perform monotonous routine activities;
- decreased concentration, absent-mindedness, forgetfulness;
- irritability;
- apathy, depression;
- sleep disturbances and accompanying insomnia weakness, lethargy, daytime sleepiness, decreased performance, constant feeling of fatigue;
- emotional lability, but usually low mood, dissatisfaction with one’s appearance, actions and behavior in general prevail
Neurasthenia
This is the most common form of alcoholic neurosis, occurring with equal frequency in both men and women. The first signs of the disease are a variety of autonomic disorders, which are often mistaken for symptoms of post-intoxication syndrome.
Note:
- increased heart rate and shortness of breath after minor physical exertion or even at rest;
- bouts of sweating;
- periodic chills, which can be abruptly replaced by hot flashes;
- decreased appetite;
- increased sensitivity to light (sometimes discomfort occurs even in normal daylight, which forces the patient to constantly close curtains, blinds, wear sunglasses, etc.), loud sounds;
- headache, aggravated by physical and emotional stress, stress;
- weather sensitivity, intolerance to heat or cold;
- digestive disorders;
- attacks of dizziness, tinnitus.
Such symptoms become an additional cause of concern. The patient constantly listens to internal sensations, the range of complaints gradually expands. At the same time, the patient seeks to limit social contacts, becomes withdrawn, and is extremely reluctant to communicate even with family members.
Hysterical alcoholic neurosis
This form of the disease is also characterized by various somatovegetative disorders, but the patient tends to exaggerate and hyperbolize them. The person strives at all costs to attract the attention of others to his serious condition and emphasizes how difficult it is for him to treat alcohol addiction. He focuses the attention of those around him on the fact that he took such a step solely for the sake of his loved ones; thoughts are often expressed that after starting therapy, “it only got worse.”
With this variant of the course of alcoholic neurosis, diagnosis is complicated by the tendency to exaggerate existing symptoms. Patients usually complain of:
- decreased skin sensitivity;
- pain in different parts of the body (joints, abdomen, chest);
- temporary deafness and blindness (can occur under the influence of stress factors);
- tremor, etc.
When examining a patient, the doctor relies more on the results of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Obsessive-phobic alcoholic neurosis
It is characterized by the appearance of obsessive fears and thoughts from which a person cannot free himself. As a rule, the main manifestation of this type of neurotic disorder is the formation of various kinds of phobias, in most cases they relate to health conditions. A person consults a doctor much more often than necessary and insists on conducting additional (by and large, unnecessary from a specialist’s point of view) studies.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that many years of alcohol abuse does not leave its mark on the body. Pathological changes primarily affect the liver and cardiovascular system. Many such diseases occur in a chronic form with periodic exacerbations, which further aggravates the symptoms of alcoholic neurosis.
Institute of Clinical Psychiatry and Psychology
Treatment of neurosis
How can you help a person in a state of neurosis?
A person experiencing neurosis needs help from loved ones. The patient needs support both during exacerbation of the disease and during remission. First aid for an attack of neurosis
One of the most effective methods of helping a patient during neurosis is verbal support.
To alleviate suffering, a number of rules should be followed when talking with a sick person. Recommendations that should be followed when supporting a person with neurosis are:
- You should not try to start a conversation first. It is necessary to be close to the sick person and let him know that he is not alone. The desire to speak out may arise spontaneously in a patient with neurosis, and it is important not to miss this moment. Don’t ask cliched questions or say phrases like “Do you want to talk about this?” or “Trust me.” Sometimes help involves turning off the light, bringing a glass of water, or attending to other needs of the patient.
- If the patient allows, you should stroke his arms and back. This will help establish closer contact with the person.
- If a neurotic ( a person with a neurotic disorder
) begins to talk about his experiences, it is necessary to give him words of encouragement. You should try to make the patient talk more about his internal sensations, feelings and emotions that bother him. - Regardless of what the patient says, it is worth letting him know that his experiences are normal. Encouraging a neurotic person to not be ashamed of his tears and sincere emotions is the main task that his loved ones should set for themselves.
