SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate plastic surgery Doctor Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers am For residents of the region For pensioners Promotions in clinic
Stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs is one of the most common manifestations of circulatory disorders in the female internal genital organs. In the future, this contributes to pathological changes in this area. The main reason for blood stagnation in the pelvis is daily sedentary work without breaks. When a person is in this position for a long time, the ligaments and muscles of the pelvis squeeze the blood vessels passing nearby, preventing blood from circulating freely. And with the advent of computers and the Internet, the number of people suffering from this phenomenon has increased many times...
Mostly women after 30-40 years of age suffer from this, although even in girls over the age of 20, gynecologists detect this condition in 20-25% of cases. After the age of 50, stagnation of blood and lymph in the pelvic organs is observed in almost 80% of women.
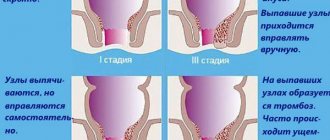
☛ Risk factors and reasons why pelvic congestion occurs: • hereditary factors; • sedentary lifestyle; • lack of regular sex life with orgasms; • adhesions in the area of the uterus and appendages; • pathological retroflexion or lateroflexion (bending of the uterus backwards or to the side); • chronic inflammation “feminine”; • protection by interrupted sexual intercourse; • taking contraceptive pills and hormonal drugs. • heavy physical and emotional stress; • pregnancy (repeated, aggravated, multiple); • complicated course of labor.
According to statistics, the problem affects young women and more often those who have 2-3 children. It is believed that during pregnancy, increased estrogen levels can affect the walls of the veins, making them weaker. Blood stagnation often occurs with a disease such as varicose veins of the pelvic organs. These are veins that have stopped functioning properly because something is wrong with the valves.
What are pelvic varicose veins
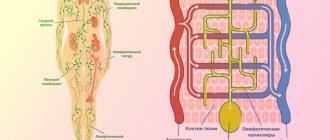
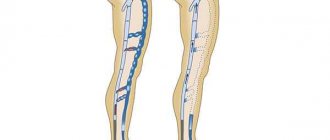
How are varicose veins of the pelvic veins formed? The principle of its formation in women is similar to varicose veins in the legs. The valves normally found in the veins that allow blood to be pushed upward towards the heart become less elastic and do not function fully. As a result, the blood in the legs stagnates and the veins dilate. We often see them in others as raised and nodular venous plexuses that can be painful, especially when standing.
These same veins exist in our pelvis, and their valves may also be poor at carrying blood to the heart. This means that the outflow is less than the inflow and some of the circulating blood accumulates inside the pelvic structures due to gravity, causing the veins to swell. These dilated, defective vessels are hidden inside our pelvis, causing pain and other discomfort in the pelvic area, but we cannot see them. Sometimes they become visible around the genitals (vulva, vagina), inner thighs, buttocks, or down the legs.
Fig.1. "Comparison of normal blood flow through a vein and disturbance of blood flow due to valve damage."
Now it is clear that in this condition the blood flow slows down, the blood stagnates in the vessels, the pressure in the veins increases, and they become deformed - they stretch, increase in diameter. Therefore, ultimately, the speed of blood circulation decreases, and this is a direct path to the formation of venous insufficiency. As a result, blood that should flow back to the heart instead remains inside the pelvis, causing what Western medicine refers to as “pelvic congestion” (excess blood flow syndrome). It puts pressure on such important organs as the uterus, ovaries with tubes, bladder and lower intestines with all the ensuing consequences for the intimate and reproductive health of a woman...
Symptoms of blood stagnation in the pelvis
The clinical manifestations of pelvic hyperemia syndrome may vary from person to person. The main symptom is constant (chronic) pain. It is felt by a woman in the lower abdomen and can radiate (spread) to the lower back, sacrum or groin area. The intensity of pain varies and it intensifies during sexual intercourse, after prolonged standing, before or during menstruation, etc.
