At the AVENU medical centers (Rostov-on-Don and Bataysk) you can take a blood test (culture) for sterility. Low cost of the procedure. Click to find out how much the analysis costs.
Bacteriological studies
Number: 446
A26.05.001
Microbiological (cultural) blood test for sterility
1600 rub.
Where can I get tested? Preparing for research
The study takes 11 days
All prices are indicated without discounts. Smear collection - 150 rubles. Taking blood from a finger - 100 rubles Taking blood from a vein - 150 rubles.
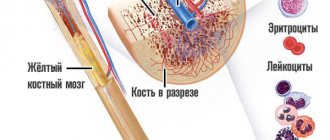
Normally, blood is sterile, that is, there are no foreign microorganisms in it.
If blood poisoning – septicemia – is suspected, blood is cultured on special nutrient media. If bacteria are present in the blood, they grow. Identification of microbes is carried out by mass spectrometry.
By exposing bacterial colonies to different classes of antibiotics, their sensitivity to the drugs is determined. This allows you to choose the optimal treatment.
Indications
Blood culture for sterility has several indications:
- elevated body temperature, which lasts for a long time, while there are no other symptoms, the cause of this condition cannot be determined;
- suspected sepsis (blood poisoning);
- suspected infections (streptococcal, staphylococcal, intestinal);
- surgical operations;
- long-term catheterization;
- presence of artificial heart valves.
Sowing is carried out on a nutrient medium that is favorable for the growth of microbes
Features and advantages of vacutainers
The three-component system for venous blood collection consists of:
- sterile vacuum tube with preservative;
- double-sided automatic needle for intravenous injection;
- automatic needle holder.
The advantages of negative pressure systems are related to their design features:
- safety, sterility and guarantee of sample integrity;
- minimizing microclots and hemolysis;
- maintaining a constant time between collection and connection with the additive;
- exact ratio of sample and additive;
- minimizing the tourniquet effect.
Why is it carried out?
The main purpose of blood culture for sterility is to detect the following pathogens in it:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- streptococcus;
- enterobacteria;
- Klebsiella;
- Yersinia;
- yeast mushrooms.
Blood culture is carried out in order to see the growth of colonies, conduct tests with chains of microorganisms, and determine their type and sensitivity to antibiotics. In addition, such an analysis allows you to find the most effective way to destroy the identified type of bacteria.
Reasons why bacteria enter the blood
Ways bacteria enter the blood:
- Surgical interventions;
- Intravenous catheterization;
- Any other invasive interventions;
- Injury;
- Internal foci of infection.
Under physiological conditions, microorganisms in the vascular bed can appear after intense physical activity or overheating of the body. Such bacteremia is called transient, is usually asymptomatic and is completely eliminated by the body's defenses.
Insufficiency of immunity (due to chronic disease, HIV, immunosuppressive therapy, etc.) is a predisposing factor to septicemia.
How is it carried out?
Blood collection for sterility is carried out several times over a certain period of time, since a one-time test cannot be considered effective. It is possible to assert that the causative agent of a disease is a specific microorganism only after conducting a series of studies (two or more) and repeatedly isolating it from blood and other biological materials (sputum, urine). In this case, the microorganism must be detected on different nutrient media simultaneously.
Blood sampling is carried out at the maximum temperature increase. It should be taken before specific antibiotic treatment begins, or at least not earlier than a day after the last dose.
To perform a sterility test, venous blood is taken
Blood for sterility is taken in the morning from a vein in the elbow area. The injection site of the syringe is carefully treated: first with alcohol (70%), then with iodine (1-2%). The syringe is injected after the injection site has completely dried. Testing requires 10 ml.
After the patient’s blood is taken, the blood is inoculated on a nutrient medium favorable for bacterial growth and kept for several days at a temperature of 37-38°C in a thermostat.
Over time, as a result of bacterial growth, colonies appear on the surface, which are visible to the naked eye. By their appearance, a laboratory technician can determine the type of microorganism. The identified bacterium is sown in a Petri dish. Paper discs soaked in various antibiotics are placed around its circumference. The Petri dish is placed in a thermostat for several days, where new colonies grow. The drug that is effective will be the one around the disc with which no bacterial growth is observed, which indicates the death of microbes or the impossibility of their development.
Today, two sowing methods are used:
- on the medium to determine sensitivity to major antibiotics;
- on the medium to detect sensitivity to a wide range of drugs.
The first results are obtained after three days. It may take 10 to 14 days to get the final result.
The test can be taken at any medical institution where there is a laboratory. is one of the largest independent laboratories offering its services in many cities of Russia. The Invitro network has been operating for about 20 years. Here you can undergo any blood test, including a sterility test.
What does a blood test show for sterility?
Date: 02/15/2019
Not every patient knows why doctors in clinics write out referrals for various examinations, including blood tests for sterility. Doctors claim that this testing is prescribed to identify bacteremia in a patient, which indicates the presence of pathogenic processes in the body. To get a reliable result and the opportunity to begin competent treatment, the patient needs to know the rules for taking blood and strictly follow some recommendations for several days.
