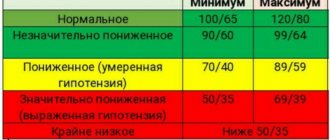
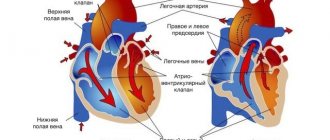
- Characteristic features of edema.
Nowadays medicine has a huge number of different drugs. Due to the growth of technological progress, most of them are produced on a synthetic basis. Such drugs often have many contraindications. Against their background, the safest are natural medicines made from natural ingredients.
Diuretic herbs are a very effective, affordable and easy-to-use remedy that can be taken for a wide variety of illnesses, including swelling of the legs in young and old people. If you need to get rid of a problem quickly and without consequences, or carry out effective prevention, you should definitely pay attention to them.
Causes of puffiness under the eyes
The cause of edema is excess fluid in the body due to poor outflow of blood and lymph. If there is increased pressure in the capillaries, then swelling on the face may also appear. Bags under the eyes may indicate low protein levels in the blood.
Edema occurs not only with pathologies of the urinary tract, but also with diseases of the heart and blood vessels, when it is also necessary to remove excess fluid from the body.
Expert Oksana Aleksandrovna Kim: about swelling
Director and chief physician of the ophthalmology clinic, has more than 10 years of practical work. In her opinion, the cause of edema may be the person himself:
- poor nutrition;
- drinking large amounts of fluids and alcohol in the evening;
- lack of sleep that has become chronic;
- excess salt.
In addition to reasons that depend on the person, swelling can also appear due to serious diseases. One of them is an allergic reaction of the body. This is an intolerance to pollen, food products, medications, household chemicals and components of animal protein compounds. No less serious reasons contributing to the occurrence of edema may be:
- infectious and viral diseases (ARVI, influenza, conjunctivitis);
- traumatic eye damage;
- chronic lack of sleep, interrupted sleep;
- constant drinking of alcohol, smoking;
- excessive consumption of salt, fatty foods, smoked meats, pickles;
- improper functioning of the pancreas (diabetes mellitus);
- increased intracranial pressure;
- stressful situations;
- cosmetics are the wrong choice;
- uncomfortable position chosen for sleeping;
- tattooing or Botox injection;
- neglect of hygienic facial cleansing.
Flu
Lack of sleep
Alcohol and smoking
Poor nutrition
Diabetes
Edema and contraindications for diuretics. 4 questions for a specialist
Last time we talked about allergic edema. Today it’s the turn for heart, kidney, and protein-free ones. This classification can hardly be called fully medical; it is rather philistine, however, in general terms it reflects the essence of things.
Why do edema appear in heart disease?
Cardiac edema is caused by chronic heart failure. Cardiac weakness is often the result of a previous myocardial infarction, valvular heart defects, or long-term hypertension. As a result, a certain area of the myocardium no longer takes part in contractions, the pumping function of the organ weakens, and blood stagnation occurs. Due to the action of gravity, fluid is most retained in the legs, so cardiac edema is primarily swelling of the legs that appears in the afternoon. Edema, invisible to the eye, often appears - accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity, pericardial cavity, and abdominal cavity. All this can cause shortness of breath, indigestion and create additional problems for the heart.
In the treatment of heart failure, diuretics are indispensable. Even if there are contraindications to taking diuretics, cardiologists prescribe them, as they say, for health reasons. Often, a course of treatment is carried out with powerful drugs, and “light” diuretics are prescribed for maintenance therapy.
This is the only way to achieve a significant prolongation of life and a serious improvement in its quality.
What is the difference between renal edema? How necessary is it to take diuretics for renal edema?
Renal edema is associated with the development of acute or chronic renal failure. The first often occurs during various intoxications, the second is a complication of kidney diseases (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis) and not only (hypertension, diabetes, amyloidosis, etc.). The favorite place for renal edema to appear is the face, and the time of appearance is morning, but later they can spread to the neck, arms, chest and abdomen. A symptom of renal edema can be an unmotivated increase in body weight, at the same time there is a decrease in the amount of urine excreted.
Treatment of renal edema is complex, and simulating a compromised kidney with diuretic drugs is not always beneficial. Although diuretics, both “mild” and powerful, still occupy a leading place in therapy. In addition, nephrology often uses herbal medicines - renal and diuretic decoctions, teas. Diuretic herbs for edema are very popular in folk medicine. If you take decoctions and teas as diuretics, be sure to inform your urologist about this.
If cardiac edema starts from the legs and goes from bottom to top, then renal edema, on the contrary, starts from the face and goes from top to bottom.
My husband developed edema, and the doctor recommended protein nutritional mixtures and did not even prescribe diuretics. Is he right?
Protein-free or hypoprotein edema is associated with a severe protein deficiency in the body, and, in particular, in the bloodstream. As a result, the oncotic pressure of the blood decreases, and it loses its ability to retain fluid in the bloodstream. The fluid leaves the lumen of the vessel and enters the tissue where it accumulates. Widespread systemic edema occurs, first on the feet and legs, then on the hands and neck. Anasarca often develops - swelling of the subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen. The cause of protein deficiency is most often its loss in the urine due to various kidney diseases, chronic cancer intoxication, systemic diseases, and in recent years, often fasting for the purpose of losing weight.
Taking diuretics to relieve protein edema is pointless, because their cause lies not in fluid retention, but in its improper distribution.
Therefore, it is much more important to restore the normal protein content in the body: eat well, receiving animal protein daily; if necessary, nutrient mixtures and even intravenous infusion of protein solutions are used.
In what situations can diuretics cause harm and are therefore contraindicated?
