How does air press on the Earth?
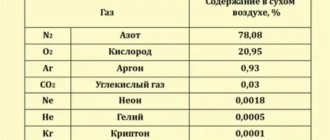
Modern physics considers the normal average pressure to be when a column of atmosphere above 1 cm2 of area weighs 1.033 kg. The indicators were obtained at zero sea level at 0⁰С, at a latitude of 45⁰. This mass raises the mercury in the barometer tube upward by 760 mm. Sometimes the indicator is recorded in other physical units - Pascals.
Barometers are used to measure quantities:
- Mercury.
- Metal (aneroids).
The main part of a mercury chamber is a sealed glass tube, with the open end lowered into a container with mercury. The earth's air presses on the silvery liquid, which rises through a tube, next to which a millimeter scale is placed.
How many millimeters the bar has risen will be the value showing how much the atmosphere presses on an area of 1 cm2.
Mercury barometer
Aneroids are made according to a different principle. In essence, it is a metal box from which the air has been pumped out. The atmosphere (it is denser than the contents of the box) puts pressure on the walls, and they bend. Through a system of levers they are connected to an arrow that points to the current value.
The atmospheric pressure fluctuates around normal values and depends on the weather. The minimum (641.3 mmHg) was recorded inside Typhoon Nancy, which originated in the Pacific Ocean and hit Japan in 1961.
The mercury in the barometer rose to a record high (815.85 mm Hg) one winter in one of the cities of the Krasnoyarsk Territory in Russia. Before this, the Khubsubul aimag in Mongolia was considered the record holder.
Definition of a cyclone
An area of low pressure in the atmosphere is a cyclone. It manifests itself in the form of a storm or even a tornado. In the center of the cyclone the pressure is much lower than at the edges.
If it formed in the northern hemisphere, the movement of air masses will occur counterclockwise. On the southern side of the planet it is the other way around. The Coriolis force moves the cyclone to the right, and in the south - to the left.
The area of low atmospheric pressure where a tornado or storm forms is initially located above the water surface. Therefore, this natural phenomenon brings with it rainy, cloudy weather. Frequent gusts of wind are caused by the difference in pressure in the center and periphery of the cyclone. An area of low atmospheric air pressure is formed with summer rains and cold snaps, and in winter with thaws and snowfalls. The air moves from the edge of the cyclone to its center, where it rises and cools.
Why is it not the same?
Atmospheric pressure changes and is affected by:
- altitude of a point above sea level;
- season;
- Times of Day;
- climate zone;
- temperature changes.
The higher, the lower
The higher the point above sea level, the more rarefied the air becomes, the lower the atmospheric pressure becomes. In the lower layers of the earth's air shell, the pressure decreases every 11 meters by 1 mm Hg.
For example, at an altitude of 20 km it is only 47 mmHg. Therefore, when rising to such a distance from the surface of the Earth, a person’s blood and interstitial fluids boil. If you are not in the pressurized cabin of an airplane or balloon, death will occur almost instantly.
It is known that different settlements on the planet have different levels of atmospheric pressure. This is logical, since they can be at different heights. For example, Chelyabinsk is built on a hill - 226 m from the zero level of the world ocean. Normal atmospheric pressure for him is 739 mm Hg.
The location of Kurgan in relation to the surface of the world's oceans is 72 m, and typical barometer readings that can be considered normal are 753 mm Hg. Art.
Temperature changes
What time of year it is - this also affects the indicator. It is higher in winter because winter air is colder and denser. In summer it is lower because the air is warmer and thinner.
The same temperature causes changes in the level of mercury during the day. Daily fluctuations occur within 4 - 5 mm, and seasonal fluctuations do not exceed 30 mm Hg. Art. All the same physical phenomena explain the fact that atmospheric pressure is constantly high in the Arctic and Antarctica, and low at the equator.
Cyclone as seen from space
Uneven heating of the air is a factor responsible for the formation of areas with low pressure around which cyclones form. A falling barometer reading may indicate the possibility of rain.
It is considered to be raining if the mercury is below 760 mm. And if you think about what atmospheric pressure is legitimately considered low and, conversely, high, then this figure will be the boundary criterion.