When visiting a doctor, patients often present the following complaints:
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- Irregular and painful periods;
- Haemorrhoids;
- Varicose veins of the external genitalia and vagina;
- Varicose veins in the legs;
- Lower back pain;
- Urinary problems;
- Chronic pelvic pain;
- Pain during and after sexual intercourse.
If a woman has more than two of the above symptoms, there is an increased likelihood of having pelvic venous stasis and varicose veins.
Possible harm to women's health
Pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS) can cause fertility problems and difficulties in women who have had two or more pregnancies. This condition can also cause the development of venous insufficiency in the lower extremities with varicose veins of the vulva and perineum. This happens because there is a direct connection between the venous plexuses of the uterus and appendages and the superficial network of the legs. This is why, in many cases of impaired blood flow and blood stagnation in the pelvic organs, women develop dilated veins in adjacent areas, especially on the inside or back of the thighs or calves.
Cosmetic defects caused by “protruding veins” and increased vascular patterns on the genitals and lower extremities are not the biggest problem with this syndrome. The danger of poor blood flow in the internal female organs lies in the multifaceted impact on many important functions of the female body.
Possible complications may be:
- Regular nagging pain in the lower abdomen of unknown cause;
- Psycho-emotional instability;
- Constant irritability, weakness, deterioration in performance;
- Decreased libido, anorgasmia;
- Ovarian hypofunction;
- Changes in the nature of menstruation;
- Inflammatory diseases of the uterus and ovaries;
- Problems with conceiving a child and carrying a pregnancy.
Diagnosis of congestion
Initially, a problem with microcirculation in this area can be identified if you perform a “female ultrasound” with a vaginal sensor. This method will allow the specialist to see the exact number, size and distribution of dilated veins in the uterus and ovaries, and optional Doppler measurements will help determine the parameters of vascular blood flow.
In advanced or difficult to differentiate cases, abdominal ultrasound, venography, laparoscopy and MRI are additionally prescribed to identify varicose dilatation.
Increased blood flow in the pelvic organs
The scheme and tactics for treating congestive processes are selected individually by the gynecologist, depending on the severity of this condition and the presence of certain symptoms. In any case, therapy should be comprehensive - aimed at restoring the tone of the venous walls and improving metabolic processes in the pelvic organs.
✅ The main ways to improve blood flow:
- The use of medications - phlebotropic drugs, vitamins and drugs that improve blood flow from venous vessels;
- Surgical intervention. Surgical treatment of the syndrome of “pelvic hyperemia” and varicose veins in the area of the pelvic organs, vulva and vagina is achieved by embolization of the pelvic veins, which can be recommended if conservative methods are unsuccessful or hopeless and only by a specialized specialist.
- Physical exercises, intimate Kegel training at home;
- Physiotherapy, manual techniques, etc.
If with p.p. Nos. 1, 2 and 3 are all more or less clear, we will focus on point No. 4. These include ways to improve blood circulation in the pelvis in women without resorting to invasive methods. The methods listed below to activate the movement of blood and lymph, reduce or eliminate venous stasis in the internal genital organs, can be used either independently or in combination with taking medications.
Only manual and similar treatment techniques, without the use of drugs, are carried out in order to prevent the development of stagnation. They are recommended for all women who lead a sedentary lifestyle or have the risk factors listed above!
CONGISTENT PNEUMONIA IN THE ELDERLY – WHAT IS THIS DISEASE DANGEROUS?
Why does congestive pneumonia appear in the elderly?
- The development of stroke, heart attack, bronchopulmonary diseases, in which in the postoperative period the patient is deprived of the ability to move independently, inevitably leads to the development of congestive pneumonia;
- The older a person gets, the more his respiratory system becomes susceptible to functional changes: weakening of the diaphragm, shallow breathing (this is inevitable for people over 65 years of age), decreased elasticity of lung tissue;
- With age, pulmonary circulation becomes more difficult. Inactive bronchial ventilation leads to the fact that, one way or another, harmful and dangerous microorganisms (anaerobes, pneumococcus, enterobacteria) begin to rapidly multiply in the area of the bronchotracheal tree and oropharynx. Their active life activity leads to the development of congestive pneumonia.
