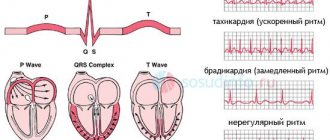
ECG (electrocardiogram) is a universal examination method that helps to identify a wide range of diseases of various types. However, the resulting graph is largely a mystery to the patient. What do negative T waves mean here, for example? Only your attending doctor will give you a complete, comprehensive answer specifically for your case. Indeed, when reading a cardiogram, not only certain knowledge is important, but also extensive work experience. In this material we will present to the reader important basic indicators, their norm, and estimated deviation values.
What it is?
This is where we will begin preparing for the ECG interpretation. The T wave is the most important indicator on the electrocardiogram, which can help the doctor make a conclusion about the recovery process after contraction of the heart ventricles. He is the most changeable in the schedule.
By its shape and location, one can judge the amplitude of heart contractions, the presence of such dangerous diseases, conditions and pathologies as myocardial damage, endocrine diseases, intoxication of the body, taking incorrectly selected medications, etc.
Let's take a closer look at deciphering the ECG and the norm for this indicator.
Normal values for adults
On the graph, this tooth coincides with the so-called repolarization phase, that is, with the reverse transition of potassium and magnesium ions through the membrane of cardiac cells. It is after this that the muscle fiber cells will be ready for the next contraction.
Now deciphering the ECG. Normal for adults:
- Along the isoline, the T will begin after the S wave.
- The direction should visually coincide with the QRS. That is, to be positive where R predominates, negative in areas where S is already dominant.
- The normal tooth shape is smooth. Its first part will be flatter.
- The amplitude reaches the 8th cell.
- The ECG leads increase from 1 to 3.
- The wave is negative in V1 and aVL.
- Always negative T in aVR.
Norms for newborns and children
Features of deciphering an ECG (we presented the norm for adults above) for newborns:
- In this case, normal T waves are low or even completely flat.
- The directions will be directly opposite to adults. What is this connected with? The baby's heart turns in the direction - it occupies its constant physiological position only for 2-4 weeks of life.
Now let's list the features of the children's ECG - older children:
- Normally, negative T in V4 can persist for up to 10 years, and in V2 and 3 for up to 15 years.
- Both in adolescents and in older young people, negative T wavelengths in the first and second chest leads of the ECG are acceptable. By the way, this type is called juvenile.
- The T height will gradually increase from 1 to 5 mm. For example, for schoolchildren it is approximately 3-7 mm. And these are indicators comparable to adults.
Normal QT interval
Normally, the QT interval does not have a constant value. The distance from the beginning of Q to the end of T depends on:
- gender and age of the subject;
- time of day;
- states of the nervous system;
- use of medications, especially analogues of stress hormones (Adrenaline, Dopamine, Hydrocortisone);
- calcium, magnesium and potassium levels in the blood.
The most significant dependence can be traced to heart rate. Therefore, the calculation formulas that take this indicator into account have been continued. The faster the heart rate, the shorter the QT. When mathematically analyzing ECG data from healthy people, an approximate pattern was derived and is reflected in the table.
| QT characteristic | Men, ms. | Women, ms. |
| Normal | 360-390 | 370-400 |
| Bit longer | 391-450 | 401-460 |
| Lengthened | 451-470 | 461-480 |
| Significantly lengthened | From 470 | From 480 |
| Shortened | 360-330 | 370-340 |
| Significantly shorter than normal | Up to 330 | Up to 340 |
What do the changes mean?
Let's take a closer look at the reasons for a negative T wave on an ECG. In general, an electrocardiogram helps diagnose the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Poor circulation in certain areas of the brain.
- General potassium deficiency.
- Diseases of endocrine nature.
- Cardiopsychoneurosis.
- Constant stress, severe nervous overload.
- Various types of intoxication of the body. Including nicotine, glycosides, aminazine, antiarrhythmic drugs.
- Hypertrophy of the cardiac ventricles.
- Injuries, infections and tumors of various nature.
- Pericarditis.