Weather-dependent people are very sensitive to pressure changes. Value below 750 mmHg. for many of them it is associated with unpleasant sensations.
Doctors explain this by the fact that when the barometer readings are low, the pressure of gases inside the body, in liquids and cavities, becomes higher than outside. This irritates the receptors in the organs and the person may feel aching in the joints.
In addition, oxygen starvation is felt, and cases of dizziness, drowsiness, and stunned state are not uncommon.
Air circulation
The formation of areas of low atmospheric air pressure is associated with the process of its circulation.
It occurs due to the tilt of the earth's axis and the heterogeneity of heating of the planet at the equator and poles. An area of low atmospheric air pressure is formed due to high temperatures at the equator. When heated, it expands and rises. And given the fact that the opposite effect occurs at the poles and increased pressure occurs, air masses circulate.
Moreover, if low pressure forms in one area, then high pressure will certainly form in another.
Name of vortices
To avoid confusion in the definition of cyclones by meteorologists, the area of low atmospheric pressure began to be called each by its own name. They reflected all his parameters, coordinates and speed of movement. It was proposed to name them with numbers and letters, the names of birds and animals. It was very popular to call cyclones by female names. It was convenient and efficient. However, in the late 70s, male names began to be used for such purposes. Such a system made it possible to avoid errors and confusion when exchanging information about an approaching storm.
Having reviewed the information presented above, we can come to the conclusion that the area of low pressure is a cyclone. It brings with it damp, cloudy weather. Based on their strength, they range from minor disturbances to terrifying hurricanes. They can bring both minor weather deterioration and extremely large destruction. Having understood the mechanism of their occurrence, one can understand why every year there is an increase in strong storms and tornadoes, which sometimes appear in areas completely unexpected for them. This is due to global warming caused by human activity on the planet.
Atmosphere pressure
Remember from your natural history course what is called atmospheric pressure.
The concept of atmospheric pressure.
Air is invisible and light. However, like any substance, it also has mass and weight. Therefore, it exerts pressure on the earth’s surface and on all bodies located on it.
This pressure is determined by the weight of a column of air as high as the entire atmosphere - from the earth's surface to its very upper boundary.
It has been established that such a column of air presses on every 1 cm2 of the surface with a force of 1 kg 33 g (correspondingly, per 1 m2 - More than 10 tons!)
So, atmospheric pressure
- This is the force with which air presses on the earth's surface and on all objects on it.
The surface area of the human body is on average 1.5 m2. The air puts pressure on it weighing 15 tons. Such pressure is capable of crushing all living things.
Why don't we feel it? This is due to the fact that there is also pressure inside the human body - internal, and it is equal to atmospheric pressure. If this balance is disturbed, the person feels unwell.
Measuring atmospheric pressure.
Atmospheric pressure is measured using a special device - a barometer. Translated from Greek, this word means “Gravity Meter.”
Weather stations use a mercury barometer
. Its main part is a glass tube 1 m long, sealed at one end. It is filled with mercury, a heavy liquid metal.
The open end of the tube is immersed in a wide bowl, also filled with mercury. When turned over, the mercury flowed out of the tube only to a certain level and stopped.
Why did it stop and not all pour out? Because the air puts pressure on the mercury in the bowl and does not release all of it from the tube.
If the atmospheric pressure decreases, the mercury in the tube decreases and vice versa. Based on the height of the mercury column in the tube on which the scale is applied, the value of atmospheric pressure in millimeters is determined.
At parallel 450 at sea level, at an air temperature of 0 0C, under air pressure, a column of mercury rises in the tube to a height of 760 mm. This air pressure is considered normal atmospheric pressure
.
If the mercury column in the tube rises above 760 mm, then the pressure is increased
, Below -
reduced
. Consequently, the pressure of the air column of the entire atmosphere is balanced by the weight of a column of mercury with a height of 760 mm.
On hikes and expeditions they use a more convenient device - an aneroid barometer
“Aneroid” translated from Greek means “without ridinium”: it does not contain mercury. Its main part is a metal elastic box from which air is pumped. This makes it very sensitive to changes in pressure from the outside.
At elevated pressures it contracts, at lower pressures it expands. These vibrations are transmitted through a special mechanism to a arrow, which indicates on the scale the amount of atmospheric pressure in millimeters of mercury.
