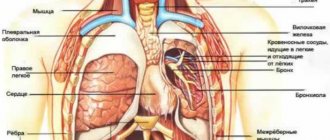
Numbness is an abnormal sensation that can occur in any part of the body, but is most often felt in the arms and legs. The symptom of numbness is often accompanied by tingling, and can be quite harmless, for example, in the hands when cooling, to a sign of a serious, life-threatening condition. Numbness is a fairly common symptom. Numbness of the limbs is often accompanied by an emotional context with a feeling of detachment and decreased emotional coloring, which is usually a sign of depression. In a physical context, numbness is usually the result of damage, poor circulation, or pathological changes to certain nerves.
In addition, there may be periodic attacks of numbness and tingling due to the presence of certain health problems, such as neuroses or a migraine attack. Also, episodes of numbness can occur during attacks of fear caused by the anticipation of life-threatening events, and in such cases the numbness is caused by shallow breathing and most often affects the fingers and the mouth area.
Numbness of the hands is manifested by a feeling of loss of sensation in the hands; patients often call this condition “asleep” hands. Numbness may be accompanied by a tingling sensation from the needle. Often such numbness occurs after sleeping with your hands under your head. Numbness in the hands is usually caused by carpal tunnel syndrome, which causes compression of the median nerve. Most often, carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by compression of the nerve in the carpal tunnel. In addition, numbness in the hands can be caused by injuries, hypothermia, or systemic diseases such as diabetes. If numbness of the hands is accompanied by shortness of breath, nausea, and palpitations, then this may be a sign of acute, life-threatening conditions and requires emergency medical attention.
Numbness in the legs is a loss of feeling or sensation in the legs, resulting from disruption of communication between the peripheral nerves and the central nervous system. Typically, numbness in the legs is associated with poor circulation in the lower extremities. This numbness most often occurs when sitting cross-legged for a long period of time. In such cases, getting up and walking can relieve the numbness after a while. But numbness in the legs can also be a sign of serious damage to nerve fibers due to mechanical factors (disc herniation, radiculopathy) or nerve damage due to somatic diseases.
Most common reasons
Numbness that lasts a short period of time is not dangerous. Particular attention should be paid to long-term symptoms, including headache, dizziness and sudden loss of consciousness.
Are your fingers going numb—the little finger and the ring finger? The reasons may be the following:
- hernia;
- Raynaud's disease;
- osteochondrosis of the lower cervical region;
- diabetes;
- bearing a child;
- injuries to the head, upper arm or cervical spine;
- climacteric condition;
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- multiple sclerosis;
- atherosclerosis.
It is important to remember that the fingers contain many small nerve endings that very quickly react to any external influence. Systematic numbness of the fingers is a good reason to contact a treating specialist, since wasting time in the presence of dangerous diseases can lead to serious consequences.
Treatment for numb fingers
Numbness in the fingers that occurs for pathological reasons will continue to bother you until the underlying disease is treated. Therapy for paresthesia is selected by the doctor who is involved in eliminating the identified causes of the pathology. Complex treatment includes medications, physiotherapy, finger exercises, massage, and warming ointments. You can also use folk remedies; their use shows excellent results if numbness in the fingers is caused by physiological reasons.
Treatment of numbness in the fingers takes from several days to several months. The duration of the course primarily depends on the root cause of the pathology.
Many people put up with periodically disturbing sensitivity problems in their fingertips. But this is an extremely wrong attitude towards one’s own health - numbness is often the initial sign of quite serious diseases. If these diseases are treated in a timely manner, then acute life-threatening complications can be avoided, therefore, when paresthesia appears that is not caused by physiological reasons, a thorough diagnosis is required.
In our clinic, experienced neurologists, therapists, and endocrinologists will conduct diagnostics, establish the diagnosis as accurately as possible and prescribe comprehensive treatment under dynamic supervision.
Among our methods, we use acupuncture, manual therapy, all types of massage, physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy under the supervision of an experienced specialist. Don't put off the problem until later. In this situation, it is necessary to make decisions quickly.
Pinched nerve in the neck
Doctors call numbness in the little finger as carpal tunnel syndrome or compression of the nerve in the elbow. The nerve fibers that provide sensation to the fingers originate in the spinal region. Eight pairs of cervical nerve roots arise from the spinal cord and then go to the intervertebral foramen. It is the eighth spinal nerve that is responsible for the sensitivity of surrounding objects from the beginning of the forearm to the little finger. Excessive stress on this nerve can lead to numbness.