CONGESTAL PNEUMONIA: SIGNS
Due to the fact that traditional pneumonia only affects small areas of lung tissue, drug treatment will be sufficient to treat it. The situation is much worse when it comes to congestive pneumonia, when fluid stagnates in the lungs and bronchi.
Attention! Elderly people may only suffer from weakness or lack of appetite, since other symptoms are often vague, so they may not even be aware of the presence of a dangerous disease.
Hypostatic pneumonia can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- The appearance of chills;
- The occurrence of drowsiness and weakness;
- Continuous cough;
- Increased sweating (the body loses its ability to thermoregulate);
- The occurrence of shortness of breath;
- Sudden changes in body temperature;
- Slight secretion of sputum during coughing;
- Audible wheezing.
Since this disease is insidious, it is very important to diagnose it in a timely manner.
CONGESTIVE PNEUMONIA: DIAGNOSTIC MEASURES IN ELDERLY PEOPLE
This disease does not have any special symptoms, so the main task of loved ones is to sound the alarm in time, and the main task of the attending physician of an elderly person is to diagnose the disease in time. Some previously suffered diseases, as well as diseases that have become chronic, can signal the possible development of hypostatic pneumonia, namely: stroke, heart attack, cardiosclerosis, heart disease, atherosclerosis, kidney inflammation, diabetes mellitus, asthmatic syndrome, pulmonary emphysema. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to resort to:
- X-ray examination. However, the image will be characterized by opacities that identify fluid in the lung. In this case, stagnant clots, characteristic, for example, of bronchopneumonia, are also visible in the image as clouding. In other words, congestive pneumonia can be confused with another disease, and not every medical institution is equipped with equipment for examining a bedridden patient;
- Ultrasound examination. By taking an ultrasound image and thus examining the pleural cavity, you can detect the exact location of the stagnant fluid;
- Steto- or phonendoscope - listening to the lungs. The presence of this disease will be confirmed by hoarse breathing and moist rales.
Localization of secondary pneumonia is the lower lobe of the right lung (the area farthest from the heart). If the doctor diagnoses this disease incorrectly, the elderly person may fall into a coma. Untimely or incorrect treatment also leads to urinary incontinence, depression, and sudden mood swings. This symptomatology is similar to cyanide dementia, so the doctor may make a mistake with the diagnosis.
Another cause of medical error may be the symptom of shortness of breath, since the doctor may regard it as a sign of heart failure. If the diagnosis was made incorrectly, and therefore the wrong treatment was prescribed, or the person consulted a doctor late, consequences may occur in the form of:
- Impaired blood outflow, which will inevitably lead to the pulmonary veins becoming overfilled;
- Leakage of blood plasma through the walls of blood vessels. The pulmonary alveoli begin to accumulate fluid, thus, pathogenic bacteria begin to develop;
The process of replacing lung tissue with connective tissue begins.
CONGISTENT PNEUMONIA: TREATMENT METHODS FOR ELDERLY PEOPLE
This disease requires hospital treatment and continuous monitoring by doctors. Since the disease is infectious, broad-spectrum antibiotics are required. In addition, it is necessary to restore normal ventilation of the lungs, which means that a diuretic, an expectorant, an antioxidant, and an immunomodulator will be prescribed.
In order to ease the work of the heart, the doctor will prescribe a glycoside and a drug to improve metabolism. To free the bronchi and trachea from sputum, it is necessary to prescribe bronchoscopy. If the pleural cavity is filled with fluid, a diuretic and puncture are necessary. This therapeutic complex will allow you to quickly stabilize the patient’s condition.
In addition, it is necessary to resort to physiotherapeutic methods: a course of massage, inhalations and oxygen masks. It is also useful to perform breathing exercises, especially the Buteyko and Strelnikova complex.
