What is a normal heart rate in children?
For each age, there are certain indicators that can be checked in pediatric cardiology in Saratov. During the appointment, the doctor listens to the heart, determines or excludes the presence of murmurs, and also counts the number of heartbeats. If necessary, an ECG or ultrasound of the heart may be prescribed. An experienced pediatric cardiologist in Saratov will draw the attention of parents to the fact that the heart rate decreases every year. If at birth 150-160 heart beats are considered normal, then by the age of 12–13 years this number is equal to 75 beats.
The pulse rate directly shows how the heart copes with its function and how efficiently it pumps blood. If there are too many contractions, the heart muscle may become fatigued and heart failure may develop.
Possible complications
It is necessary to find out the cause of the constant high or low pulse and begin timely treatment. If this rule is ignored, there is a high probability of complications.
Possible consequences:
- loss of consciousness;
- impaired blood circulation in the brain and other organs;
- the formation of blood clots in the heart;
- heart failure;
- death.
Pulse is a criterion by which the state of human health can be determined. PS has different characteristics - frequency, rhythm, content. Most often, the pulse is detected at the wrist or neck. After measurement, the value is compared with the norm. In adolescence (12–17 years), the pulse is slightly higher than in adults. PS may deviate from the optimal value up or down.
This indicates physiological (stress, poor diet, being in an unventilated area) or pathological (cardiovascular, endocrine diseases) reasons. If the pulse deviates from the norm for a long time, you need to visit a specialist.
The doctor will prescribe diagnosis and treatment. The most important thing is to reduce the likelihood of complications. To do this, you must follow your doctor's recommendations.
Why is it important to monitor your heart rate?
When visiting pediatric cardiology in Saratov, the specialist will pay attention to the fact that sometimes too high a pulse rate does not provoke painful sensations. It is extremely important to monitor the child’s behavior and reaction after physical activity, as well as after emotional outbursts. A small patient may complain of shortness of breath, headache, pain in the sternum radiating to the arm, as well as severe fatigue after:
- active physical exercise;
- long walks at a calm rhythm;
- walking up to low floors.
An increased heart rate in a child can also be observed after emotional stress. A pediatric cardiologist in Saratov will explain that laughter, as well as tears, prolonged viewing of cartoons, and strong emotional reactions can cause an increase in heart rate. It is important to measure the indicators after such a condition, and in addition, parents must make a lot of effort to check the frequency of contractions in the usual way.
Heart rate norms
In the fetus
You can notice fluctuations in the baby’s heart at the beginning of the first trimester; the rhythm is rapid and changes with the development of the fetus. Pulse at 6–8 weeks is 110–130 beats, from 8 to 11 it reaches 190, from 11 weeks – 140–160, varies several times a day.
In newborns
- The heart rate of a baby (the first 4 weeks after birth) with anxiety increases to 160–200 beats.
- 120–140 beats is normal.
- Children born prematurely have a higher heart rate than a child born at full term.
In infants
A baby is considered a child from 30 days to 1 year. By the age of one year, the baby’s normal heart rate is 132 beats. Normally, the heart rate in children increases to 162.
In young years
In a child under 7 years of age, the nervous system is at a stage of intensive development, which is the reason for the increase in heart rate in children. For a 2-year-old child, the normal heart rate is 124 beats; physical activity or stress leads to a frequency of 94 to 154 beats.
In preschoolers
The age of preschoolers is conventionally divided into three periods:
- junior preschool age - from 3 to 4 years;
- average preschool age - from 4 to 5 years;
- senior preschool age - from 6 to 7 years.
The normal pulse rate for 6-year-old children, as can be seen from the table, is 106 beats.
The heart rate of school-age children is 80–120 beats.
In children 9–10 years old, the normal heart rate is considered to be 108 beats per minute.
- Sinus tachycardia of the heart: what is it, main symptoms and treatment
Why does the heart rate increase?
During emotional or physical stress, adrenaline is released, which irritates the cerebral cortex. The hormone cortisol may also be released. Its excess causes insomnia and an overly alert state. It is especially dangerous if the child's heart rate increases in the evening, when he should lie down, relax and fall asleep. Adrenaline, entering the blood, causes its increased speed, and the heart begins to pump blood faster, which means it works with increased load.
Additional reasons why the heart rate may increase include:
- infectious and viral diseases suffered by a woman during pregnancy,
- natal injuries;
- acute illnesses of a child with increased body temperature;
- undergone surgical interventions.
A pediatric cardiologist in Saratov often diagnoses palpitations, other types of heart rhythm disturbances, heart murmurs, and blood pressure fluctuations. These symptoms can be caused by both diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and a number of other conditions: disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, nervous system, and kidneys. To identify the cause of the disease, a complete examination is required.
Sometimes for such an examination in pediatric cardiology in Saratov, the Holter heart rate monitoring method is prescribed, with the help of which the heart rate is recorded for 24 hours. Over the course of a day, a child’s emotional background and mood changes, there is physical activity, periods of sleep and quiet activities, and academic workload, which affects the functioning of the heart. And when deciphering the recording of the circadian rhythm, the pediatric cardiologist in Saratov sees what changes have occurred in the work of the heart.
How to determine
The pulse of a teenager (12 - 18 years old) must be monitored to compare it with the norm.
Measurements can be taken at the following locations:
- wrist;
- ulnar artery (slightly below the elbow);
- elbow bend;
- armpit;
- temple area;
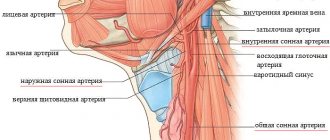
- neck (carotid artery);
- lower jaw and corner of the mouth;
- inner thigh;
- bend of the leg (below the knee);
- foot.
