Almost every patient who is admitted to the physiotherapy department for neurological complications of osteochondrosis, such as protrusion and hernia of the spine, is prescribed various options for electrotherapy. One of the most common and effective methods of using direct electric current is electrophoresis. Is it possible to do electrophoresis for herniated intervertebral discs? How does this treatment work? What are the possible contraindications, and with what drugs can this therapeutic effect be carried out?
Cervical hernia on MRI.
Mechanism of action of electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is one of the methods of percutaneous administration of drugs. Knowing the specific density and resistance of body tissues, the parameters of the electric current, and the physicochemical properties of the drug substance, it is possible to accurately determine the concentration of the drug at a given depth, including in paravertebral tissues. What kind of treatment method is this, and how does electrophoresis work?
Recall that the ordered movement of charged particles along a conductor is called electric current. The human body is a collection of conductors of the second kind, where there is no movement of free electrons, unlike metals. But in tissues there is movement of free ions in liquids charged both positively and negatively. Drug electrophoresis is based on this property.
If you place electrodes (cathode and anode) on the human body and induce a direct current, then a potential difference arises between the electrodes, and the movement of various ions in the underlying liquids between the electrodes occurs, both from “plus to minus” and vice versa. It is known that each cell contains up to 70% water, so even dense tissues can be considered permeable to direct current, with the exception of bone.
If a medicinal substance is placed on one of the electrodes, which dissociates into ions under the influence of current, then it begins to move into the tissue according to the potential difference. The movement of a drug that has broken up (dissociated) into ions in a solvent is described by simple rules:
- positively charged ions are repelled from the anode as ions of the same name (also a “positive” electrode);
- negatively charged drugs are repelled from the cathode (“negative” electrode).
Medicines move under the influence of Coulomb forces of electrostatic repulsion of like charges and attraction of opposite ones, which follow the direction of the current. Inside the skin, the medicine accumulates in the depths in the form of a depot, and from there it is slowly consumed in the tissues for up to 2 weeks. Electrophoresis not only allows the medicine to remain in the body for a long time, but also allows you to significantly increase their activity by placing them directly where they are needed, for example, to the deep back muscles. This means that even a small amount of the medicinal substance, about 5% of the amount applied to the electrodes, produces a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Description of the procedure
When an electric current is combined with medicinal substances, ions are formed - positively charged "+" particles. They penetrate deep into tissues up to 5 mm and at the same time transfer the health complex through the skin into the cells of the body.
An integral part of electrophoresis is the cathode and anode - differently charged electrodes that create an electric field. One of them is placed on a problem area on the patient’s body, the other is clamped in the hand or secured to an area of the body according to the diagram that is attached to the device.
Depending on the effect expected from electrophoresis, either an anode or a cathode is placed on the problem area:
- The “-” cathode conducts alkaline solutions that improve blood flow in the skin, soften it, and stimulate nerve endings. The cathode is often chosen for cosmetic purposes for oily and mature skin.
- The “+” anode conducts acidic solutions to strengthen the skin, relax the body, and improve microcirculation. It is chosen when it is necessary to get rid of redness, inflammation, swelling, and narrowing of pores.
The effect of procedures with an anode or cathode on the body is shown in more detail in the table:
The effect of differently charged electrodes on the body during a galvanic electrophoresis session
| Reaction | Anode "+" | Cathode "-" |
| Changing the acidity of skin pH | Increased acidity (decrease pH) | Alkalinization (increasing pH) |
| Vascular reaction | Arterial hyperemia | Arterial hyperemia |
| Receptor response | Decreased excitability and sensitivity | Increased excitability and sensitivity |
| Skin pore reaction | Closing Pores | Opening of pores |
| Sebaceous and sweat glands | Decreased secretion | Increased secretion |
Electrophoresis can be performed in a clinic or independently at home using special devices. There is nothing complicated in this procedure, just be careful: do not confuse the cathode (negative electrode) and the anode (positive). To do this, you need to study the instructions for use in detail.