Characteristics of the study
Blood culture for sterility - what is it and why is it called that? This examination is one of the most important, as it gives doctors the opportunity to identify the presence of microorganisms in the blood, which indicate the development of various pathologies and internal inflammatory processes. In a healthy person, the blood and other body fluids should be sterile, and if the test shows the opposite result, this indicates the presence of some kind of disease. To determine a violation of sterility, hematological culture on various nutrient media is most often prescribed.
Indications for use
The main purpose of the analysis is to identify the presence of harmful microorganisms that provoke the inflammatory process. The diagnostician may prescribe the patient to donate blood for microbiological testing in the following cases
- if the patient suffers from specific symptoms, but doctors for a long time cannot determine what is the primary source of the pathological process;
- the physician assumes the presence of a septic infection in the patient;
- the presence of complications caused by improper surgical intervention;
- placing a catheter in internal organs for a long time;
- a person periodically suffers from high body temperature, but doctors cannot determine what causes such a reaction in the body;
- the presence in the body of an implant that is in direct contact with the biological media of the body.
The absolute indication for testing behavior is the presence of artificial myocardial valves. To obtain a reliable analysis result, you will have to wait at least 10 days, since the germination of pathogenic microorganisms will take several days.
Experts warn that the speed of this process depends on the type of pathogen. It is worth noting that after collecting biomaterial, many patients are prescribed antibiotics (based on the presenting symptoms), but choosing a more competent and optimal treatment regimen is possible only after receiving hemotest data.
What testing allows us to identify In most cases, bacterial culture for sterility is prescribed to detect harmful bacteria and microbes in the blood, such as:
Blood testing
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- yeast fungi;
- mold spores;
- enterobacteria.
This study is necessary for patients who have reduced body defenses, as well as for people suffering from dangerous pathologies such as HIV, tuberculosis, and acute infectious diseases. In addition, testing is often prescribed if doctors cannot decide on the optimal treatment regimen.
What diseases can culture help identify? Testing for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms allows us to determine the presence of the following pathologies:
Sepsis.
- Meningitis.
- Pyoderma.
- Endocarditis.
- Osteomyelitis.
To detect the type of blood culture, a thorough analysis of the suspected pathogen is required. If the study shows its presence in the body, doctors will need to find out how serious a danger the detected microbes pose to various systems and internal organs.
Where can testing be done? If a person needs to conduct such a test, it is better to make an appointment at a private diagnostic center. The main condition is the presence of a laboratory for microbiological research there. As practice shows, in such institutions the interpretation of the results is carried out in the shortest possible time. The cost of the procedure may vary depending on the type of clinic, but usually the price of testing varies between 400-700 rubles.
Features of preparation Since bacterial culture is a microbiological study, the reliability of the result can be affected by internal and external factors. To prevent obtaining a false result, the patient needs to perform certain preparations:
three days before the delivery of biological material, it is strictly forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages and medications (regardless of the pharmaceutical category);
- within 72 hours before the analysis, it is not recommended to eat fatty, overcooked foods and dishes with a lot of seasonings and spices;
- Smoking is prohibited 3 hours before blood collection.
If the patient ignores the rules, the likelihood of receiving an incorrect test result increases several times, which may lead to the need for secondary testing. There are contraindications. Consult your doctor. Sign up for PET-CT diagnostics!
Carrying out the procedure in adults The algorithm of actions is very simple, but the most important point is compliance with the sampling technique. The biomaterial must be taken strictly from the vein of the elbow. The physician must ensure that no external contaminants enter the bloodstream.
To prevent damage to the biomaterial, blood is drawn with a disposable sterile needle. Before proceeding, the area of the epidermis must be treated with an antiseptic solution. In most cases, about 10 ml of biomaterial is taken from the patient, after which it is placed in a bottle with a nutrient medium that prevents changes in the structure of the blood.
To reduce the risk of infection, blood is poured from a syringe into a vial placed above the burner flame. After these steps, the vial is sealed with a tight lid and placed in a special container until further research is carried out. In the rarest cases, the patient is injected with adrenaline before blood sampling, since the substance increases the accuracy of the analysis and helps to identify the maximum number of pathogens.
Analysis in children In a child, manipulations with blood are carried out differently. Biomaterial is removed only from the toe or heel. For bacterial culture, no more than 5 ml of blood is taken from children for sterility testing.
How long to wait for the result?
How long it takes to prepare an analysis is of interest to all patients. If the procedure was carried out in a modern diagnostic center, the first data can be obtained within a couple of days, but the form with the final results will be given to the patient no earlier than 10 days later. This is due to the fact that the blood will be subjected to various studies, and various reagents and substances will be added to the biomaterial.
Accuracy of the study
Doctors assure that this testing is guaranteed to provide the correct result and the ability to assess the general condition of the patient and identify the presence of certain pathologies. Inaccurate data can only appear if the patient ignored medical recommendations and preparation rules before donating the biomaterial. If all requirements are met, the probability that a person will receive reliable information about his condition reaches 95%.
What conclusions can be drawn after the analysis?