Regardless of the purpose for which diuretics are used - to stimulate the urinary function of the kidneys, correct chronic heart failure, relieve swelling or treat hypertension (one of the most common purposes when “light” diuretics are used), there are contraindications to their use.
For example, they try not to prescribe diuretics for diabetes mellitus, since many of them reduce the sensitivity of tissues to insulin. Gout and any other condition that causes elevated uric acid levels is also a factor against taking diuretics. An insufficient level of potassium in the blood is another contraindication to the prescription of diuretics - further “washing out” of potassium threatens the development of cardiac arrhythmias. On the other hand, there is a group of so-called potassium-sparing diuretics that should not be taken if potassium levels are elevated. Liver cirrhosis and liver failure are another contraindication to taking diuretics.
In most cases, when the use of diuretics is contraindicated, the use of diuretic herbal decoctions may be considered.
If you still have questions, you can ask them to a cardiologist or therapist online in the Doctis application.
How does herbal medicine work?
Herbs with a diuretic or diuretic effect have a mild effect on the human body, aimed at the pathological focus. In the absence of intolerance to any component, they have a beneficial effect on well-being. Some herbs disinfect and relieve pain, while others, by removing excess fluid with urine, act as an anti-inflammatory agent. In any case, you must first consult with your doctor which natural diuretics can be used for your diagnosis.
Diuretic herbs:
- normalize pressure, both fundus and intracranial;
- slow down the penetration of salt into the renal tubules;
- improve renal blood circulation;
- act as antioxidants;
- influence the course of epilepsy (beneficial);
- relieve muscle spasms.
Indications for taking diuretic herbs
You cannot use diuretic herbs on your own. A consultation with a nephrologist or urologist and examination to make a diagnosis are required. With long-term use of the diuretic herb, periodic replacement is necessary. The doctor should advise on the daily dosage and stages of preparing a decoction or tincture at home.
Indications for the use of natural diuretics:
- diseases of the urinary system with the presence of hypertension, inflammation, swelling;
- taking antibiotics for a long time;
- alcohol abuse, the consequences of a hangover, to remove toxic substances from the body;
- consequences of intoxication after food poisoning;
- prevention of stone formation after removal.
Decoctions and infusions are not a panacea for excess weight. Excess fat remains, only liquid leaves.
Possibilities of herbal medicine in the metaphylaxis of calcium oxalate urolithiasis
M.Yu. Prosyannikov, O.V. Konstantinova, N.V. Anokhin, D.A. Voitko
- Prosyannikov M.Yu. – Ph.D., Head. Department of Urolithiasis, Research Institute of Urology and Interventional Radiology named after. ON THE. Lopatkina – branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution “National Medical Research Center of Radiology” of the Ministry of Health of Russia, [email protected] AuthorID 791050
- Konstantinova O.V. – Doctor of Medical Sciences, Chief Researcher of the Department of Urolithiasis, Research Institute of Urology and Interventional Radiology named after. ON THE. Lopatkina - branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center of Radiology" of the Ministry of Health of Russia., AuthorID 679965
- Anokhin N.V. – Candidate of Medical Sciences, Researcher, Department of Urolithiasis, Research Institute of Urology and Interventional Radiology named after. ON THE. Lopatkina - branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center of Radiology" of the Ministry of Health of Russia., AuthorID 880749
- Voitko D.A. – Candidate of Medical Sciences, Researcher, Department of Urolithiasis, Research Institute of Urology and Interventional Radiology named after. ON THE. Lopatkina - branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center of Radiology" of the Ministry of Health of Russia., AuthorID 942353
Calcium urolithiasis is the most common form of urolithiasis (UCD). One of the characteristic features of urolithiasis is frequent relapses of stone formation processes. However, many aspects of the pathogenesis of KSD are not fully understood.
According to one of the most common theories of the pathogenesis of KSD, it is believed that the processes of lithogenesis are based on two mechanisms: the presence of Randall’s plaque in the kidney parenchyma and the presence of urine supersaturated with stone-forming substances. Randall's plaque always consists of calcium phosphate salts, and its further growth occurs due to the deposition of calcium salt crystals on the existing calcium phosphate base [1].
In this case, a prerequisite for the growth of calcium oxalate stones is the oversaturation of urine with stone-forming substances [2,3]. These include calcium, uric acid, oxalate (calcium salt of oxalic acid) [4,5]. An increased concentration of these substances leads to their precipitation, which initiates lithogenesis. The crystals gradually adhere to Randall's plaque, consisting of calcium phosphate, and urinary stone growth occurs (Fig. 1).
Specialists can prevent the process of stone formation by influencing the main stages of the pathogenesis of urolithiasis. One of the areas of metaphylaxis of urolithiasis is the impact on lipid peroxidation, as one of the causes of the formation of Randall's plaques. In this case, antioxidants are the drugs of choice [7].
In addition to influencing the formation of Randall's plaques, prevention of recurrent stone formation in urolithiasis is possible by reducing the concentration of the main stone-forming substances in the urine - calcium, oxalates, uric acid. It is known that hypercalciuria, hyperoxaluria, and hyperuricuria can initiate the formation of calcium oxalate stones [8,9].
Hyperoxaluria is one of the most common metabolic lithogenic disorders detected in calcium urolithiasis. Oxalate is an organic salt of oxalic acid. At physiological urine pH levels, oxalate forms a soluble salt with sodium and potassium. However, when combined with calcium, oxalic acid forms a water-insoluble compound - calcium oxalate [10].