Also, not all medicinal drugs are suitable for electrophoresis - only “charged” drugs, and this should be indicated by the corresponding labeling on the drug packaging.
How does the device for electrophoresis work?
The standard technique for performing the electrophoresis procedure for protrusions or hernias is as follows. Stationary Amplipulse-5 (about 39 thousand rubles), or portable Potok (11 thousand rubles) devices, or more modern devices are used.
Any device is an alternating current rectifier, previously electron tube, currently semiconductor, with regulation of the current strength on the electrodes. Almost all devices operate from a standard alternating current network with a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 220 V, are manufactured according to the second class of protection and, accordingly, do not require grounding devices. The device must be equipped with a milliammeter (either analog with an arrow, or digital in modern devices). There is a potentiometer, or rheostat, that allows you to slowly and smoothly regulate the current in the patient circuit between the electrodes. In older models, there is a separate shunt to the ammeter, which allows you to switch the limits of the measured current from 5 and 50 milliamps.
Apparatus.
In new models, the shunt is integrated into the microcircuit. The device is equipped with output terminals with mandatory polarity markings: “plus” - red and “minus” - white. The kit includes marked wires and a variety of electrodes that can be used as an anode, and in another circuit, as a cathode, since both electrodes are made of the same material. Electrodes are usually made of thin lead because they can bend and follow the curves of the body. Electrodes must be regularly cleaned of lead oxide as oxidized electrodes become less effective. Modern electrodes are made of special fabric impregnated with graphite. They are non-toxic, elastic, and conduct electricity well.
The essence of the procedure and methodology
The method of effectively administering drugs to the site of an inflammatory or any other kind of lesion is used in the practice of physiotherapists with enviable regularity. The therapeutic effect that can be achieved with its help is formed on a cumulative basis and lasts on average up to 20 days. Among the most popular types of EF are:
- Cutaneous . To place the electrodes, select a clean area of skin without inflammation and, ideally, without moles. Pads are installed under the electrodes, which are pre-wetted in a medicinal solution, and after application they are secured with clamps or special weights.
- Endonasal . The device for such a procedure is equipped with paired electrodes in turunda attachments and an additional bundle of paired indifferent electrodes. Turundas are inserted into the nostrils, and zero electrodes are attached to the forehead and temples.
- Endaural . The electrode, protected by turunda, is moistened with the medicine and inserted into the ear canal. Additionally, a hydrophilic pad with a conductive plate is applied to the turunda before insertion. The entire structure is fixed with a bandage or a bag of sand.
The areas of focus and the algorithm for performing the procedure depend on the localization of the pathological processes that need to be eliminated. To make the session as easy as possible and beneficial, you must:
- before carrying out it, have a good rest, do not be nervous or worry;
- eat food at least an hour and a half in advance;
- After you leave the office, take another half hour to have a good rest.
After the session, you should also avoid physical activity and do not heat the injection site.
The patient should receive all recommendations from a physiotherapist, who conducts a preliminary examination, gets acquainted with the person’s medical history and determines the tactics of the upcoming treatment. All further manipulations prescribed by the specialist are performed by the nurse.
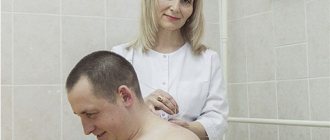
With the frequently used cutaneous attachment of electrodes, the procedure follows the following algorithm:
- the nurse examines the skin on the treated area;
- then, in accordance with the doctor’s prescriptions, attachments with electrodes are installed on the skin;
- The patient is covered with a sheet and the current level is adjusted.
During the session, the nurse monitors the patient's condition and controls the operation of the devices. If slight tingling from the electrodes is acceptable, then if there is unpleasant or painful sensation, the session is stopped. If everything goes according to plan and there are no complaints, the procedure lasts from 15 to 30 minutes. The number of sessions is calculated by the doctor, taking into account the indications for electrophoresis and the severity of the effect obtained. It is recommended to conduct sessions daily without intervals of 1 or more days.