- Thromboembolism.
- Myocarditis, etc.
Tall T waves in precordial leads
Tall T waves in the chest leads are accompanied by angina pectoris. It can be both stable and progressive, that is, threatening the development of myocardial infarction. In this case, it is important to take into account the clinical picture and other ECG changes. A typical sign of ischemic waves is their symmetry.
High T can also manifest itself as:
- hyperkalemia (excessive intake of potassium, taking drugs that inhibit its excretion);
- anemia;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- left ventricular hypertrophy.
Main deviations
Negative T waves are just one type of deviation of this electrocardiogram indicator from the norm. But there is a whole list of them - each name will talk about its own violation.
The main ones will be:
- Negative T waves.
- Two-phase.
- Flat.
- Smoothed.
- Inversion.
- Coronary.
- Depression.
- Decreased performance.
- Raising the tooth.
- High performance.
We will provide an explanation of a number of deviations in the following sections of the article.
Negative T
What does a negative T wave on an ECG indicate first? It indicates coronary heart disease. A negative T wave can also be caused by a heart attack if the deviation is accompanied by changes in the QRS complex.
The changes that the ECG graph will show allow us to judge the stage of necrosis of the damaged heart muscle:
- Acute stage. On the graph, abnormal QS, Q, ST segment will pass above the line. T is positive.
- Subacute stage. Characterized by negative T.
- Scarring. The T wave is slightly negative or positive.
Negative T waves in all leads of the electrocardiogram do not always indicate a serious pathology. Such indicators will be normal if the patient has rapid breathing and is worried. In addition, negative T may indicate that the person being examined has recently dined heavily on a dish containing a large percentage of carbohydrates. Therefore, proper preparation for an ECG is important to avoid false suspicions.
Negative T may also demonstrate an individual feature of the heart of completely healthy people.
ST Down Shift
A pronounced downward ST shift is a sign of insufficient myocardial nutrition - coronary heart disease. It is clinically manifested by angina pectoris, heart attack, and post-infarction cardiosclerosis. Similar changes, but without clear localization, are characteristic of:
- overdose of cardiac glycosides;
- use of diuretics;
- tachycardia;
- increased and frequent breathing;
- hypertrophy of the ventricles of the heart;
- intraventricular conduction disorders.
The T wave reflects the process of ventricular repolarization after their contraction. This is the most labile wave on the ECG; its changes may be the first sign of impaired blood supply to the myocardium in coronary heart disease. To make a diagnosis, you need to compare the clinical symptoms and other signs on the cardiogram.
Pathologies indicated by negative T
However, in most cases, this indicator indicates various kinds of pathological conditions. A negative T wave will be observed in the following diseases and disorders:
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Condition after frequent extrasystoles, paroxysmal tachycardia.
- The so-called “pulmonary heart”.
- Violation of the nervous or hormonal regulation of the heart - diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, diseases affecting the adrenal glands or pituitary gland.
- A number of cardiac pathologies - cardiomyopathy, heart attack, inflammatory process in the pericardium, myocardium, angina pectoris, mitral valve prolapse, endocarditis.
Two-phase T
Another name is a sign of a “roller coaster”. The T wave first falls below the isoline, after which it crosses it, becoming positive.
A biphasic T wave may indicate the following abnormalities:
- Blockade of the Hiss bundle branch elements.
- Intoxication with glycoside drugs.
- Hypertrophy of the left cardiac ventricle.
- Increased percentage of calcium in the blood.
Shortening of the QT interval on the ECG
Shortening the QT interval on the ECG is dangerous, as it provokes complex types of rhythm disturbances. This syndrome can be a congenital feature, and also appears when:
- treatment with cardiac glycosides in the usual dose, progresses with its increase;
- increased concentrations of potassium and calcium in the blood;
- fever;
- a shift in the blood reaction to the acidic side (acidosis).
