CPK (creatine kinase, creatine phosphokinase) in the blood: what it is, reasons for increased enzyme levels.
Among the numerous enzymes contained in human blood, there is one enzyme that is necessary in every cell of the body, and most of all in the cells of nervous tissue and muscles. This element is called creatine kinase or creatine phosphokinase .
KFC: what is it?
Creatine kinase is an enzyme that accelerates the transfer of a phosphoryl residue from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to creatine. In this case, adenosine diphosphate is formed, and the energy that was previously hidden in the high-energy bonds of ATP is released and used. These complex biochemical processes provide the muscles with the energy they need to contract.
Since muscles contract almost continuously (heart function, intestinal motility, regulation of blood vessel lumens, swallowing, etc.), creatine kinase is continuously used by the body.
Creatine kinase, like other enzymes, is a protein and therefore composed of amino acids. Amino acids enter the body with protein foods, and then the necessary proteins or other amino acids are formed from them.
Loss of muscle mass or lack of dietary protein can affect the amount of creatine kinase in the blood.
Additional events
CPK analysis alone is rarely enough to make a diagnosis. Research is used to state a fact: something is wrong. What exactly is being found out in other ways.
- Interview and anamnesis collection. You need to understand what complaints there are. To put forward hypotheses and consider disease options. This is the first step.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract. The liver is mainly examined. She is one of the main culprits of the problem.
- ECG and echocardiography. To assess the condition of the heart. Deviations such as coronary heart disease, especially previous heart attacks, will certainly affect the CPK indicators.
- Electroencephalography of the brain.
- Study of vessels of cerebral structures, vertebral arteries.
- Blood chemistry. In particular, ALT and AST indicators. They are also called liver tests.
- Electromyography. Of necessity. To evaluate muscle contractility. If the concentration of CPK and ATP is insufficient, it usually decreases.
- MRI or CT if necessary. Basically, if the doctor does not fully understand the structural state of a particular system or a specific organ. Basically, that's enough. At the discretion of specialists, the list can be expanded.
CPK or creatine phosphokinase is a catalyst, an enzyme that accelerates the production of ATP. Substances that allow the body to exist and carry out activities at all.
All deviations definitely need to be carefully checked. Look for the cause of the disorder and, if necessary, treat it.
Causes of increased creatine kinase
So what causes an increase in the concentration of creatine kinase in the blood? There are a great many such reasons, among them are dystrophies, burns, cancer, and simply intense physical activity. Well, most often the reasons are the following:
- Polymyositis (an autoimmune disease in which cells of the immune system begin to attack muscle tissue, causing damage to almost all muscles);
- Myocardial dystrophy (dystrophy of the heart muscle);
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle);
- Oncological diseases (most often at the stage of tumor decay, which is usually accompanied by severe poisoning of the body);
- Convulsions, especially common during epilepsy;
- Overdose of certain drugs (statins, fibrates, amphotericin);
- Alcoholism, alcohol poisoning;
As for muscle overwork, an increase in creatine kinase is observed only in cases where the muscles begin to break down from overwork. This is accompanied by acute pain (sores) associated with the accumulation of metabolic products in muscle tissue.
It happens that creatine kinase also increases after surgery, and the more difficult the postoperative period is, the greater the likelihood of an increase in the concentration of this substance.
Interestingly, constantly elevated levels of creatine kinase can be observed in mentally ill people, namely those suffering from schizophrenia, manic-depressive psychosis , and those who abuse psychotropic drugs.
Indications and results
Indications for analysis are:
- Meloxicam: use of intramuscular form in rheumatology
- early diagnosis of myocardial infarction (analysis is required within the next 2-4 hours);
- differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction, when this attack is combined with a mild or uncomplicated attack of angina.
In addition, this test is prescribed to all patients who are being treated for any heart disease in order to exclude the possibility of a heart attack. It is knowledge of the level of CPK (what it is, described above) that will help specialists determine the condition of the heart. An increase in this substance in the blood can signal possible heart problems. If this phenomenon is permanent, then the doctor in most cases decides on preventive treatment, which will stop the development of the disease in the future.
Blood CPK (what it is, you can find out at the beginning of the article) is elevated in the following cases:
- myocardial infarction (increased values are diagnosed in the first 2-4 hours, the maximum is reached after 24 hours; after 3-6 days the value decreases, but normalization does not occur);
- muscle dystrophy;
- Reye's syndrome (acute hepatic encephalopathy);
- state of shock;
- various poisonings, in particular with alcohol and sleeping pills;
- infectious lesions of the myocardium.