Advantages and disadvantages
The general advantages of electrophoresis are as follows:
- the drug is administered actively and purposefully, since only those drugs that have an ionic form in solution are selected for electrophoresis, and the drug accumulates under the skin;
- the drug acts for a long time, has a therapeutic effect several days and even weeks after the end of the course;
- the medicine can be administered specifically, that is, paravertebrally or deep into the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the spine, if we are talking about protrusions and hernias;
- An important point is the almost complete absence of adverse reactions, because the medicine does not pass through the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and does not irritate the gastric mucosa. Quite often, the drugs for electrophoresis that are used for protrusions or hernias will be nicotinic acid and aminophylline, and in the case of electrophoresis there is no need to be afraid of their usual side effects characteristic of oral use;
- electrophoresis differs favorably from injections in the method of drug delivery. After all, if there is a spasm of capillaries in the pathological focus, such as in chronic back pain due to the presence of a protrusion or hernia, then the injection often does not resolve for a long time. And the electric current is guaranteed to deliver medications evenly exactly where they are needed, bypassing the blood;
- electrophoresis helps to bring into the depths of the tissues only the medicine that is necessary: no impurities, ballast substances, which are contained in abundance in tablets, do not enter biological tissues during electrophoresis. In the same way, no associated solvent, without which various injections and intravenous infusions are impossible, is used. Therefore, the body is not loaded with excess fluid, microcirculation is not disrupted, and post-injection infiltrates and complications do not form;
- finally, electrophoresis is a completely painless, bloodless, and atraumatic method of drug administration, which is well tolerated by both adults and children.
Electrophoresis also has disadvantages. The most important of them is that not all drugs are suitable for this method of treatment, since not all of them disintegrate into ions, and having disintegrated, not all remain active in a dissociated state. Medicines that do not dissociate into ions are unsuitable for electrophoresis, that is, electrically neutral molecules. The second drawback is that a small electric current is not capable of creating fairly high concentrations of the drug, and it cannot be increased, otherwise the procedure will turn into an unpleasant and painful procedure. Finally, under the influence of electric current, many drugs change their activity, or even become useless, such as some anticoagulants.
Features of electrophoresis in children
When prescribing treatment, pediatricians often choose auxiliary therapy - electrophoresis (or iontophoresis). It is safe, has minimal risks of side effects, and allows small doses of drugs to be administered to areas with pathological changes. The procedure is painless for a small patient; tissues are not damaged when the medicine is administered.
Its popularity is due to the fact that current can have a positive effect on the human body:
- dilates blood vessels;
- relaxes muscles;
- relieves inflammation;
- stimulates the immune system;
- regulates hormonal levels.
Electrophoresis in children and adults differs because:
- Children's skin is thin and immature and has fewer cell layers.
- The skin of children absorbs substances faster and has low resistance to current.
- Up to four months, infants do not have developed sweat glands, and thermoregulation is not well developed.
- The epidermis in children has a high ability to regenerate.
Due to these factors, treatment with electrophoresis should be carried out under the supervision of medical personnel and parents, taking precautions.
For young children, the procedure should not exceed 7-8 minutes. For older children, the duration increases to 15-20 minutes.
Indications and contraindications
Electrophoresis is very similar to galvanization. Galvanization is different in that it applies direct current, but does not contain any medicine. Therefore, electrophoresis can also be called “medicinal galvanization.” Indications for electrophoresis will be:
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system (myositis, rheumatism, osteochondrosis and its complications);
- compression neurovascular syndromes;
- plexitis, neuritis and neuralgia;
- syndrome of acute pain in the neck (cervicago), chest and lower back - lumbago;
- chronic myofascial tonic syndrome, causing constant back pain.
Many of the above conditions are inevitable companions of discogenic exacerbations of osteochondrosis.