There are 2 main ways in which oxalate appears in the human body: exogenous and endogenous. 85-90% of oxalate in the human body is synthesized endogenously. The pathways of oxalate metabolism in hepatocytes are presented in Figure 2. Some of the processes presented take place in peroxisomes, and some in the cytoplasm of cells. Endogenous oxalate is synthesized from 2 main sources: ascorbic acid and glyoxylate [11]. The main route of oxalate synthesis is the oxidation of glyoxylate, the main source of which is glycolate. These metabolic reactions are catalyzed by several key enzymes, including alcohol dehydrogenase 1 (ADH-1), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), hydroxy acid oxidase 1 (HAO-1), xanthine oxidase (XO), alanine glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGAT) and glyoxylate reductase (GRHPR) [11]. In addition to ascorbic acid and glyoxylate, other compounds such as various amino acids (tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine), creatinine, purines, and even glucose and other carbohydrates can serve as oxalate precursors [12,13]. Various conditions can affect the synthesis of oxalates. One of the most important parameters is the pH of the intracellular fluid. Changes in this parameter can affect enzyme activity [14].
Fig.1. Modern ideas about the pathogenesis of stone formation in urolithiasis, the formation of Randall's plaque [6] Fig.1. Modern views on the pathogenesis of stone formation in the ICD, the formation of Randall plaque [6]
Exogenous oxalate comes from food and is absorbed mainly in the large intestine. Exogenous oxalate enters the human body mainly through consumption of leaves, nuts, fruits and bark of plant products. In the modern diet, the main source of oxalate is potatoes, chocolate, and tea. Food products of animal origin practically do not contain oxalates [11]. It must be emphasized that only 2-10% of consumed oxalate is absorbed from food, while most of the oxalate (90-98%) serves as a source of nutrition for bacteria in the intestine or is excreted in the feces [15].
Rice. Pathways for the synthesis of endogenous oxalate in the body [14] 2. The synthesis of endogenous oxalate in the body [14]
The ratio of endogenous and exogenous oxalate in the body depends mainly on the patient’s diet and the amount of oxalate in the food consumed. Both the supply of exogenous oxalate and the synthesis of endogenous oxalate contribute to the maintenance of oxalate levels in the blood. Most of the blood oxalate (90-95%) is excreted from the body by the kidneys, while only 5-10% of oxalate is excreted by the intestines (Fig. 3). A certain amount of endogenous oxalate is excreted from the body along with bile. A small portion of oxalate is returned to hepatocytes, and thus constantly circulates in the body [16,17].
Rice. 3. Metabolism of oxalate in the human body [14 ] 3. Oxalate metabolism in the human body [14]
It is believed that oxalate does not play any significant role in human metabolism and is an end product of metabolism, like uric acid. If it were not for the high affinity of oxalate for calcium and the low solubility of the calcium oxalate salt, oxalate metabolism would not be of much interest. At the same time, urine oxalate is one of the significant lithogenic factors in ICD.
Filtration, reabsorption and secretion of oxalate occur in the kidneys [18]. Glomerular filtration of oxalates depends on the level of oxalates in the blood plasma. At the same time, tubular transport (reabsorption and secretion) of oxalates occurs under the influence of the transport protein SLC26A1, which ensures the absorption of oxalate into the cell through the basolateral membrane in exchange for sulfate [19]. This protein has also been shown to influence intestinal oxalate secretion, with a defect in SLC26A1 contributing to increased intestinal absorption of oxalate in the small intestine [20]. Tubular secretion and glomerular filtration have been shown to be critical in the regulation of plasma oxalate levels, as a strong correlation has been demonstrated between high plasma oxalate levels and oxalate secretion [21].
Thus, reducing the level of oxalate excretion in the urine is one of the leading values in the metaphylaxis of calcium urolithiasis.
It is possible to reduce the concentration of the main stone-forming substances in the urine in patients with urolithiasis by prescribing medications, for example, citrate mixtures, thiazide diuretics, etc. [22]. However, synthetic substances of chemical origin used in the metaphylaxis of KSD will always have a wide range of side effects. The side effects of such drugs are especially noticeable when taken for a long time, which is necessary specifically for the metaphylaxis of urolithiasis. In addition, many patients have a rather negative attitude towards the need to take non-herbal medicines for a long time.
In this situation, the prescription of herbal medicines is very justified and is an option of choice. In addition, the positive effect of many herbs on lithogenesis processes has been well studied, and the effectiveness of their use has been scientifically proven.
In the metaphylaxis of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate urolithiasis, herbal extracts of Phyllanthus niruri, Fucus vesiculosus, and Desmodium styraxolifolia have been successfully used for a long time [23,24].
Phyllanthus niruri (Fig. 4) is a tropical annual plant belonging to the Euphorbiaceae family that is found in the wild. Conducted by ND Pucci et al. in 2018, a study that analyzed data from 56 patients diagnosed with urolithiasis found that taking P. niruri for 12 weeks statistically significantly reduced urinary oxalate concentrations by 48.81% and reduced urinary uric acid levels by 70% [ 25].
ME Barros et al, in their work modeling the calcium oxalate form of urolithiasis in rats, showed that the use of P. niruri extract for 40 days reduces the weight and number of calcium oxalate stones in rats by 3.8 times. In addition, consumption of P. niruri makes the developing stones smoother in shape and less hard, which significantly facilitates their passage from the urinary tract [23].
Researchers from Brazil JL Nishiura et al. after studying the effect of taking P. niruri on the biochemical parameters of 24-hour urine in patients with calcium oxalate urolithiasis, they came to the conclusion that the plant extract normalizes calcium metabolism in patients with hypercalciuria, reducing its excretion by 41.2% [26].
Inhibitors of stone formation have a great influence on the processes of lithogenesis: citrates, magnesium, glycosaminoglycans. A reduced level of excretion of these substances is one of the main metabolic risk factors for the development of KSD [27]. AM Freitas et al. In an experiment on rats, the level of citrates, magnesium and glycosaminoglycans in urine was studied after administration of P. niruri extract to experimental animals. The scientists found that urinary citrate and magnesium levels did not increase with P. niruri supplementation. However, the level of excretion of glycosaminoglycones increased statistically significantly, which confirms the ability of P. niruri to prevent the development of KSD [28].