Short QT syndrome can be constant and repeated from cycle to cycle or paroxysmal due to changes in heart rate. Patients with such disorders are prone to dizziness, lightheadedness, and sudden loss of consciousness. In severe cases, there is a risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Smoothed tooth
On the graph, T will appear somewhat flattened. The following reasons can lead to smoothing of the indicator:
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, antidepressants, Cordarone.
- The patient is in a state of excitement or fear.
- Myocardial infarction, which is in the scarring stage.
- Diabetes.
- Excessive consumption of sugar, sweet foods and drinks before the examination.
- Neurocirculatory dystonia.
- Hypokalemia.
Nonspecific ST-T changes
Nonspecific ST-T changes include all minor violations of ST height, smoothing or the opposite direction of T. They “do not reach” obvious pathologies, but the doctor pays attention to them when deciphering them. This can be important, since if there are complaints of heart pain, further examination is necessary. It is also carried out with risk factors:
- high pressure,
- smoking,
- elderly age,
- high cholesterol,
- sedentary lifestyle.
The main causes of nonspecific symptoms include:
- imbalance of electrolytes (potassium, magnesium, calcium);
- use of medications;
- angina pectoris;
- infectious diseases, pulmonary pathology;
- pain attack;
- consumption of large amounts of food, alcoholic beverages;
- left ventricular hypertrophy;
- cerebrovascular accident.
Since all these factors are diverse, when making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the symptoms and, if necessary, prescribes blood tests, an ECG using the Holter method (24-hour monitoring), and stress tests with exercise.
Reduced rate
This refers to the amplitude of the T wave - it will be less than 10% of the QRS complex. What does this deviation from the norm indicate?
There are several reasons for a reduced T-wave:
- Obesity, excess body weight.
- Cardiosclerosis.
- Hypothyroidism.
- The patient's advanced age.
- Tonsillitis.
- Myocardial dystrophy.
- Anemia.
- Dyshormonal cardiopathy.
Also, the cause of the deviation may be the patient taking corticosteroid drugs.
Inversion
Inversion - in other words, the inversion of the T wave. What does this look like on an electrocardiogram? The tooth changes its position relative to the isoline. That is, in leads with positive (normal) T, it suddenly reverses its own polarity.
Inversion will not always indicate pathology. It is considered normal with a juvenile configuration (if observed only in the right leads), signs of early repolarization, which is typical for professional athletes.
Inversion of T at the same time will be a sign of a number of diseases and pathologies:
- Bleeding in the brain.
- Recent attack of tachycardia.
- Ischemia of the brain or myocardium.
- Disturbances in the conduction of impulses along the Hiss bundle.
- A state of severe stress.
ECG changes and their meanings
Most often, changes are suspected of coronary heart disease, but such a disorder may be a sign of other diseases:
- thromboembolism,
- myocarditis, pericarditis,
- tumors, infections and injuries,
- ventricular hypertrophy,
- intoxication, including cardiac glycosides, antiarrhythmic drugs, aminazine, nicotine,
- stress, neurocirculatory dystonia,
- diseases of the endocrine system,
- potassium deficiency,
- decreased blood circulation in the brain,
- osteochondrosis.
Therefore, to make a diagnosis, all clinical signs and changes in the cardiogram are taken into account as a whole.
Two-phase
On the cardiogram, T first decreases below the isoline, and then crosses it and becomes positive. This symptom is called the “roller coaster” syndrome. May occur in the following pathologies:
- left ventricular hypertrophy;
- Hiss bundle branch block;
- increased calcium levels in the blood;
- intoxication with cardiac glycosides.
Biphasic T wave with left ventricular hypertrophy
Smoothed
Flattening of the T wave can be caused by:
- taking alcohol, Cordarone or antidepressants;
- diabetes mellitus or eating a lot of sweets;
- fear, excitement;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- hypokalemia;
- myocardial infarction in the scarring stage.
Decrease in indicator
A reduced T is indicated by its amplitude, which is less than 10% of the QRS complex. This symptom on the ECG causes:
- coronary insufficiency,
- cardiosclerosis,
- obesity,
- elderly age,
- hypothyroidism,
- dishormonal cardiomyopathy,
- myocardial dystrophy,
- taking corticosteroids,
- anemia,
- tonsillitis.