Electrophoresis is indicated in the initial stages of hypertension and coronary heart disease (with the exception of unstable angina). This method is used for pathologies of the lungs and bronchi, gastrointestinal tract, various gynecological and urological pathologies, diseases of the ENT organs and in many other cases.
General contraindications to electrophoresis include any tumor growth, both malignant and benign, active tuberculosis, suppuration, streptoderma, erysipelas at the sites where electrodes are applied and bleeding wounds, disorders of the integrity of the skin such as eczema and psoriasis, skin mycoses .
Special contraindications include intolerance to exposure to electric current, foreign metal prostheses in the intended area of influence, severe cardiovascular insufficiency, and heart rhythm disturbances.
Indications for electrophoresis with aminophylline
For the procedure, aminophylline is used in solution. If we talk about the advantages of this particular method of drug delivery:
- the medication is delivered to the desired location in an active state;
- delivery is targeted to a specific focus of the disease, which reduces unnecessary effects on the entire body;
- With this method of transportation, the substance tends to accumulate and thereby increase the duration of its effect.
Electrophoresis with aminophylline is indicated in the following cases:
- Bronchial asthma.
- Impaired muscle tone (muscle spasms).
- Hypertonic disease.
- Diseases of the large intestine.
- Spinal diseases: osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis, Schmorl's hernia.
- Poor circulation in the kidneys and brain.
- Psoriasis.
- Scleroderma.
- Diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Lymphadenitis.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Tracheitis.
- Furunculosis.
- Bedsores.
- Some diseases of the nervous system.
Is it possible to do electrophoresis for a herniated disc?
The therapeutic effect of electrophoresis consists of two factors:
- direct influence of electric current, that is, galvanization;
- additional effect of the administered drug.
The therapeutic effect of direct current is to shift the ratio of ions in tissues. The receptors are irritated, local and even general reflex reactions occur. The permeability of cell membranes changes, blood vessels dilate, blood circulation and lymph flow increase. Soft tissues are better supplied with blood and regenerate, and the resorption of inflammatory infiltrates is enhanced. These changes have a beneficial effect on foci of chronic inflammation, which often cause persistent pain in various parts of the spine in the presence of protrusions and hernias.
The effect of a drug depends on its ability to dissociate, that is, break down into ions. And most often for complications of osteochondrosis, the following medications are used:
- novocaine (+);
- aminophylline (-);
- lidase (+);
- analgin (-);
- pyridoxine (vitamin B6, +);
- thiamine (vitamin B1,+);
- cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12,+).
For each medicinal substance, it is indicated in parentheses on which electrode it should be applied, and accordingly, it is this electrode that should be adjacent to the corresponding part of the spine. After all, the medicinal substance is repelled from the electrode, being similarly charged. An electrode of opposite polarity should be located on a different surface of the body, or at a considerable distance, but on the same surface, to create a skin depot.
You should know that many medications require preliminary preparation, so Lidase is taken in an amount of 64 units and diluted in distilled water, which is acidified with a weak solution of hydrochloric acid so that the final pH of the solution is from 5 to 5.2.
Electrophoresis of analgin, sodium salicylate, baralgin
The drugs have not only anti-inflammatory, but also a pronounced analgesic effect.
Indications
- arthrosis;
- spondylosis;
- in case of acute inflammation in the acute stage with severe pain.
Mode of application
The procedure is similar to galvanization: electrodes with a drug solution on a medicinal pad are installed on painful areas.
Peculiarities
A negatively charged electrode with a medicinal pad is placed on the painful area with the highest pain severity. Electrophoresis solution:
- diluted 1/10 50% ampoule solution of analgin;
- 5% sodium salicylate solution;
- 2% baralgin solution.
The amount of solution per napkin is 2-15 ml.
Duration of treatment
Daily procedures are carried out for 10-20 days for 15-30 minutes.
How is the session conducted?