The administration of P. niruri has a positive effect on the passage of urinary stones in the early postoperative period after lithotripsy. According to a study conducted by S. Micali et al., regular intake of P. niruri after external lithotripsy of the lower calyx of the kidney statistically significantly increases the frequency of spontaneous passage of urinary stone fragments compared with similar indicators in patients from the control group (p = 0.01) [ 29].
Thus, the effectiveness of the use of P. niruri has been proven, both in the metaphylaxis of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate urolithiasis, regardless of the identified metabolic lithogenic disorders, and in the early postoperative period after crushing urinary stones to increase the effectiveness of lithokinetic therapy.
The herb extract Fucus vesiculosus (Fig. 5) is successfully used to treat patients not only with urolithiasis, but also with many other diseases. Fucus vesiculosus - brown algae - is a multicellular plant more than a meter in length, growing in the form of a bush. Grows on rocky sea soil. In the Russian Federation it is found on the coast of the northern seas (Baltic, Barents, White, etc.).
According to N.A. Fucus vesiculosus in the concentration range from 40 to 1000 mg/ml exhibits antimicrobial activity against both gram-positive cocci and gram-negative enterobacteria [30]. The antimicrobial activity of Fucus vesiculosus is associated with the presence of flavonoids and other compounds in the algae [31].
Rice. 4. Phyllanthus niruri
Rice. 5. Fucus vesiculosus
Rice. 6.Desmodium styracifolium
Data from N.A. Boev is confirmed by the results of A.P.’s study. Godovalova et al. In their work, the authors also came to the conclusion that the infusion of Fucus vesiculosus has antistaphylococcal activity and an antibacterial effect against representatives of the intestinal microflora [32].
Moreover, Russian scientists E.V. Zhurishkina et al. showed that the effect of fucoidan, which is contained in the cell walls of brown algae, on malignant cells leads to the induction of apoptosis and disruption of the cell cycle of tumor cells [33].
Thus, Fucus vesiculosus is a plant that exhibits diverse biological activities: antitumor, antibacterial, antiviral, anticoagulant, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory [34].
The use of Fucus vesiculosus in urolithiasis is due to its effect on metabolic lithogenic processes. It has been proven that fucoidan helps reduce the concentration of oxalate in the urine by 3.72 times, reduces the excretion of calcium in the urine by 83%, reduces the excretion of phosphates by 34.2%, increases the level of urinary excretion of citrates by 25.4% and glycosaminoglycones by 3. 17 times [35].
Moreover, it has been proven that Fucus vesiculosus reduces the concentration of one of the markers of lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress, malondialdehyde, in rats with simulated calcium oxalate urolithiasis compared to the control group [36].
Desmodium styracifolium (Fig. 6) is a herbal remedy traditionally used in Chinese medicine for the treatment of urolithiasis and officially registered in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia [37]. In vitro studies have confirmed that D. styracifolium reduces the risk of relapse of calcium oxalate urolithiasis by inhibiting the growth and aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals [38].
Researchers from China Jun Mi et al. studied the effect of D. styracifolium on rats in a simulated ethylene glycol model of urolithiasis. The authors found that the use of D. styracifolium extract in medium and high doses increases the level of citrate excretion in the urine, reduces the content of total calcium in the urine, and stimulates an increase in diuresis. It should be emphasized that when taking D. styracifolium, a decrease in the level of malondialdehyde, a secondary product of lipid peroxidation, was observed in the blood of experimental mice [39]. Thus, D. styracifolium extract slows down the processes of lipid peroxidation and inhibits the initiation of stone formation processes.
One of the herbal medicines that combines extracts of the above-described plants is the biologically active food additive “Oxalit” (hereinafter referred to as the Drug), produced by “SH PHARMA”, Russia. The drug contains extracts of the herbs Fucus vesiculosus, Phyllanthus niruri and Desmodium styraxolifolia.
The use of the drug is justified in patients with urolithiasis when hyperoxaluria and hypercalciuria are detected in a biochemical analysis of urine. In addition, the proven antioxidant properties of the D. styracifolium extract, the identified inhibitory activity of P. niruri, and the antibacterial effect of Fucus vesiculosus allow the drug to be prescribed for the metaphylaxis of KSD, including the idiopathic form of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate urolithiasis.
One of the options for using the Drug is its use to improve lithokinetic therapy after a session of external lithotripsy.
As noted, P. niruri extract stimulates the passage of fragments of urinary stones after lithotripsy sessions.
The above-described effects of active substances suggest the possibility of their use in the anti-relapse treatment of patients with urolithiasis. The use of preparations containing extracts of Phyllanthus niruri, Fucus vesiculosus and Desmodium styracifolium can be an addition to the traditional conservative therapy described in various national recommendations, approved for use in calcium oxalate urolithiasis. To assess the complex effect of all the described components on the metabolism of a patient suffering from urolithiasis, as well as to determine their role in the metaphylaxis of urolithiasis, further clinical studies are necessary.
LITERATURE
- Taylor ER, Stoller ML. Vascular theory of the formation of Randall plaques. Urolithiasis 2015;43(Suppl 1):41-5. doi:10.1007/s00240-014-0718-4.
- Pak CY, Sakhaee K, Moe OW, Poindexter J, Adams-Huet B, Pearle MS, et al. Defining hypercalciuria in nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 2011;80(7):777-82. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.227. Epub 2011 Jul 20.
- Pearle MS, Lotan Y. Urinary lithiasis: etiology, epidemiology and pathogenesis. Campbell-Walsh Urology, ninth edition. [Edit. Alan J. Wein]. Philadelphia, PA, 2007 2: 1363-1392.