Herniated discs and arthritis are the most common causes of pinched nerves in the cervical spine. The vertebrae are separated by special discs that can become displaced, changing their normal position, and form a hernia. A hernia formed below the seventh cervical vertebra significantly increases the load on the eighth spinal nerve, which results in a decrease in the overall sensitivity of the little finger.
Over time, the free space between adjacent vertebrae begins to decrease. Arthritis provokes an inflammatory process in the intervertebral joints, reducing the gaps through which the nerve roots pass. Arthritis between the seventh vertebra and the first thoracic vertebra increases the load on the eighth cervical root, leading to numbness in the fingers - the little and ring fingers.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
The spinal roots branch into a large number of nerves that give sensation to the muscles of the arms. The ulnar nerve originates in the eighth cervical and first thoracic nerve roots. It runs between the muscles along the inside of the elbow and provides sensation to the forearm, little finger and ring finger. When exposed to physical force (for example, hitting something hard), the structure of the nerve fibers is disrupted, which leads to a feeling of numbness. In this case, two fingers go numb at once: the little finger and the ring finger. In this case, the person feels as if he is receiving an electric shock.
Some muscle pressure can lead to increased pressure on the elbow nerve. Most often, this happens when the muscles and tunnel structures compress the nerve, causing the little finger and ring finger of the left hand to go numb. The condition of the ulnar nerve can worsen if the elbow is injured or if prolonged stress is placed on it (for example, if you lean on the surface of your arm for a long time).
Raynaud's syndrome
Damage to arteries and arterioles due to various traumatic factors leads to spasms of blood vessels located in the fingertips. In the early stages, the little finger and ring finger become numb, and loss of sensation in 1-3 toes is possible. Short-term spasms are quickly replaced by redness and warming of the skin due to dilated blood vessels.
As Raynaud's syndrome develops, the clinical picture changes and new symptoms are added - first, the hands and feet become bluish and swell; then trophic ulcers appear due to the death of the soft tissues of the phalanges of the fingers.
This pathology is due to several reasons:
- frequent hypothermia of the extremities;
- permanent injury to fingers;
- systemic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, vasculitis);
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- working with vibrating tools.
Raynaud's disease goes through 3 stages, each of which provokes the appearance of new symptoms.
Treatment of Raynaud's disease can be conservative and surgical. The main principle of conservative therapy is the exclusion of traumatic factors - hypothermia, vibration exposure, etc. The underlying disease against which this syndrome developed is required to be identified and treated.
Medicines that may be prescribed include the following:
- vasodilators, calcium antagonists – Nifedipine, Approstadil;
- selective calcium channel blockers - Verapamil, Nicardipine Diltiazem;
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors – Captopril;
- selective blockers of serotonin HS2 receptors – Ketansirin;
- antiplatelet agents – Dipyridamole, Pentoxifylline;
- dextrans with low molecular weight - Reopoliglucin.
- If, despite treatment, there is no improvement and the fingers still become numb, surgical intervention is performed - sympathectomy or ganglionectomy.
Pinched nerve
The ulnar nerve fibers run along the inner forearm and then pass through a tunnel, which is otherwise called Guyon's canal. It is through the little finger that the nerve enters the hand. When a nerve is pinched in the elbow area or when carpal tunnel syndrome occurs, the sensitivity of the little finger is greatly deteriorated. Increased stress on the nerve in Guyon's tunnel can be caused by diseases of the blood vessels, tumor processes, arthritis and cystitis. All this leads to the fact that the fingers on the hand go numb: the little finger and the ring finger.
Diagnostics
In addition to numbness, pain in the hand, tingling in the fingers, and awkwardness in the hand may also be observed. To diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome (carpal tunnel syndrome), provocative tests are used when the nerve is compressed or stretched:
- Flen test - holding the arm in a maximally bent position at the wrist for 1-2 minutes.
- Tinel test - compression of the nerve in the wrist area or tapping with a hammer in the projection of the nerve
The test is considered positive if numbness, pins and needles, pain, and tingling occur in a typical area.
The next diagnostic method, ENMG, is the “gold” standard. The level and extent of nerve damage can be determined.
Receiving microtrauma
Short nerve endings (up to three millimeters in diameter) entangle the fingers in a network. Physical impact on any of these nerves can result in numbness of the little finger in the area where the injury occurred.
Microtraumas most often occur due to injury or traumatic exposure. In these cases, surgery is most often necessary to restore damaged nerves and restore the previous sensitivity.
Additional reasons
Are your fingers going numb—the little finger and the ring finger? The reasons may be the following:
- Serious illness. Loss of sensitivity in the little finger may indicate the presence of a disease. For example, diabetes can damage nerve endings. This process is called diabetic neuropathy. This disorder usually occurs when blood sugar levels remain high for a long time or when blood circulation is poor.