Before starting work, prepare the device by changing the limit value of the ammeter depending on the current strength prescribed by the doctor. Electrodes with pads moistened with the appropriate preparation are applied and secured to the patient. It is strictly forbidden to apply electrodes directly to the body, since as a result of chemical reactions, either an acidic or an alkaline environment can form under the electrode and cause a chemical burn. Between the electrode and the body there must be a pad of calico or flannel, at least 5 mm thick, moistened with water. This kind of gasket reduces skin resistance, helps eliminate the effect of electrolysis on the skin, and makes the penetration of the medicinal substance more uniform. The electrodes are connected to the wires with terminals, the wires are connected to the “output” of the device, observing the polarity, and the device is connected to the network.
Application of electrodes
It is extremely important to place the electrodes correctly. For cervical osteochondrosis, a galvanic collar can be used, when one of the collar-shaped electrodes is located on the back, neck and shoulder girdle, and the second in the lumbar region. Accordingly, if a doctor prescribes a drug with a positively charged sign, then an anode should be placed on the shoulders so that the medicinal substance is repelled from it and penetrates deep into the skin. If a medicinal substance with the opposite sign is prescribed for electrophoresis, then this electrode should be the cathode. The standard current strength for cervical osteochondrosis is from 6 to 15 milliamps, and the session duration is from 5 to 15 minutes. Procedures can be performed daily or every other day; the course consists of an average of 15 procedures. After each procedure, the time gradually increases by 2 minutes, and the current strength is increased by 2 milliamps. In the case of lumbosacral osteochondrosis, one of the electrodes is applied to the lumbosacral region, and two paired electrodes of opposite polarity can be located on the anterior surfaces of the thighs. The current strength is also up to 15 milliamps, the duration of one session is up to 20 minutes, the duration of the course is up to 20 procedures, either daily or every other day. When conducting electrophoresis for protrusions and hernias in the thoracic region, special techniques for applying electrodes are also used.
After the signal light comes on, the required current strength is set using a potentiometer, depending on the readings of the device. It is important that the current strength at the very beginning needs to be set less than necessary, since then the current will spontaneously increase somewhat, since the skin resistance under the electrodes will decrease. After 3-4 minutes, the current strength is finally adjusted taking into account the patient’s sensations. There should be no burning sensation, unpleasant sensation, or feeling of “goosebumps” under the electrodes.
After the required time has passed, the current strength is gradually reduced to 0, and only then the electrodes and pads are removed from the patient.
During the procedure, the patient may feel a slight tingling or warmth under the electrodes, but without pain or discomfort. If a strong burning sensation or severe pain occurs, it is necessary to reduce the current strength or stop the procedure.
Indications for use in infants
Electrophoresis with aminophylline is also used for infants. There is a misconception that this is dangerous for children of this age. But this is far from true. On the contrary, the procedure only has a positive effect. Therefore, it is prescribed to infants starting from the first month of life with the following diseases:
- Skin burns.
- Congenital heart defects.
- Tonsillitis.
- Sinusitis, sinusitis.
Otitis.- Cystitis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Hepatitis.
- Colitis.
- Enterocolitis.
- Stomatitis.
- Cystitis.
- Diathesis.
- Bronchitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Dysplasia and subluxation of joints.
- Increased and decreased muscle tone.
- Torticollis.
- Birth injuries.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Lymphadenitis.
- Slow development.
Electrophoresis of aloe (mud squeezes)
The components of therapeutic mud and aloe improve tissue nutrition, have a resorption and trophic effect, and anesthetize the affected tissue areas.
Indications
- progressive course of spondylosis and arthrosis beyond the acute stage;
- pain syndrome;
- fibrous and articular changes;
- increase in joint size;
- dystrophic changes;
- circulatory disorders.
Treatment method
Under the anode and cathode, pads moistened with a medicinal solution (diluted ¼) with water or a squeeze of medicinal mud are placed. The amount of liquid is 5-15 ml.
The duration of the procedure is 15-30 minutes, treatment is carried out daily for 10-20 days.