- Petrov S.B., Levkovsky S.N., Levkovsky N.S. Saturation of urine with poorly soluble stone-forming compounds in healthy people and patients with urolithiasis. Clinical Pathophysiology 2004;(2):28-33. [Petrov SB, Levkovskiy SN, Levkovskiy NS Saturation of urine with slightly soluble stone-forming compounds in healthy and urolithiasis patients. Klinicheskaya pathofiziologiya=Clinical pathophysiology 2004 2: 28-33. (In Russian)].
- Türk C, Petřík A, Sarica K, Seitz C, Skolarikos A, Straub M, Knoll T. Guidelines on Diagnosis and Conservative Management of Urolithiasis. Eur Urol 2016;69(3):468-74. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.07.040
- Bird VY, Khan SR. How do stones form? Is unification of theories on stone formation possible? Arch Esp Urol 2017;70(1):12–2
- Kizivat T, Smolić M, Marić I, Tolušić Levak M, Smolić R, Bilić Čurčić I et al. Antioxidant Pre-Treatment Reduces the Toxic Effects of Oxalate on Renal Epithelial Cells in a Cell Culture Model of Urolithiasis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(1):E109. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14010109
- Konstantinova O.V. Prediction and principles of prevention of ICD. dis. ... MD M.: 1999. M., 2000, 234 p. (In Russian)].
- Pearle MS, Goldfarb DS, Assimos DG, Curhan G, Denu-Ciocca CJ, Matlaga BR et al. Medical management of kidney stones: AUA guideline. J Urol 2014;192(2):316-24. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.05.0062015
- Bhasin B, Urekli HM, Atta MG. Primary and secondary hyperoxaluria: understanding the enigma. World J Nephrol. 2015;4(2):235-44. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.235..
- Shekarriz B, Schwartz BF, Stoller ML, Terries MK, Talavera F. Hyperoxaluria [Electronic resource]. Jun, 2021. Available at: Emedicine.medscape.com
- Hagler L, Herman RH. Oxalate metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 1973;26:758-65.
- Yanagawa M, Maeda-Nakai E, Yamakawa K, Yamamoto I, Kawamura J, Tada S, Ichiyama A. The formation of oxalate from glycolate in rat and human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1990;1036:24-33.
- Brzica H, Breljak D, Burckhardt BC, Burckhardt G, Sabolić I. Oxalate: from the environment to kidney stones. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 2013;64(4):609-30. doi: 10.2478/10004-1254-64-2013-2428
- Chen Z, Ye Z, Zeng L, Yang W. Clinical investigation on gastric oxalate absorption. Chin Med J 2003; 116:1749-51.
- Williams AW, Wilson DM. Dietary intake, absorption, metabolism and excretion of oxalate. Semin Nephrol 1990;10:2-8.
- Hautman RE. The stomach: a new and powerful oxalate absorption site in man. J Urol 1993;149:1401-4.
- Knight TF, Sansom SC, Senekjian HO, Weinman EJ. Oxalate secretion in the rat proximal tubule. Am J Physiol 1981;240:295–298
- Mount DB, Romero MF. The SLC26 gene family of multifunctional anion exchangers. Pflugers Arch 2004;447:710–721
- Jiang Z, Asplin JR, Evan AP, Rajendran VM, Velazquez H, Nottoli TP et al. Calcium oxalate urolithiasis in mice lacking anion transporter Slc26a6. Nat Genet 2006;38(4):474
- Bergsland KJ, Zisman AL, Asplin JR, Worcester EM, Coe FL. Evidence for net renal tubule oxalate secretion in patients with calcium kidney stones. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2011;300:311–318
- Jung H, Andonian S, Assimos D, Averch T, Geavlete P, Kohjimoto Y, et al. Urolithiasis: evaluation, dietary factors, and medical management: an update of the 2014 SIU-ICUD international consultation on stone disease. World J Urol 2017;35(9):1331-1340. Doi: 10.1007/s00345-017-2000-1
- Barros ME, Lima R, Mercuri LP, Matos JR, Schor N, Boim MA Effect of extract of Phyllanthus niruri on crystal deposition in experimental urolithiasis. Urol Res 2006;34(6):351-7
- Coothan KV, Anthony J, Sreenivasan PP, Palaninathan V. Physico-chemical alterations of urine in experimental hyperoxaluria: a biochemical approach with fucoidan J Pharm Pharmacol 2007;59(3):419-27
- Pucci ND, Marchini GS, Mazzucchi E, Reis ST, Srougi M, Evazian D, et al. Effect of phyllanthus niruri on metabolic parameters of patients with kidney stone: a perspective for disease prevention. Int Braz J Urol 2018;44(4):758-764. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0521
- Nishiura JL, Campos AH, Boim MA, Heilberg IP, Schor N. Phyllanthus niruri normalizes elevated urinary calcium levels in calcium stone forming (CSF) patients. Urol Res 2004;32:362–366. doi: 10.1007/s00240-004-0432-8
- Robertson WG. Do “inhibitors of crystallization” play any role in the prevention of kidney stones? A critique. Urolithiasis 2017;45(1):43-56. doi: 10.1007/s00240-016-0953-y.
- Freitas AM, Schor N, Boim MA. The effect of Phyllanthus niruri on urinary inhibitors of calcium oxalate crystallization and other factors associated with renal stone formation. BJU In. 2002;89(9):829-34
- Micali S, Sighinolfi MC, Celia A, De Stefani S, Grande M, Cicero AF, Bianchi G. Can Phyllanthus niruri affect the efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for renal stones? A randomized, prospective, longterm study. J Urol 2006;176(3):1020-2
- Boev I.A. Antimicrobial activity of marine brown algae. Science and innovation of the 21st century. Materials of the III All-Russian Conference of Young Scientists. 2021 Publisher: Surgut State University (Surgut). pp. 105-107. .