A reduced level of CPK in the blood (what it is, described above) is observed with a decrease in muscle mass, a sedentary lifestyle, and also acts as an indirect sign of the development of thyrotoxicosis (intoxication with thyroid hormones that are produced by the thyroid gland).
Reasons for the downgrade
Of course, in certain situations, creatinine kinase can drop sharply. This happens in the main period when a person’s muscle mass decreases. Any fluctuations in muscle mass can be a consequence of natural processes, as well as the results of various diseases. Typically, muscle mass decreases with age, a phenomenon called sarcopenia . A painful decrease in muscle mass is observed, for example, with prolonged fasting, lack of protein food, and infectious lesions of muscle tissue.
Also, a decrease in creatine kinase can be observed with alcoholic liver damage and liver cirrhosis. of ascorbic acid, aspirin, and amicocin also leads to similar results . Pregnant women also experience a slight decrease in the concentration of creatine kinase, which is quickly replenished after childbirth.
Neither an increase nor a decrease in creatine kinase is not a specific sign by which one can judge the presence of any disease in the body.
We see that there are a large number of diseases associated with fluctuations in the concentration of this enzyme, so before drawing conclusions about the patient’s health, additional examination should be carried out.
CPK levels in women
There are a number of features of the female body associated with the metabolism of creatine kinase. Firstly, due to the fact that women have less developed skeletal muscles, the concentration of this enzyme in their blood is noticeably lower than in men.
Secondly, the amount of creatine kinase may decrease slightly , while the amount of this enzyme in the placenta and placental blood, on the contrary, is higher than in the rest of the human bloodstream. This affects the amount of blood enzyme in a newborn baby, which is also higher.
Thirdly, the gene for congenital muscular dystrophy is often detected in young women. This is a rare genetic disease, the gene for which is located on the X chromosome, as well as the gene responsible for hemophilia. Just like hemophilia, muscular dystrophy most often affects boys. A woman who carries the gene has a 100% chance of having a son with the disease .
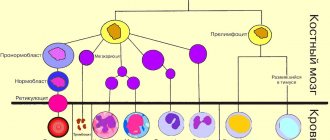
Creatine phosphokinase
In the structure of creatine kinase there are 2 subunits: M - muscle (muscle) and B - brain (brain). In this regard, three isoforms of this enzyme are distinguished:
- CPK-MM - found mainly in skeletal muscles;
- CPK-MB – localized in the myocardium;
- CPK-BB is an enzyme of nervous tissue.
Total creatine phosphokinase and its isomers can be determined in the blood.
Consequently, when a certain type of tissue is damaged, an increase in the activity of the corresponding isoform of creatine phosphokinase is characteristic. What increases and under what diseases will be discussed below.
Changes in the body during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the level of creatine kinase decreases slightly, which has virtually no effect on the mother’s well-being or her health in the future. This decrease is associated not only with bearing a child, but with the fact that the lifestyle of the expectant mother changes, or physical activity decreases significantly, especially in the later stages.
At the same time, the fetus's creatine kinase levels are elevated. For comparison: if an adult woman has 167 units of creatine kinase per liter in her blood, then a fetus in late pregnancy has 650 or more .
Enzyme content in children
In children, the level of creatine kinase in the blood is very high, especially in the first days of life. So, for the first 5 days, the level of creatine kinase remains the same as that of the fetus before birth, that is, about 650 units per liter of blood. However, over the next 6 months, the amount of enzyme decreases by 2-2.5 times.
Until the age of one year, the amount of creatine kinase continues to fall; at the age of about one year it is about 200 units per liter. Then, due to the child's increasing activity, the amount of creatine kinase increases again. In time, this coincides with teaching a child to walk, run, manipulate objects, and so on.
But, if by the age of three the amount of creatine kinase reaches 220 units , then it begins to fall again, and by the age of six it is already 149 units.
From the age of 9-10 years, a child begins puberty, and the concentration of blood enzymes in girls and boys begins to differ.
The reasons for deviations from the norm in children are the same as in adults, with the exception, of course, of pregnancy. It should be borne in mind that children are more likely than adults to be overtired, and also often experience a lack of protein due to poor nutrition.
What are the dangers of deviation from the norm?
Creatine kinase itself is not a toxic substance, so an excess does not pose any threat to the human body.
Serious threats to it are those diseases that caused an excess of this enzyme, for example, cancer, heart attacks, inflammatory processes in the muscles, various poisonings, and so on.