The T wave on the ECG is smoothed
The T wave can be smoothed in the same conditions as an absent wave, since both definitions characterize low-amplitude oscillations. It should be taken into account that violation of the rules for ECG registration can also cause smoothing of T. It also occurs in metabolic diseases - low function of the thyroid gland (myxedema, hypothyroidism). It can be found in completely healthy people throughout the day in several cardiac cycles (according to Holter monitoring).
Inversion
Inversion (turning over) of the T wave means a change in its position relative to the isoline, that is, in leads with a positive T, it changes its polarity to negative and vice versa. Such deviations can also be normal - in the right chest leads with a juvenile ECG configuration or a sign of early repolarization in athletes.
T wave inversion in leads II, III, aVF, V1-V6 in a 27-year-old athlete
Diseases that are accompanied by T inversion:
- myocardial or cerebral ischemia,
- influence of stress hormones,
- bleeding in the brain,
- attack of tachycardia,
- violation of impulse conduction along the branches of the Hiss bundle.
Negative T wave
For coronary heart disease, a characteristic sign is the appearance of negative T waves on the ECG, and if they are accompanied by changes in the QRS complex, then the diagnosis of a heart attack is considered confirmed. In this case, changes in the cardiogram depend on the stage of myocardial necrosis:
- acute – abnormal Q or QS, ST segment above the line, T positive;
- subacute – ST on the isoline, negative T;
- in the scar stage, weakly negative or positive T.
A negative T wave in leads V5-V6 (highlighted in red) indicates ischemia.
A variant of the norm may be the appearance of negative T wave with frequent breathing, excitement, after a heavy meal, which contains a lot of carbohydrates, as well as with individual characteristics in some healthy people. Therefore, the detection of negative values cannot be considered a serious illness.
Pathological conditions that are accompanied by negative T waves:
- heart disease - angina pectoris, heart attack, cardiomyopathy, inflammation of the myocardium, pericardium, endocarditis, mitral valve prolapse;
- violation of hormonal and nervous regulation of cardiac activity (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland);
- pulmonary heart;
- after paroxysmal tachycardia or frequent extrasystoles;
- subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is accompanied by negative T waves
Absence of T wave on ECG
The absence of T on the ECG means that its amplitude is so low that it merges with the isoelectric line of the heart. This happens when:
- drinking alcohol;
- against the backdrop of excitement, anxiety;
- cardiomyopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus;
- neurocirculatory dystonia (with a sudden change in body position or after rapid breathing);
- insufficient intake of potassium or its loss through sweat, urine, intestinal contents (diarrhea);
- scarring of myocardial infarction;
- use of antidepressants.
High rate
Normally, in those leads where the highest R is recorded, the maximum amplitude is noted; in V3 - V5 it reaches 15 - 17 mm. Very high T can occur when the influence on the heart of the parasympathetic nervous system, hyperkalemia, subendocardial ischemia (first minutes), alcoholic or menopausal cardiomyopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy, and anemia predominate.
Changes in the T wave on the ECG during ischemia: a - normal, b - negative symmetrical "coronary" T wave, c - high positive symmetrical "coronary" T wave, d, e - biphasic T wave, f - reduced T wave, g - smoothed T wave, z - weakly negative T wave.
Flat
A slightly inverted or flattened T may be either a normal variant or a manifestation of ischemic and dystrophic processes in the heart muscle. It occurs with complete blockade of the conduction pathways in the ventricles, myocardial hypertrophy, acute or chronic pancreatitis, taking antiarrhythmic medications, and hormonal and electrolyte imbalance.
Coronary
When the heart muscle is hypoxic, the fibers located under the inner membrane, the endocardium, are most affected. The T wave reflects the ability of the endocardium to maintain a negative electrical potential, therefore, in case of coronary insufficiency, it changes its direction and becomes this shape:
- isosceles;
- negative (negative);
- pointed.