- Cushnie TP, Lamb AJ. Recent advances in understanding the antibacterial properties of flavonoids Int. Antimicrobial Agents. 2011. Vol. 38. P. 99 107
- Godovalov A.P., Bykova L.P. Antimicrobial activity of some plant derivatives. Modern scientific research and development 2017;2(1):58-61 (In Russian)].
- Zhurishkina E.V., Stepanov S.I., Shvetsova S.V., Kulminskaya A.A., Lapina I.M. Comparative analysis of the effect of fucoidan from the algae Fucus vesiculosis and fractions obtained from it using anion exchange chromatography on HeLa G-63, Hep G2 and Chang liver cells. Cytology 2017;59(2): 148-155.
- Cumashi A, Ushakova NA, Preobrazhenskaya ME, D'Incecco A, Piccoli A, et al. A study comparative of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007;17(5):541-52.
- Coothan KV, Anthony J, Sreenivasan PP, Palaninathan V. Physico-chemical alterations of urine in experimental hyperoxaluria: a biochemical approach with fucoidan J Pharm Pharmacol 2007;59(3):419-27
- Veena CK, Josephine A, Preetha SP, Varalakshmi P, Sundarapandiyan R. Renal peroxidative changes mediated by oxalate: the protective role of fucoidan. Life Sci 2006;79(19):1789-95.
- The State Pharmacopoeia Committee of China Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People's Republic of China, 2005, vol.1. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing
- Gohel MD, Wong SP. Chinese herbal medicines and their efficacy in treating renal stones. Urol Res 2006;34(6):365–372. doi: 10.1007/s00240-006-0068-y
- Jun Mi, Jianmin Duan, Jun Zhang, Jianzhong Lu, Hanzhang Wang, et al. Evaluation of antiurolithic effect and the possible mechanisms of Desmodium styracifolium and Pyrrosiae petiolosa in rats. Urol Res 2012;40(2):151-61. doi: 10.1007/s00240-011-0401-y
The article was published in the journal “Experimental and Clinical Urology” No. 3 2021, pp. 104-108
Topics and tags
Urolithiasis disease
Magazine
Journal "Experimental and Clinical Urology" Issue No. 3, 2019
Comments
To post comments you must log in or register
Contraindications for taking diuretic herbs
A preliminary consultation with a specialist is required if there is swelling; the use of diuretic herbs is not recommended for children, pregnant women and the elderly.
Absolute contraindications for the following diagnoses:
- disturbances in the outflow of bile;
- kidney damage or nephrosis;
- diabetes;
- gout;
- kidney stones, especially large ones;
- deficiency of zinc, potassium;
- state of acute renal failure.
Also, do not forget about allergic reactions of individuals to individual components.
When purchasing medicinal herbs, pay attention to the expiration date. Use without violating them, because the usefulness of the product becomes imaginary, now it may contain components harmful to health.
You can collect the necessary herbs yourself, following all the necessary rules for drying and proper storage.
Side effects
By using diuretic herbs for swelling uncontrollably, there is a risk that symptoms of dehydration may appear:
- general malaise, weakness;
- headache;
- allergic reactions;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- constant thirst;
- broken stool;
- convulsive conditions of the lower extremities;
- reluctance to eat;
- hormonal imbalance;
- cardiopalmus;
- impossibility of emptying the bladder when the urge appears.
It is important to note that the appearance of even one of the signs described above should serve as a reason to stop taking the herbal mixture. A more complex case may even require emergency assistance from specialists. Taking decoctions and infusions while expecting a baby, depending on the timing, can provoke a miscarriage or the threat of a frozen pregnancy.
Causes of edema during pregnancy
Expecting a child is a period when many body systems rearrange their work. Not only does a woman’s body change, the load on organs and systems and the features of their functioning change. These factors influence the accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the expectant mother and the formation of edema.
Changing your diet. It is known that the tastes of pregnant women change: many begin to eat salty and spicy foods. Salt retains water, so you need to carefully monitor your diet.
Weight gain. The uterus grows in size and puts pressure on the vessels, which leads to fluid retention.
Varicose veins This is a common cause of swelling of the lower extremities during pregnancy. Expectant mothers, unfortunately, often encounter vein problems. This may be due to weight gain, increased blood flow, hormonal changes affecting blood vessels, etc. Pregnant women are recommended to undergo regular examinations with a phlebologist, who will give recommendations not only during pregnancy, but also during childbirth, when the veins are under increased stress.
Changes in kidney function. Often they may not be able to cope with the increase in the volume of fluid circulating in the body. To check your kidney function, be sure to see your doctor.
Please note : the cause of edema during pregnancy can be disturbances in the functioning of various organs and systems. In particular, the cardiovascular system and the thyroid gland. Therefore, if the expectant mother notices the accumulation of fluid, she needs to inform the attending physician about this in order to exclude serious pathologies.
The most popular plants
Parsley seeds
Parsley is used in the treatment of swelling and has proven itself to be an effective and gentle remedy. The use of infusions and decoctions will remove excess fluid and harmful substances from the human body. By adding parsley, roots or seeds, you can prevent the occurrence of edema. The plant contains a large amount of flavonoids. These are antioxidants that fight the effects of free radicals on the body: they prevent the accumulation of excess fluid and tone tissues and cells.