Dependence of pressure on terrain altitude and air temperature.
Atmospheric pressure depends on the altitude of the area. The higher the sea level, the lower the air pressure. It decreases because as it rises, the height of the column of air that presses on the earth’s surface decreases.
In addition, with altitude the pressure also drops because the density of the air itself decreases. At an altitude of 5 km, atmospheric pressure is reduced by half compared to normal pressure at sea level. In the troposphere, with rise for every 100 m, the pressure decreases by approximately 10 mm Hg. Art.
Knowing how pressure changes, you can calculate both the absolute and relative height of a place. There is also a special barometer - altimeter
, In which, along with the atmospheric pressure scale, there is also an altitude scale.
So, each area will have its own normal pressure: at sea level - 760 mm Hg, in the mountains, depending on the height - lower. For example, for Kyiv, which lies at altitudes of 140-200 m above sea level, the average pressure will be 746 mm Hg. Art.
Atmospheric pressure also depends on air temperature. When heated, the volume of air increases, it becomes less dense and light.
As a result, atmospheric pressure also decreases. When cooling, the opposite phenomena occur. Consequently, as the air temperature changes, the pressure continuously changes.
During the day it increases twice (morning and evening) and decreases twice (after noon and after midnight). In winter, when the air is cold and heavy, the pressure is higher than in summer, when it is warmer and lighter.
So, changes in pressure can predict weather changes. A decrease in pressure indicates precipitation, an increase indicates dry weather. Changes in atmospheric pressure affect people's well-being.
Distribution of atmospheric pressure on Earth.
Atmospheric pressure, like air temperature, is distributed on Earth in stripes: there are belts of low and high pressure. Their formation is associated with heating and air movement.
Above the equator, the air warms up well. Because of this, it expands, becomes less dense, and therefore lighter. Lighter air rises - upward movement of air occurs. Therefore, there, near the surface of the Earth, low pressure
. Above the poles, where temperatures are low throughout the year, the air cools and becomes denser and heavier.
Therefore, it drops - a downward movement of air occurs - and the pressure increases. high-pressure belts formed at the poles
. The air rising above the equator spreads towards the poles.
But, before reaching them, at altitude it cools, becomes heavier and descends at parallels 30-350 in both hemispheres. As a result, high pressure belts
.
In temperate latitudes, at parallels 60-650 of both hemispheres, low pressure belts
.
Thus, there is a close dependence of atmospheric pressure on the distribution of heat and air temperatures on Earth, when ascending and descending air movements cause uneven heating of the earth's surface.
Questions and tasks
1. Determine how much the air in the classroom weighs if its length is 8 m, width 6 m, height 3 m.
2. Why does atmospheric pressure decrease with altitude?
3. Why does the pressure change in the same place? How does a change in air temperature affect this?
4. Determine approximately the relative height of the mountain peak if the barometer shows 720 mm at the base of the mountain, and 420 mm at the top.
5. How is atmospheric pressure distributed on Earth?
6. Remember what the absolute height of your area is. Calculate what atmospheric pressure can be considered normal for your area.
Types of cyclones
An area of low atmospheric air pressure varies in strength. There are 4 types of cyclones:
- A disturbance characterized by air movement at a speed of no more than 17 m/s.
- Depression – speed is in the range of 17-20 m/s.
- I call a storm a cyclone whose center moves up to 38 m/s.
- If the movement of the “eye of the storm” exceeds 39 m/s, it is already a hurricane.
tropical vortex
The vortices of tropical latitudes are much stronger than the cyclones that form in temperate latitudes.
In the area of 5-20 degrees southern and northern latitude, similar natural phenomena occur above the ocean surface. Where an area of low atmospheric pressure is formed, air masses move. However, in tropical cyclones it is sometimes very high. Reaches 10-30 m/s. . The weather here is calm. The wider it is, the more destructive the storm. Usually the “eye of the storm” is 30 km, but sometimes it reaches 70 km. Global warming leads to an increase in the power of cyclones in tropical latitudes. Of course, similar weather phenomena of minor magnitude also occur. However, powerful storms and hurricanes sometimes reach European countries and America, where they leave colossal destruction with numerous casualties.