Be sure to perform a set of exercises that can normalize diaphragmatic breathing:
- Taking a lying position, fold your hands on your stomach and take a slow breath, then exhale through your mouth. At the same time, try to tense your abdominal muscles and press with your hands, creating a resistance effect in order to enhance exhalation;
- Taking a standing position, spreading your arms to the sides and spreading your legs wide, inhale. Then exhale slowly, move your arms forward, bend down, and at the same time make sure that your stomach is pulled in.
In order for sputum to be expelled more easily, it is necessary to carry out positional “drainage”, which consists in the fact that the body takes certain positions, so that the liquid flows into the area of reflexogenic zones, which causes a cough. It is necessary to take several deep breaths through the nose and exhale through the mouth, while the teeth should be clenched tightly, and then cough strongly. 30 minutes before the start of this complex, you need to drink a warm decoction: linden, plantain or coltsfoot, or just tea with honey or milk.
After being discharged home, it is necessary to continue treatment through traditional medicine.
CONGISTENT PNEUMONIA: TREATMENT WITH TRADITIONAL MEDICINE
Various decoctions help perfectly in the fight against this disease:
- Decoction of thyme or creeping thyme: 2 tbsp. spoons, brew one and a half liters of boiling water, then strain and take at least 4 times a day, ½ tbsp. before meals;
- Bearberry decoction: 1 tbsp. Brew a spoon with a glass of boiling water, divide into three parts and consume each of them 30 minutes after eating;
- Decoction of viburnum berries: 2 tbsp. Brew spoons with a glass of boiling water and leave overnight. Then add honey and take 2 tbsp. spoons after meals;
- A decoction of a collection of herbs: chamomile, St. John's wort, nettle, calendula, raspberry, marshmallow, elecampane, sage, plantain and calamus. It is necessary to mix all these herbs in 3 tbsp. spoons of each.
- Brew 2 tbsp. spoons of the collection with boiling water (0.5 l.), leave overnight, strain and take half a glass. The course of admission is about three months;
- The medicine “urbech”, whose homeland is Dagestan. Grind apricot kernels (3 kg) and flax seeds (3 kg), be sure to store the mixture in the refrigerator. When treatment is necessary, you need to take butter (1/2 pack), add 1 tbsp. spoon of the mixture and bring to a boil, then remove from heat, let cool and add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of honey. Then put it in the refrigerator and let it harden; if necessary, add it to the patient’s porridge or simply spread it on bread.
SURGICAL INTERVENTION FOR HYPOSTATIC PNEUMONIA
Most often, bedridden patients who cannot breathe need surgical intervention. In order to alleviate suffering, the doctor may prescribe a chest puncture. Thus, it becomes possible to “pump out” the fluid and free the lungs. The procedure is performed only in a hospital, by a qualified surgeon and under general anesthesia.
HYPOSTATIC PNEUMONIA IN ELDERLY PEOPLE: PREVENTIVE MEASURES
As you know, it is better to prevent the development of any disease than to treat it later. Since hypostatic pneumonia is a complication of another disease, older people need to take care and follow the following rules:
- Always ensure that your feet are dry and warm;
- Practice daily walks in the fresh air;
- Take time for proper daily rest;
- To refuse from bad habits;
- Pay attention to proper and nutritious nutrition;
- Allergy sufferers should especially monitor the condition of their disease;
It is mandatory to undergo the vaccination procedure in order to prevent the development of influenza during its epidemic.
If we are talking about a bedridden elderly person, then relatives need to prevent the development of congestive pneumonia: turn the patient over more often, massage his chest, use cups and mustard plasters, perform the previously described physical exercises with him, make sure that the room in which the person is lying , it was well ventilated and the air was humidified.
Modern medicine makes it possible to treat hypostatic pneumonia in older people without any problems, only if they timely seek qualified medical help and correct diagnosis. At the same time, the desire of the patient himself and his efforts during therapeutic exercises are also important, so relatives need to adjust the patient accordingly. And after treatment, it is important for an elderly person to lead a healthy and active lifestyle.