Parsley seeds
Celery
The juice of the plant contains a large amount of minerals, almost all the vitamins necessary to maintain the human body in a healthy state. Traditional medicine uses celery to treat edema. Sodium, potassium and magnesium, which maintain water-salt balance, are contained in the juice of the plant. When consuming celery, the liver and kidneys are stimulated and the elimination of toxic substances is accelerated. Excess water is released from the body and the normal ratio of fluid in the interstitial space and tissues is restored. Scientists who have conducted research on the plant are confident that its action can be compared to ginseng.
Celery should not be taken by both pregnant and nursing mothers. The specific taste of breast milk depends on it and its production decreases.
Celery
Anise
It is used when it is necessary to remove swelling due to pathologies of the urinary tract. To prepare the infusion, you need to take only raw seeds. Pour two liters of boiling water over a teaspoon of raw materials. Leave for 3 days. Before each meal you should take a tablespoon. The seeds will help relieve swelling and normalize metabolism. Anise should not be used by pregnant women.
Anise
Linen
The fastest acting remedy. The patient feels the urge to urinate after the first intake of flax. In just 1-2 days, the fluid that caused the swelling can be removed from the body. The decoction is prepared from 3 tablespoons of flax seeds, which are poured with a liter of boiling water. The mixture should brew. If the resulting decoction is too bitter, add a little honey or a few drops of lemon juice to it. Treatment with seeds should be carried out when it is possible to be at home, since flax is a very strong natural diuretic.
Linen
Lingonberry leaves
Lingonberry leaves are saturated with minerals and vitamins: calcium, potassium, sodium, phosphorus, C, B. It is used as a prophylactic, immunostimulant and for the treatment of vitamin deficiency. The flavonoids that make up the plant have a positive effect on blood vessels, tone them, and normalize blood pressure. Protein, which is easily digestible, will help during rehabilitation after poisoning, after serious illnesses and a strict diet. All substances are antioxidants. They protect the cells of the human body from the effects of free radicals, which disrupt the process of normal tissue reproduction and accelerate aging.
Lingonberry leaves
Shepherd's Purse
The plant has astringent and anti-inflammatory properties.
Using shepherd's purse externally, as a lotion, relieves swelling, reduces inflammation, and can stop the bleeding of small wounds on the mucous membranes and on the surface of the skin. The use of medicinal herbs helps with the removal of stones, with diseases of the excretory system, and is used for inflammatory, severe processes. Shepherd's purse has a vasodilator, diuretic, and antifever effect. The plant normalizes sleep, has a calming effect and counteracts depression and stress. Traditional medicine uses shepherd's purse to cleanse the liver, kidneys, gall bladder, and for the heart muscle - as an additional vitamin.
Shepherd's Purse
List of other diuretic herbs
For convenience, diuretic herbs are divided into categories depending on their effect.
Medicinal fees
Among the medicinal fees, the following can be distinguished:
- Diuretic collection No. 1. Contains bearberry, cornflower and licorice in a 3:1:1 ratio. Removes moisture, destroys germs and suppresses infections.
- Diuretic collection No. 2. Contains licorice, bearberry and cornflower. The drug helps relieve pain in kidney pathologies and reduces foci of inflammation.
- Diuretic collection No. 3. Contains horsetail, juniper and wheatgrass root. The product is potent, so it is used with caution. Most often, the collection is prescribed to patients suffering from an allergy to licorice root.
- Collection of herbs No. 6. Contains lemongrass, corn silk, horsetail and chamomile. Helps restore water-salt balance.
Diuretic herbal mixtures are presented in various combinations.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Relieving inflammation helps reduce pain due to pathologies of the urinary system.
This is useful for cystitis and pyelonephritis. Internal swelling disappears due to the elimination of stagnation and excessive blood flow to the damaged area. The most powerful anti-inflammatory diuretics are the following herbs:
- burdock root;
- pink radiola;
- stinging nettle;
- lingonberry leaves;
- parsley;
- corn silk;
- marshmallow
For hypertension and heart failure
For hypertension, it is advisable to take herbs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels. This promotes proper blood circulation and helps the cardiovascular system withstand high stress without side effects.
Herbal tea for hypertension strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
For heart failure and hypertension, the following herbs and berries are brewed:
- shepherd's purse;
- red rowan;
- swampy dried grass;
- barberry roots;
- motherwort;
- mint;
- lemon balm.
For facial swelling
If you experience frequent swelling of the face, it is recommended to pay attention to the symptom. Its location indirectly indicates the source of the problem. For example, swelling in the upper lip or brow ridges indicates cardiac pathology.
Swelling of the eyelids is a sign of kidney disease.
The following remedies help with facial swelling:
- half fell;
- flax seeds;
- beet leaves;
- corn silk.
A decoction of corn silk will eliminate swelling on the face.
For the kidneys
For infectious pathologies of the urinary system, horsetail and knotweed are used. Herbs increase fluid circulation, prevent congestion, destroy bacteria, and relieve inflammation from damaged tissues.
For swelling of the legs
Swelling of the legs is most often observed due to impaired lymph outflow, pathology of the liver, heart, thyroid gland, and renal failure.
To improve the condition, use chamomile, horsetail, bearberry, nettle or lemon balm.
For weight loss
Diuretic herbs are used as an adjuvant. On their own, they will not provide sustainable weight loss, but they can improve the results of diet and exercise. For weight loss, horsetail, bear ears, and lingonberry leaves are used. The latter are the mildest and safest remedy.
Natural diuretics for facial swelling
The following plants:
- flax seeds;
- half fell;
- corn silk;
- beet leaves.
flax seeds
Half-fallen
Corn silk
Beet leaves
Herbs for swollen legs
Horsetail
Eating horsetail helps eliminate the problem of protein in urine. The plant stimulates urination and disinfects the urinary tract. Herbal decoctions help relieve swelling of the heart and kidneys. Along with the diuretic effect, an analgesic effect was also detected. Horsetail has long been used in the treatment of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system, internal bleeding, and the presence of kidney stones.