- The result of a stroke. With numbness in the hands and partial paralysis, there is a high chance of having a stroke. This diagnosis is considered very serious and therefore requires urgent medical attention. The little finger may lose its former sensitivity due to a stroke. Blood clots or damaged blood vessels interfere with normal blood circulation. Sudden loss of sensation or a burning sensation in the fingers, especially in only the right or only the left hand, may indicate a stroke. If you have such symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible for a diagnosis.
- Carpal, ulnar neuropathy. The little finger and ring finger of the right hand go numb, most often due to neuropathy. Most people are right-handed, so it is their right hand that bears the greatest load, which leads to injury to the ulnar nerve and numbness in the fingers.
- Raynaud's disease, in which the hands become cold and blue, is not fully understood. Multiple hand injuries can lead to this disease. Numbness in most cases is localized at the ends of the fingers in cold weather due to a sudden spasm of the blood vessels.
- Multiple sclerosis, which occurs due to disruption of the integrity of the myelin sheath of neurons, also leads to numbness of the limbs. But in this case, the patient has a peculiar gait.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome has the following symptoms: numbness of the hands, tissue swelling, loss of sensation, pain. This syndrome occurs most often in people who, due to their specialization, must perform the same movements throughout the day. If treatment is not started promptly, carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to atrophy of the thumb.
- During menopause, as well as when carrying a child, the fingers begin to go numb due to tissue swelling, which often leads to compression of the nerve bundle in the wrist area. If symptoms occur frequently, it is important to carefully examine the cardiovascular system.
Causes of hand numbness
A fairly common complaint that occurs due to compression of the nerves in the canal formed by ligaments, tendons, muscles, and bones in the area of the wrist joint.
The dimensions of some canals, in principle, have a rather narrow structure, and when another cause of narrowing is superimposed, for example, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, trauma, etc., this contributes to the development of “tunnel syndromes.”
More often, the symptom occurs at night or during constant work with a forced position of the hand (typing at a computer and working with a mouse, knitting, driving). In this scenario, there is a high probability that there is a tunnel neuropathy. At the same time, we do not take into account situations when there was pressure from the outside, for example, the hand was “rested”.
Depending on which nerve is more involved in the pathological process, there may be different limits of sensitivity impairment, for example:
- If the median nerve is affected, this is the thumb, index, middle fingers and half of the ring finger
- Ulnar nerve - numbness of the little finger and half of the ring finger
- Radial nerve – numbness of the dorsum of the hand
Sometimes it may seem to you that the whole hand is numb, but with careful observation it is possible to determine which fingers are numb, or these are some features of innervation, when one of the nerves innervates a slightly larger area.
Carrying out diagnostics
When visiting your doctor, it is important to describe in detail all the symptoms and signs of discomfort in your hand. A detailed description of numbness will help to conduct a proper examination and make an accurate diagnosis.
If the right little finger and ring finger are numb, then it is best to pay increased attention to the functioning of the heart muscle. In the morning, the patient has a tingling sensation on one side. The main symptoms appear later: the little finger and ring finger go numb at night.
- A feeling of numbness in the middle finger indicates a lack of certain vitamins in the body. In this case, experts advise completely changing your diet, and, if possible, going to see an endocrinologist.
- If the index finger of the left hand is numb, it is important to pay attention to possible narrowing of blood vessels or the presence of diseases in the cervical spine.
- Is the little finger and ring finger of your left hand going numb? The cause may be osteochondrosis. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to see a doctor. If you have osteochondrosis, you need to start treatment immediately, as the condition can quickly worsen.
- The ring finger on the right hand may lose sensitivity due to excessive fatigue. In this case, it is best to just rest. This often happens to women who do any kind of needlework.
- Numbness in the middle finger of the right hand requires the help of an orthopedist. In most cases, this symptom indicates damage to the elbow joint.
- Numbness of the thumb on the right hand indicates the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- When there is numbness in the little fingers on both hands, it is immediately important to pay increased attention to the functioning of the internal organs and systems.
- The two thumbs lose sensation if any of the problems described are present. If, against the background of numbness, the patient has impaired fine motor skills, an unsteady gait, or weakness, then it would be best to undergo examination in the neurological department.
- If the little finger and ring finger on both hands become numb, this indicates a complication of cervical osteochondrosis. It is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner.