- You should not clarify details or ask leading questions. But if a person with neurosis begins to talk about what worries him, you should listen to him carefully and show your participation in the conversation. A good way of support is a personal story in which a relative of the patient can talk about similar moments he experienced. You should avoid standard phrases like “I understand how hard it is for you now” or “the same thing happened to me.” All suffering and experiences are individual, and even the closest people cannot be aware of what a neurotic person is experiencing. The best option would be the phrase: “It’s not easy for you now, but I’ll be there and help you get through it.”
In addition to emotional support, a patient with neurosis can benefit from physical measures aimed at relieving physical stress and diverting attention from the stress factor. Relieving muscle tension during neurosis
During stress, various muscle groups tense, which provokes discomfort and increases the level of anxiety.
Being close to the patient, a loved one can offer him help in carrying out exercises that will promote relaxation. Muscle relaxation techniques include:
- normalization of breathing;
- massage;
- exercise to calm down;
- water procedures.
Breathing regulation
In stressful situations, the patient involuntarily begins to hold exhalation, which increases the amount of oxygen in the blood.
The result of such actions is an increased feeling of anxiety and a deterioration in physical well-being. To alleviate the condition of a neurotic person, during an attack you should help him normalize the respiratory process. Ways to regulate breathing are:
- cross breathing;
- belly breathing;
- breathing into a paper bag.
Cross breathing
The stages of the cross breathing procedure are:
- close your right nostril with your fingers and take a deep breath with your left;
- close your left nostril with your fingers and exhale air with your right;
- repeat the exercise 3 times;
- Next, you should close your left nostril and draw in air with your right;
- close your right nostril and exhale with your left;
- repeat the exercise 3 times.
Belly breathing
To carry out this exercise, a person with a neurotic disorder should be asked to fold his arms so that one hand is on top and the other is on the bottom of the abdomen.
Next, at counts 1,2,3, the patient needs to draw in air and inflate his stomach. On the count of 4.5 you need to hold your breath, and then exhale on the count of 6,7,8,9,10. The exhalation should be long and more extended than the inhalation. The person next to the neurotic person should recite the count out loud, making sure that the patient inhales through the nose and exhales through the mouth. Breathing into a Paper Bag
Breathing through a paper bag will help reduce the amount of oxygen that enters the lungs and increase the amount of carbon dioxide.
This will allow the patient to normalize the respiratory process and return to normal. To start breathing, you need to put the bag to your face and press it tightly with your hands so that air does not enter inside. After this, you should ask the patient to start inhaling and exhaling into the bag until breathing returns to normal. An alternative to a paper bag can be cupped palms placed over the neurotic’s mouth and nose. Massage for neurosis
Massaging certain muscle groups helps to get rid of physical and emotional stress.
The muscles of the neck, shoulders, and head are the most vulnerable to stress. It is in these areas that patients feel tightness at the time of anxiety most strongly. Before starting the massage, you should ask the patient to wash his face with cold water and take a comfortable position in a chair or armchair. A person helping a neurotic person should begin the massage with the shoulders and neck. To do this, you can use gentle tapping and kneading movements. After the tension in your shoulders and neck has subsided, you need to start massaging your temples with light circular movements. All actions during the massage should be coordinated with the patient’s sensations. If he experiences discomfort, the session should be stopped. After the temporal zone, you need to proceed to the points that are located on the inner corners of the eyebrows. You need to massage with the tip of the index or middle finger of your right hand. In this case, it is necessary to support the patient’s head from behind with your left hand. When performing a massage, it should be taken into account that the duration of pressure on one point should not exceed 45 seconds. After the eyes, you should proceed to the scalp. You need to massage in a circular motion, moving from the hair growth area to the crown, then to the neck and back. Muscle relaxation
One of the effective methods to get rid of muscle tightness during stress is progressive muscle relaxation.
This method includes two stages - tension and subsequent relaxation of various muscle groups. The help of a loved one consists of sequentially indicating the parts of the body that need to be tensed and relaxed. The assistant can also turn on relaxing music, dim the lights, or fulfill the patient’s request, which will help him better concentrate on performing the exercises. The parts of the body that need to be consistently tensed and relaxed are:
- right foot ( if the patient is left-handed, he should start with the left foot
); - left foot;
- right shin;
- left shin;
- right thigh;
- left thigh;
- thighs, buttocks;
- rib cage;
- back;
- right arm, including hand;
- left arm with hand;
- neck;
- shoulders;
- facial muscles.