Today, sterility testing is indispensable, as it makes it possible to evaluate blood cultures and conduct research using various pathogenic organisms. In addition, during the study, you can find out how the body reacts to the consumption of certain drugs, thanks to which doctors will be able to choose the best treatment regimen. If a person periodically increases body temperature for no apparent reason, you should not hesitate to make an appointment with a specialist, who, after conducting a physiological examination and collecting an anamnesis, will issue a referral for further diagnostics. We cannot exclude the possibility that one of the first on the list will be a blood test for sterility, since based on this testing it is possible to draw conclusions about the general condition of the patient and prescribe a competent treatment regimen.
Author: : Alsherieva Kuralai Kurmanalievna
head of the bacteriological laboratory
Regional medical center. 02/15/2019
Carrying out the procedure in newborns
Some newborns require blood testing for sterility. Every expectant mother should know what this is and not be afraid if the doctor carries out additional diagnostic procedures immediately after the birth of the baby.
A blood test for sterility may be necessary in the following cases:
- immediately after birth, the child’s temperature rises above 39, there are no reflexes, he constantly spits up, etc.;
- the birth was premature;
- during pregnancy, the expectant mother suffered serious illnesses caused by staphylococci or streptococci;
- there is a risk of intrauterine infection;
- the child has developmental anomalies of internal organs;
- if ompholitis of newborns is suspected - purulent inflammation of the umbilical wound.
The peculiarity of the analysis for a child lies in the method of blood sampling. A child's fingers are too small to grasp enough material. Therefore, to conduct a blood test for sterility, venous blood or capillary blood from the heel is used.
The veins of the child in the elbow, where the sampling procedure is carried out in adults, are quite small and difficult to feel.
Vessels from other parts of the body can be used:
- Veins of the head.
- Veins of the back of the hand.
- Veins of the forearm.
- Calf veins
There are rules for analysis that parents should know:
- the child must be calm, not cry or hysterical. Therefore, it is better to take a rattle or musical toy with you for analysis;
- on the day of blood sampling, it is recommended to give the child a little more fluid than usual when feeding;
- The baby's skin and limbs should be warm before the test. Therefore, you cannot go to the laboratory immediately after leaving the street. The child needs to be woken up, undressed and sat with him in the room for 10-15 minutes;
- It is not recommended to take blood samples from a sleeping or drowsy baby; this can frighten him greatly.
What diseases can be detected
Using a blood sterility test, the following diseases can be diagnosed:
- Sepsis. This is a general infection of the body in which a huge number of bacteria or fungi enter the blood. The danger of the disease is that the infection spreads through the blood to all organs and leads to rapid death without treatment.
- Meningitis. Infectious lesions of the membranes of the spinal cord and brain. One of the ways of infection with the bacterial form of meningitis is hematogenous. The blood carries the infection from the inflammatory focus in the tissues or organs to the brain.
- Pyoderma. A severe skin infection caused by coccus bacteria. Infection can occur due to a small scratch, after which the pathogens spread through the blood to other parts of the body.
- Endocarditis. An inflammatory focus in the inner lining of the heart. The main causative agent is streptococci. Appears in the presence of a primary infectious disease.
- Osteomyelitis. An infectious disease of the bones and bone marrow, which is accompanied by necrosis and purulent discharge. The pathogen enters the bone through the blood from the infectious focus. Less commonly, bacterial infection occurs through an open wound when it is contaminated.
- Tuberculosis. A disease of the respiratory system (less commonly of other systems), which occurs due to infection with Koch bacilli. When inoculating for sterility, it is possible not only to determine the presence of the pathogen, but also its resistance to drugs.
Rules for blood sampling
The result of the study directly depends on the correctness of the blood test for sterility.
What is a sterility test and how to draw blood correctly.
Blood sampling is carried out in the following stages:
- The test is taken by a nurse who should tell you about the method of collecting blood.
- Most often, a vein in the elbow or on the back of the hand is used to collect blood. In rare cases, the material is taken from the fingers.
- For manipulation, the medical worker uses only sterile instruments. The gloves and syringe must be new and discarded immediately after analysis.
- Before inserting the needle, the skin is thoroughly treated with a disinfectant solution in a 5 by 5 cm square at the injection site.
- The blood volume must be at least 10 ml. The less material there is, the higher the risk of a false negative or false positive result.
- A catheter should not be used when drawing blood. It is a source of infection and can contaminate the material.
- To ensure accurate results, blood is taken from both hands at intervals of half an hour.
- The nurse removes the needle from the syringe over the flame of the burner, and injects the contents into a test tube with a liquid nutrient medium. The edges of the tube are burned and closed with a sterile rubber stopper.
- The test tube is placed in a thermostat with a temperature favorable for the life of bacteria (38-39 degrees) and moved to the laboratory.
In some cases, a small dose of adrenaline may be administered to the patient half an hour before blood sampling. This causes the spleen to contract and speed up blood flow. Used for infection of internal organs.
How long does it take for the result to be ready?
After about 3 days, the person being studied can learn that their blood is sterile. Within a few days, doctors can tell about the presence of bacteria and their approximate quantity.
The exact final result is ready in about 10 days. During this time, specialists “grow” infectious pathogens in special dishes. Also during this period, the resistance of bacteria and fungi to various antibiotics is studied.