A lack of creatine kinase can affect the functioning of muscles and the nervous system . It causes muscle weakness, fatigue, dizziness, problems with attention and the ability to perform physical work.
References
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, 2013. - 16 p.
- Encyclopedia of clinical laboratory tests / ed. WELL. Titsa. - M.: "Labinform", 1997. - P. 279-281
- Kumar, V., Abbas, A., Fausto, N. et al. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2014. - 1464 p.
- Cabaniss, C. Creatine Kinase. In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition. Boston: Butterworths, 1990.
- Aujla, R., Patel, R. Creatine Phosphokinase. StatPearls, 2020.
Preparing for the study
In order to find out what the concentration of creatine kinase is in your blood, you can go to a regular hospital. The concentration of creatine kinase is determined during a routine biochemical blood test. One day is enough to receive test results. Such an analysis costs about 370 rubles. To carry it out, blood is taken from a vein. Referrals for analysis can be obtained from a general practitioner, oncologist, cardiologist, and other specialists.
You should prepare for that crowd the same way as any other: the analysis is done in the morning on an empty stomach , 8 hours after the last meal. It is advisable not to smoke, drink, or take medications 3 days before the test. Since the amount of enzyme directly depends on physical activity, you should also not engage in sports or heavy physical labor.
When is a test ordered?
There are quite a lot of reasons for research:
Muscle pain
Muscle discomfort is a clear and common sign of myositis. Local inflammatory process.
Against the background of this phenomenon, the concentration of CPK increases. The more intense the muscle damage, the higher the enzyme levels.
It is convenient to study fractions if you need to assess the dynamics of the state. For example, before and after treatment.
Alcohol poisoning
In this case, diagnostics are prescribed to examine the safety of energy metabolism. Ethanol, an alcohol, acts as a kind of inhibitor and slows down ATP synthesis. Paradoxically, CPK is growing at the same time.
As a result, muscle strength decreases and the metabolic rate in the brain decreases. If this phenomenon reaches critical proportions (for example, after heavy alcohol consumption, at the level of a lethal dose), irreversible changes are likely.
A study of the amount of creatine phosphokinase is designed to assess the degree of impairment. And then track how the recovery process is going.
Tachycardia, any abnormalities of the heart
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and therefore indirectly creatine phosphokinase, plays a key role in the functioning of the muscular organ.
Because without a sufficient amount of these substances, contractility would be impossible in principle. Any deviations immediately make themselves known.
In the early stages, the body tries to compensate for the violation using the accumulated reserve of strength. Own resources. The number of contractions per minute increases. Once the internal potential is exhausted, the heart stops beating with sufficient force.
Attention:
If the concentration of CPK continues to increase, and the myocardial function is also low, the organ’s functioning is likely to stop.
Doctors have the opportunity to catch pathology at its earliest stages. Although tachycardia develops for other reasons.
Rheumatic carditis
We are talking about inflammation of autoimmune origin. By its nature, such a disorder poses a danger to biochemical processes in general. As a result of a false response of the body's defenses, the concentration of CPK increases.
As the muscle layer is destroyed, isoenzymes begin to leak into the blood and no longer provide the internal resource and safety margin of the myocardium. How it ends is already clear. Cardiac arrest and death of the patient are possible.
Suspicion of stroke and recent acute cerebral blood flow deficits
Violations of the integrity of cerebral tissues. In the first case, the study indirectly confirms damage to the nerve structures. In the second, it allows you to determine the severity of the disorder.
The signs of a pre-stroke condition are described in detail here, and signs of a stroke - here.
Inflammatory processes
Any etiology. Mostly infectious. Toxins produced by bacteria, as well as those remaining from the destruction of the body’s own cells, inhibit and slow down the production of CPK. Based on the results of the analysis, one can judge the severity of inflammation.
High load on the myocardium
There can be many options for this. For example, sports training or physical, exhausting work. Categories of patients who face such stress are at increased risk.
In this situation, a blood test for CPK is prescribed as a preventive measure. Research needs to be done regularly. At least 2 times a year. Can be done more often as needed.
All deviations are a clear cause for concern. Energy metabolism must be maintained. This is where cardioprotectors and other drugs come to the rescue. That's another question.
The list of indications is far from complete. A blood test for creatine phosphokinase is prescribed for tumor processes to confirm the etiology of mental disorders. Whether it is necessary to take the test in a particular case is decided by a specialized specialist.