These signs characterize the ischemic wave, or it is also called coronary. Manifestations on the ECG are maximum in those leads where the greatest damage is localized, and in mirror (reciprocal) leads it is sharp and isosceles, but positive. The more pronounced the T wave, the deeper the degree of myocardial necrosis.
Rise of the T wave on the ECG
Moderate physical stress, hyperkalemia, infectious processes in the body, thyrotoxicosis, and anemia lead to an increase in the amplitude of T waves. Elevated T without changes in well-being can occur in healthy people, and can also be a symptom of vegetative-vascular disorders with a predominance of vagal tone.
Depression
A reduced T wave can be a manifestation of cardiomyodystrophy; it occurs with pneumonia, rheumatism, scarlet fever, acute inflammatory process in the kidneys, cor pulmonale and hypertrophic increase in the muscular layer of the myocardium.
The T wave is positive
Normally, T waves in leads should be positive: first, second standard, aVL, aVF, V3-V6. If it appears where in healthy people it is negative or close to the isoelectric line, then this indicates a lack of blood flow through the arteries of the heart (myocardial ischemia), blockade of the branches of the His bundle. Temporary changes are caused by stress, an attack of rapid heartbeat, and intense exercise in athletes.
Flat T
A flattened, slightly inverted T is a controversial indicator. In individual cases it will be the norm. In some patients, it speaks of cardiac muscle dysfunction, ischemic, and degenerative processes.
May accompany the following serious diseases and dangerous conditions:
- Complete blockade of the ventricular pathways.
- Chronic or acute pancreatitis.
- Myocardial hypertrophy.
- Electrolyte or hormonal imbalance.
In addition, a flat T wave can be observed with systemic use of antiarrhythmic medications.
Nonspecific T wave changes
Nonspecific changes in the T wave include all its deviations from the norm that cannot be associated with any disease. There are such ECG descriptions:
- variant of the norm;
- with strong compression of the limbs with electrode cuffs;
- after taking cardiac glycosides, diuretics, and some drugs to lower blood pressure;
- with frequent and intense breathing;
- due to abdominal pain;
- associated with an imbalance of the main blood electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium) with vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, and drinking alcohol on the eve of diagnosis.
In the absence of symptoms (heart pain, shortness of breath, rapid resting pulse, rhythm disturbances, swelling, enlarged liver), such changes are considered minor and do not require treatment. If there are signs of cardiac disease, then daily Holter ECG monitoring is necessary to clarify the diagnosis. It will show whether the restoration of cardiac polarity will be impaired during normal physical activity.
In some cases, nonspecific disturbances in the shape and size of the T wave occur when:
- insufficient nutrition of the myocardium (ischemic disease);
- increased blood pressure, especially with concomitant hypertrophy (thickening of the heart muscle) of the left ventricle;
- violation of intraventricular conduction (branch block).
A synonym for nonspecific changes in the T wave is a doctor’s conclusion: a violation of ventricular repolarization.
Coronary T
On the cardiogram, the T wave reflects the ability of the endocardium to maintain an electrical negative potential. It follows from this that with coronary insufficiency the tooth will change its direction. When violated, it is visualized in one of the following forms:
- Negative, negative.
- Isosceles.
- Pointed.
All of the above are so-called ischemic waves. Another name for them is coronary.
An important feature is that the waves will be most visible on the cardiogram in those areas where the greatest damage is observed. In mirror leads the indicator will be sharp and isosceles. The more pronounced the T on the graph, the more severe the myocardial damage.
Prong lift
An increase in amplitude can be a consequence of moderate physical overstrain of the patient, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, hyperkalemia, and various types of infections. This is also an individual norm for a number of healthy people.
The rise of the T wave may be one of the signs of vegetative-vascular pathologies with a predominance of vagal tone.
The T wave is an important indicator on the ECG. A specialist based on his deviations judges the development of diseases in the patient, the presence of dysfunctions - not only cardiac, but also nervous, hormonal, infectious or inflammatory.