To begin the session, it is necessary to help the patient get rid of shoes and clothes that hinder his movements. The body position can be either horizontal ( lying on the sofa or on the floor
), and semi-vertical (
sitting in a chair or on a chair
).
The choice depends on the patient's personal preferences. Next, tense your right foot. The patient should be asked to squeeze the muscles as hard as he can. After 5 seconds, the foot should be relaxed and held in this state for several seconds. Such actions should be carried out with all parts of the body, taking into account the condition of a person with a neurotic disorder. Water procedures
Water has a relaxing effect on the nervous system.
You can increase the effectiveness of water procedures using essential oils of those plants that have a sedative or tonic effect. Types of water procedures for neurosis are:
- inhalation;
- wraps;
- baths.
Inhalations
To carry out this procedure, pour half a liter of hot water into a deep bowl made of glass, ceramic or steel and add 10 drops of essential oil.
Cover the patient's head with a terry towel and ask him to inhale the steam for 5 to 7 minutes. After completing the procedure, the face of a person with neurosis must be wiped dry. After inhalation, you should lie down and refrain from going outside for an hour. Wraps
This procedure has a gentle effect on the body and is widely practiced for neuroses.
Add 10 drops of essential oil to a container of warm water in the amount of 2 liters. Soak a sheet made of natural fibers in the liquid, wring it out and wrap it around the patient’s body. The duration of stay in the sheet is no more than 15 – 20 minutes. Baths
A bath with the addition of essential oils will help get rid of muscle pain.
Also, such procedures have a calming and relaxing effect on the nervous system. In order for the essential oil to be better distributed in the water, you should mix it with table or sea salt, honey, and cream. The duration of the first bath should not exceed 10 minutes. Subsequently, the session can be increased to 15 minutes. The water temperature should be selected according to the patient's condition. At 30 degrees the bath has a tonic and invigorating effect, at 37 degrees it has a calming effect. To prevent the bath from causing a worsening of the condition, these procedures should not be performed after meals or at a body temperature above 37 degrees. Contraindications for baths with essential oils are skin lesions, epilepsy, diabetes, and cancer. Essential oils for neurosis
Before carrying out any procedures using essential oils, you should conduct a test to identify the patient's allergy to this product.
To do this, apply a drop of oil to the crook of your elbow. Signs of intolerance to essential oils are shortness of breath, increased heart rate, redness of the skin, and headache. Essential oils that can be used for water procedures for neurosis are
:
- anise oil – eliminates tearfulness, fights stress and reduces nervous system excitement;
- orange oil – promotes healthy sleep, improves mood;
- basil oil – normalizes the overall tone of the body;
- clove oil – eliminates headaches, helps restore strength after physical and mental fatigue;
- jasmine oil – promotes sound and healthy sleep;
- lavender oil – fights depression, reduces nervous system excitement;
- Rose oil – increases performance and causes a feeling of vigor.
Distraction from stress
A patient with a neurotic disorder tends to focus his attention on internal sensations, which aggravates his condition.
A close environment can help the patient switch attention to other factors, which will make the fight against neurosis more effective. Factors that can distract the patient during an attack are:
- Concentration of attention on surrounding objects
- the patient should be asked to take a verbal inventory of everything in the room. It is necessary to ask the patient to describe in detail the furniture, accessories, textiles, and toys. You can remember the stories associated with the purchase or use of each item. - Performing daily duties
- if the patient’s physical condition allows, you should try to involve him in cleaning, washing dishes or preparing food. - Hobby
– doing what you love will allow you to escape from internal stress. - Music
– calm music will help you relax and take your mind off negative thoughts. Listening to music can be combined with doing household chores or other activities. - Counting
– counting the days remaining until a vacation or other event will allow you to take your mind off stress. The patient can also be asked to draw up an estimate for the planned repairs and other topics of interest to him that require concentration and a rational approach. - Games
- board games, logic games and other types of games will help a neurotic person reduce their anxiety level.