The most common places where the pulse is measured are the extremities (wrist) and neck.
To monitor the indicator at home, the following methods can be used:
- Palpation. You should choose the hand on which the pulsation is better. If everything is the same, then you need a limb close to the heart. You need to find a point that has a pronounced pulsation and press it with your ring finger. Next, count the number of blows in 1 minute, compare the result with the norm. You can use another method - count the number of beats for 6 seconds, then multiply the number by 10. If it is impossible to hear the pulse on the wrist, measurement on the carotid artery is allowed. To do this, you need to sit or lay the person down and press on the artery with your index finger. Next, count the number of beats in 6 or 60 seconds. In the first case, multiply the indicator by 10.
- Using an electronic tonometer . Modern devices can count pulse together with measuring blood pressure. The result is displayed on the tonometer screen.
- Heart rate monitor. The device is designed to analyze heart rate, monitor the load and functionality of the heart. There are different types of heart rate monitors - on the chest, on the finger, on the arm.
Before measuring, you must adhere to the following rules:
- exclude physical activity;
- rest before measurement for 5 – 10 minutes;
- eliminate stress 1 – 2 hours before measurement;
- stop smoking 2 - 3 hours before measuring your pulse;
- do not drink strong coffee or alcohol;
- do not measure your pulse after a hot bath or swimming;
- Do not eat heavily or fast before taking measurements;
- you need to take measurements 1 – 2 hours after waking up;
- remove tight clothing, as it can compress the artery.
Critical age periods
For young patients, there are critical periods during which an elevated heart rate is often observed. Most often, the child cannot explain exactly how bad he feels and what is the reason for such physiological changes. He feels pressure in his chest, dizziness, sometimes chills, and may even lose consciousness. You should not allow such frequent reactions to occur, and you should visit a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov as soon as you notice the first symptoms. A small patient may be afraid that his body reacted this way to running, watching his favorite movie and the fact that he received a gift that he had dreamed of for so long.
Diagnostics
At each appointment, the pediatrician conducts auscultation (listening with a phonendoscope) and examination of the chest to check the functioning of the child’s heart, even if the patient came in for ARVI. Pathological murmur is easily auscultated by a cardiologist. It indicates heart problems, even if the patient is not worried about anything or does not attach importance to some symptoms (in addition, children are sometimes afraid to report their problems and worries).
Basic diagnostic methods in cardiology:
- ECG (assessment of the conduction of electrical impulses through the heart muscle);
- Daily ECG monitoring;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- Echo-CG (study of the morphology and functional state of the heart);
- Doppler echo-CG (study of blood flow in the chambers of the heart and great vessels);
- Plain radiography of the chest (determining the size and location of the cardiac shadow);
- Coronary angiography (study of coronary vessels);
- CT;
- MRI.
It is important to identify the disease in time: the earlier treatment is started, the better the effect. However, most violations can only be detected using special equipment. In addition, the baby is not able to voice complaints, so instrumental diagnostics in pediatrics cannot be avoided.
What are the future risks of a high pulse?
If you do not notice in time and do not contact pediatric cardiology in Saratov for adequate treatment, the child will experience frequent painful sensations over time, and in addition, he may develop associated disorders:
- with vessels, veins and arteries;
- with the nervous system;
- with hormonal background.
A pediatric cardiologist in Saratov, based on the monitoring results and tests obtained, will determine and make an accurate diagnosis, which will allow you to prescribe treatment, the effectiveness of which will not be long in coming. It is also important to record changes after a certain time in order to adjust the medication course and prescribe additional physiotherapeutic procedures, and choose the appropriate sport. It is important to take measurements immediately after physical activity of varying strength and intensity, after strong positive or negative psychological reactions. Pulse rate measurements after sleep are also important for a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov to determine the diagnosis and prescribe effective and appropriate treatment.
Over time, as the child grows up, it is necessary to teach him to monitor his pulse rate, especially after physical or emotional stress. There are drugs that can quickly restore the pulse rate, and in addition, maintenance therapy. Every year a little patient must learn to listen to his body, and an experienced pediatric cardiologist in Saratov will help with this.
Make an appointment with a cardiologist
Choose a doctor
Prevention
{banner_banstat9}
For the proper development of the cardiovascular system, from childhood, parents must teach their child simple rules of behavior that guarantee the prevention of any diseases. These include:
- active lifestyle, fight against physical inactivity;
- playing sports according to age;
- hardening;
- balanced diet;
- morning exercises;
- walks in the open air;
- clothing according to the season and weather;
- refusal of large amounts of flour and sweets;
- calm and friendly atmosphere in the family;
- 8-9 hour sleep;
- correct indoor microclimate.
This lifestyle will help the baby grow up strong, courageous, balanced, and friendly, which will certainly affect the condition of the heart and blood vessels, and will guarantee a normal pulse in accordance with age.
The immune system
The immune system of a physiologically immature child is already capable of responding when encountering foreign microorganisms, but this response can also proceed inadequately, violently, or, conversely, with a delayed reaction. In subsequent periods of the child’s development, an increased allergic mood of the body is observed, and various types of diathesis arise in such children. There is also a reduced ability to produce substances that provide protection to the mucous membranes, so infectious agents more easily, compared to a full-term baby, damage these membranes, causing focal infections. High sensitivity to viral infections. In 60-80% of cases they occur in an asymptomatic manner.