Manifestations of finger paresthesia
With paresthesia, numbness, slight tightness of the fingers, and sometimes tingling are felt. Impaired sensitivity prevents you from grasping small objects or performing precise work with your fingers. Based on these signs, it is difficult to make a preliminary diagnosis, however, numbness in some diseases affects only certain fingers:
- Numbness in the little finger of the left hand, as well as the appearance of similar changes in the ring and middle fingers, can be caused by pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. Paresthesia is more pronounced at night;
- Numbness of the fingers of one hand that spreads to the hand occurs during a stroke. In the acute phase of cerebrovascular accident, coordination of movements is also impaired, consciousness becomes confused, and there may be paralysis of one side of the face;
- Numbness of the thumb, index and middle fingers on one of the hands or on both at once is one of the symptoms of compression of the nerves in the spine with osteochondrosis of the neck;
- Paresthesia of the thumb and index finger is a characteristic sign of carpal tunnel syndrome;
- Simultaneous numbness of the fingers on the lower and upper extremities often worries patients with diabetes.
If you complain about numbness, you can initially contact your GP. After examination and clarification of other symptoms of deterioration in well-being, the doctor refers you for examination to specialized specialists - a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, surgeon.
Diagnostic procedures
The main goal of diagnostic measures is to establish the cause of numbness, as well as the possibility of pathological changes in the body. First, the patient must donate blood for laboratory testing, which will help identify the presence of toxins. This analysis is especially important for those who work in enterprises with increased harm to the body.
From hardware research the following is used:
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- Dopplerography of arterial vessels of the neck and spine;
- computed tomography;
- echoencephalography.
Each of these methods helps to obtain additional information about the patient’s condition, which makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, as well as create an effective treatment.
Using a special x-ray, you can take a series of pictures that will help determine exactly where the damage to the nerve roots and blood vessels is widespread. Doppler ultrasound of the arteries is important for assessing the general condition of the vessels. It uses ultrasound radiation, which does not cause any discomfort to the patient.
Using MRI and CT, the spinal column and brain are carefully examined. Echoencephalography, which uses ultrasound, helps to accurately determine the size of the pathological process that occurs in parts of the brain. Sensors installed next to the skull produce ultrasonic waves of a certain frequency and perceive echoes. Currently, such research is used only in hospitals that do not have computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
Electroencephalography helps to identify even minimal changes in brain function. Electrodes attached to the head are connected to a device that detects all changes in the electrical activity of the waves and gives readings on the monitor in the form of a broken line.
The results of diagnostic procedures and an accurate study of all the patient’s symptoms of illness help the doctor to correctly determine the cause of numbness in the fingers and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
Based on the medical history, study of symptoms and physical examination, the doctor prescribes an examination plan, which includes both instrumental and laboratory examination methods.
To treat numbness, first of all, it is necessary to find out the cause of this symptom. If numbness is associated with circulatory disorders, diabetes or multiple sclerosis, the underlying disease is treated, both with the help of conservative treatment methods and surgical methods (for example, for vascular diseases). For orthopedic problems, such as disc herniation, osteochondrosis, treatment can also be either conservative or surgical (for example, when it is necessary to decompress the nerve root).
Which doctor will help?
Due to the fact that there are a large number of reasons for the loss of sensitivity in the fingers, it is important to seek help from several specialists at once who could accurately determine the source of the lesion: a surgeon, a neurologist, a cardiologist. All of them must conduct a full study, as a result of which it will be possible to prescribe correct and effective treatment.
Most often, therapy comes down to doing therapeutic exercises, taking medications and using external ointments.
Therapeutic measures
In each individual case, individual treatment is required. For osteochondrosis and carpal tunnel syndrome, massage of the collar area and a complex of physical therapy help to cope with the problem. Special physical exercises are used to develop atrophied muscles after a hand injury.
Taking medications in each case will go well with manual therapy, taking a vitamin complex, and physiotherapy. Treatment with ultrasound, laser and magnetic therapy helps improve blood circulation and has a positive effect on all regeneration processes.
Non-traditional methods are also widely used in therapy: vacuum procedures, hirudotherapy, acupuncture.
To avoid numbness in your fingers, it is important to follow some preventative measures:
- avoid wearing heavy things for a long time;
- walk more;
- introduce into your diet as many products as possible containing vitamins B12;
- during monotonous work, it is important to take a break for physical activity;
- avoid severe stress;
- get rid of bad habits (stop drinking alcohol and smoking);
- dress warmly when it's cold outside.
All the recommendations described will help significantly reduce the chance of loss of sensitivity in the fingers, and will reduce the risk of vascular diseases and damage to nerve fibers.