Help in preventing neurosis
The participation of family members and loved ones in the prevention of neurotic disorders will help prevent relapses (
repeated exacerbations
) of this disease.
Actions that relatives of a neurotic person can take for preventive purposes are:
- a joint visit to a psychotherapist;
- control of medication intake;
- assistance in changing lifestyle.
Doctor's help for neurosis
In most cases, neuroses arise against the background of a large number of factors, which only a doctor can understand.
The specialist will determine the causes of the disease and prescribe treatment. The difficulty is that many people are resistant and do not want to see a therapist. Close people should act without pressure, gently explaining to the patient that they are worried about his health. An impressive argument in favor of visiting a doctor will be the fact that the specialist works anonymously. If this is possible, relatives of the neurotic person can arrange the first meeting with the doctor on neutral territory or in a place where the patient will not feel constrained. Taking medications
If a doctor prescribes medications, relatives should ensure that the medications are available at home and monitor their use by the patient.
When prescribing serious psychotropic drugs, loved ones should study contraindications and side effects to prevent trouble. Lifestyle for neurotic disorders
Improper lifestyle is a factor that aggravates neurosis.
Therefore, the patient’s environment should help him change his habits and lifestyle. The rules of life with neurosis are:
- Balanced diet
- the patient’s menu should include a sufficient amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats so that the body is provided with energy. The condition of a neurotic person can be aggravated by alcoholic drinks, tobacco products, and caffeine. Also, you should not abuse fatty, salty, spicy and fried foods. - Physical activity
– people with neurosis benefit from physical activity. The effectiveness of classes increases if they are carried out in the fresh air. This could be roller skating, jogging or walking in the park, or cycling. The presence of a loved one nearby is an effective motivation to systematically play sports. - Timely and healthy rest
- sleep has a great influence on the restoration of the nervous system, preventing overstrain and emotional breakdowns. The benefits of a good night's sleep cannot be offset by other means. Therefore, family members of a neurotic person should assist in normalizing his sleep. Ways to help ensure an effective night's rest include a relaxing bath before bed, a regularly ventilated bedroom, and no caffeine or tobacco products at least 6 hours before bedtime. - Having a hobby
- doing what you love helps you take your mind off problems at work or other unpleasant factors.
The close environment may interest the patient by inviting him to do some activities together ( embroidery, fishing, cooking
) or visiting a gym, dance studio, or gun range. - Limiting the influence of external negative factors
- in a family where a person with neurosis lives, watching horror films and listening to heavy music should be minimized.
General recommendations for relatives of patients who suffer from neurotic disorders
Patients with neurosis often feel lonely and abandoned. Such people rarely seek help because they experience self-doubt and confusion. Neurotics often get offended over trifles and make scandals for no reason. Being around such people can be very difficult. Relatives must understand that their relative is going through a difficult period and needs support and care. At critical moments, those around the neurotic should stock up on endurance and patience. There is no need to provoke conflicts and focus attention on the mistakes made by the neurotic.
Psychotherapy for neurosis
Psychotherapy is the main method of treating neuroses, in which the patient is influenced not by medications, but by information. With this method of treatment, the main effect is on the patient’s psyche. There are many methods of psychotherapy, which differ in the number of participants in it ( group and individual
), by task (
search and corrective
), and so on.
For various forms of neurosis, the psychotherapist chooses the technique that, in his opinion, is most effective in this case. The most commonly used methods of psychotherapy for neuroses are:
- group therapy;
- art therapy;
- autogenic training;
- psychodrama;
- psychoanalysis.
Group therapy
With this type of therapy, classes take place in groups of 6–8 people, which are held 1–2 times a week.
During the sessions, the features of various situations and conflicts that patients tell are analyzed, and ways to overcome neurosis are considered. Each participant talks about how he copes with the disease. The main focus is on the fact that neurosis is a completely curable disease. One of the options for group therapy is intrafamily therapy, in which the conversation is carried out among members of the entire family. The effectiveness of family psychotherapy is very high, since it establishes the source of mental trauma. Knowing the traumatic factor, it becomes easier to improve the climate in the family. It is not only the therapist who influences, but also all members of the discussion. Art therapy
Treatment with various art methods (
visual, theatrical, musical
) to reduce stress.
This achievement in art therapy is called sublimation. This means that the energy of internal tension, which the patient relieves himself, is redirected to achieving certain goals in art. At the same time, the abilities of self-expression and self-knowledge develop. Autogenic training
This is a method of self-hypnosis in which relaxation is initially achieved, and then suggestions are made on various functions of the body.
Sessions are carried out lying or sitting, the arm muscles relax. Then follows a series of exercises aimed at reducing tension. For example, the patient lies down on the couch and repeats the phrase “The body is heavy” a certain number of times, then “I am completely calm.” When the patient is completely relaxed, ri, “heaviness,” and “warmth” are asked. In order to master this technique, the patient sometimes needs several months. The advantage of this method is that it can be done at home using an audio recording. Using this method, you can learn to control not only your mental processes, but also physiological ones ( for example, breathing
).
This therapy is very effective for neurasthenia. Psychodrama
This method uses dramatic improvisation to explore the patient's inner world in more detail.
Psychodrama is used both in group therapy and in individual therapy ( monodrama
).
The session initially begins with a warm-up, to achieve which various games and exercises are performed. Then there is a choice of a participant who will work on his problem in a psychodramatic action. This participant can choose a partner from the group to play out his situation. The drama lasts 30 minutes – 2 hours. In psychodrama, both real actions and actions from the past can be played out. Psychoanalysis
There are more than 20 concepts of modern psychoanalysis.
Classical psychoanalysis is based on the verbalization of thoughts through various associations, narration of dreams and fantasies. At this time, the psychotherapist is trying to analyze the unconscious conflicts that are the cause of neurosis. Thus, an analysis of complexes, desires and experiences repressed into the unconscious takes place. The stages of psychoanalysis are:
- Stage 1 – accumulation of material by interpreting dreams and making associations;
- Stage 2 – interpretation, by interpreting conflict situations;
- Stage 3 – resistance analysis;
- Stage 4 – development and restructuring of the psyche.
To analyze the received data ( for example, dreams
) Freudian psychoanalytic symbolism is often used.
Freud's symbols are:
- ring road - hopelessness of the situation;
- wall is an obstacle;
- snake, canes, skyscrapers ( straight, hard objects
) – phallic symbols (
symbols of the penis
); - hats, caves are symbols of female genital organs;
- ladder - career path.
Opinions about the effectiveness of this method are mixed. Some experts say that psychoanalysis is more effective than other methods of psychotherapy. Others deny the “theory of the unconscious” and, as a consequence, the method of psychoanalysis itself.
PART #1
PART #2
PART #4
PART #5
Source: https://www.polismed.com/articles-nevroz-prichiny-simptomy-lechenie.html
Treatment and prevention measures
Therapy is always selected individually, taking into account the severity of the clinical manifestations of the disease. Consultations with a psychotherapist are required. At the same time, the treatment of alcoholic neurosis requires an integrated approach. On the one hand, the doctor needs to support the patient in his desire to completely get rid of the craving for alcohol, on the other hand, it is important to de-actualize the trigger factors for the development of a neurotic disorder.
For this purpose, different methods of psychotherapeutic influence are used: cognitive-behavioral, rational, psychodynamic. Many patients benefit from various autogenic training techniques aimed at relaxation, reducing internal tension and anxiety.
If the causes of the disease are related to difficulties in relationships with loved ones, family therapy is indicated. It is important to learn to avoid mutual reproaches, accusations and claims.
Drug therapy for alcoholic neurosis includes:
antidepressants from the group of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors;- anxiolytics;
- for sleep disorders - benzodiazepine tranquilizers (usually prescribed in a short course for 2-3 weeks);
- complexes with B vitamins, magnesium.
The duration of treatment is determined individually, but the duration of taking antidepressants and vitamin preparations is usually at least 6–8 months.
It is recommended to continue the course of psychotherapy after completion of rehabilitation. A specialist will help you cope with all the difficulties of social adaptation, tell you how to properly get out of certain conflict situations, and how to resist the temptation to drink in company. There is no need to try to overcome psycho-emotional discomfort on your own - contact a specialized specialist!