Why do my fingers go numb? Looking for reasons
What is behind the numbness of the fingers? It turns out that this symptom can be accompanied by a number of diseases. Doctors from the Expert Clinic Smolensk told us about the causes of numbness in the fingers: neurologist Irina Sergeevna Ignatieva, cardiologist Irina Anatolyevna Vataeva, endocrinologist Elena Sergeevna Pankratova.
Irina Ignatieva, neurologist
– Irina Sergeevna, what diseases can be accompanied by numbness of the fingers or toes?
– A number of diseases can lead to numbness in the fingers. In particular, polyneuropathy, radiculopathy, Raynaud's disease, anemia, vascular diseases.
– Which doctor should I go to if numbness in my fingers is the main or only symptom?
– First, you need to consult a general practitioner. You can also make an appointment with a neurologist.
– What examinations are prescribed for a person with such a symptom?
– A patient with numbness in the fingers is prescribed a number of laboratory tests: a general blood test and a biochemical test are required; a blood test for iron and vitamin B12 levels, thyroid hormones, a coagulogram, and a general urinalysis may also be required. In addition to laboratory tests, instrumental diagnostic methods are used: electroneuromyography, MRI, ultrasound of the extremities, ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
– What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Why is it accompanied by numbness in the fingers?
– Carpal tunnel syndrome is a complex of disorders caused by compression and entrapment of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. The walls of the carpal tunnel are formed by natural anatomical structures (bones, muscles, tendons). Normally, the median nerve passes freely through the canal. When the structures that form the walls are damaged, compression or pinching occurs. In this case, the person may feel numbness, tingling or pain in the hand. People whose work requires stereotypical hand movements are especially susceptible to carpal tunnel syndrome: musicians (pianists, guitarists), office workers, dentists, seamstresses, assemblers of small parts, etc. For prevention, it is necessary to arrange the workplace ergonomically and monitor the correct position of the hand. When working the same type of work, it is important to take a break at least once an hour.
People who are especially susceptible to carpal tunnel syndrome are
whose work requires stereotypical hand movements:
musicians (pianists, guitarists),
office workers, dentists,
seamstresses, small parts assemblers, etc.
– Could numbness in the fingers be the first symptom of neurodegenerative diseases?
– Among such pathologies, the most common are Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are characterized by numbness of the fingers in the early stages. It may signal the onset of an illness.
You can read more about Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease in our articles:
Everything you wanted to know about Alzheimer's disease but were afraid to ask
Parkinson's disease: courage to be imperfect
Elena Pankratova, endocrinologist
– Elena Sergeevna, what are the causes of numbness in the toes in diabetes mellitus?
– Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by the development of hyperglycemia syndrome (increased blood glucose levels). It leads to diabetic polyneuropathy. This is a very common complication of diabetes. Due to chronic hyperglycemia, toxic damage occurs to Schwann cells that form nerve fibers. Diabetic polyneuropathy is manifested by impaired sensitivity and numbness in the lower extremities.
Want to learn more about diabetes? Read our article
Irina Vataeva, cardiologist
– Irina Anatolyevna, can cardiac pathologies be accompanied by numbness in the fingers?
- Yes, it is quite. For example, with coronary heart disease, people often have numbness in their left hand (not only the fingers, but the entire limb).
Read more about coronary heart disease here
Numbness of the fingers may indicate atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels.
– Can numbness in the toes also be a sign of problems with blood vessels?
– Yes, pathologies of the blood vessels of the lower extremities often manifest themselves as numbness of the fingers. In particular, this symptom is characteristic of obliterating atherosclerosis. These diseases are usually treated by a vascular surgeon.
– Why does numbness occur in the fingers due to Raynaud's disease?
– First of all, it is worth noting that there is the concept of “Raynaud’s disease” and “Raynaud’s syndrome”; they should be distinguished. Raynaud's disease is a primary condition. Its reasons have not been precisely established. Raynaud's syndrome (Raynaud's phenomenon) occurs against the background of other diseases. In any case, circulatory disturbances in the upper extremities appear. It also manifests itself as numbness in the fingers.
– How to treat numbness in the fingers until an accurate diagnosis has been made? Are there any recommendations for symptomatic therapy?
– I.S. Ignatieva: I would not recommend using any medications while the diagnosis is unknown. One symptom can be a manifestation of various diseases, including very serious ones. It is important to correctly diagnose the disease and begin appropriate treatment.
– I.A. Vataeva: You always first need to establish the cause. This is not the case when it is worth fighting the symptom.
You can make an appointment with specialists here
ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Daria Ushkova
The editors recommend:
How to treat hernias and protrusions of the spine?
Go there - I don’t know where, cure that - I don’t know what: vegetative-vascular dystonia - diagnosis or fiction?
Serious question: what happens to the heart during an angina attack?