In case of exacerbation of diseases of the stomach or intestines, it is better to consult a doctor. The use of herbal infusion is not recommended for nephrosis, nephritis, pregnant women, and children. Adverse reactions are extremely rare. Long-term, improper use of medicinal herbs can provoke digestive upset and allergic reactions.
Horsetail
Chamomile
Chamomile has not only a diuretic effect, but also analgesic, anti-inflammatory, choleretic, carminative, astringent, sedative, antispasmodic and antiallergic. The plant contains chamazulene. It is this substance that calms the nervous system, stimulates brain function, activating blood circulation in the brain vessels, and has a beneficial effect on the digestive organs.
Chamomile has a calming, positive effect on all skin types, therefore it relieves various inflammations and itching, helps eliminate swelling and redness. During pregnancy, use is prohibited, and when breastfeeding, use must be approached with caution. Before using chamomile infusions and decoctions, it is necessary to consult a doctor for those people who take vital medications and those who have chronic diseases. If you are hypersensitive, do not use the plant for treatment.
Chamomile
Bearberry
The plant has a powerful diuretic effect. To prepare the decoction, pour a teaspoon of leaves into 100 ml of boiling water and simmer over low heat for up to half an hour. Then strain, add another 100 ml of boiled water to the broth. Use 40 minutes before meals, 1 tablespoon, 6 times a day.
Bearberry
Nettle
Dried and fresh stems, leaves and oil are used as a diuretic.
- Nettle massage oil: to prepare it, chop fresh leaves and mix with sunflower oil in the same ratio. Then the resulting mass is heated in a water bath until it boils. When cooled, rub into the skin of the feet.
- An infusion of a mixture of herbs and nettles: mix equal parts of nettle leaves, St. John's wort and chamomile (1 tsp each), then pour boiling water over it and let steep for 1 hour. Next, divide the infusion into 5 parts, take before meals during the day.
Nettle
Melissa
The herb is a strong natural diuretic. Reduces pain symptoms in pathologies of the excretory system, urolithiasis. Relieves inflammatory processes, the presence of intoxication, improves the acidity of urine. To prepare the decoction, pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of dry stems and leaves of the plant, boil for 10 minutes and strain. Take 1 tablespoon before meals.
Melissa
List of the best diuretic herbs
The list of the best diuretic herbs includes milk thistle, thyme, calendula, horsetail, bearberry, etc. They differ in their effects and dosages.
Milk thistle
Milk thistle not only has a diuretic effect, but also cleanses the liver of toxins, accelerating cell regeneration. In the pharmacy the product can be found in the form of seeds, powder or meal. The first option is preferable, but you will have to grind the grains yourself to release the active substances. 2 tsp. raw materials pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, cover and leave for 15 minutes. Then the liquid is drained and drunk up to 3 times a day, regardless of meals.
Thyme
Thyme stimulates urination, relieves pain and inflammation, and destroys bacteria. It stimulates the digestion of food and, in case of pulmonary diseases, facilitates the removal of fluid from the bronchi. To prepare the medicine 1 tbsp. l. dried herbs, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes and filter. The product is drunk half an hour before meals, up to 4-5 times a day.
Thyme removes water and toxic substances from the body.
Calendula
Calendula relieves swelling and inflammation, destroys bacteria and viruses, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, and also activates regeneration processes. To brew tea, 2 tbsp. l. inflorescences are poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. Cover the container with a lid and place in a dark place for 15 minutes. At the end, the liquid is filtered. Drink 100 ml of tea up to 3 times a day.
Horsetail
Horsetail enhances fluid removal, stops bleeding, enhances tissue regeneration and relieves inflammation. The plant has an antimicrobial effect, improves the condition of the renal ducts and vascular walls, which is most useful for cystitis and pyelonephritis. The medicine is prepared from 4 tbsp. l. dry horsetail. It is poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water and left for 20 minutes. The product is drunk warm. Dosage - 2 tbsp. l. infusion up to 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Bearberry
Bearberry helps remove excess moisture from the body by irritating the kidney tissue. The product has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. To prepare the decoction 1 tbsp. l. dry leaves are ground to a powder. 250 ml of hot water is poured into the mass. The mixture is placed in a water bath for 20 minutes, then allowed to brew for 40 minutes and filtered. After this, the volume is adjusted to the original volume by adding water. The drug is taken 50 ml half an hour after meals up to 3 times a day.
Bearberry normalizes metabolism and eliminates swelling.
Rose hip
Rosehip not only removes moisture from tissues, but also has an anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effect. It protects the kidneys and liver, prevents the development of cancer, and heals wounds. 1 tbsp. l. The berries are passed through a meat grinder, placed in a saucepan and poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. Cover the container with a lid and steam for 30 minutes. Then filter the liquid, pour in another 2 cups of boiling water and leave again for half an hour. Ready-made tea is drunk up to 3-4 times a day, 250 ml.
Nettle
Nettle has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. It stops bleeding, normalizes the activity of the immune system, blood sugar and cholesterol levels. The product reduces pain in the back, neck and lower back, cleanses the body of toxins. The decoction is prepared from 1 tbsp. l. leaves and 1 tbsp. water. The mixture is brought to a boil. Leave the container under a towel in a warm place for 1 hour. The finished broth is filtered. Take up to 1-2 glasses daily; for internal bleeding, the portion is increased to 1 liter.
Chamomile
Chamomile is not only a diuretic, but also an antispasmodic. This helps ease urination during cystitis. The product relieves inflammation, calms a person, dilates blood vessels, improves blood circulation. The infusion is prepared from 2 tbsp. l. inflorescences and 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture is left covered until completely cooled. The finished product is taken 1 tbsp. before meals up to 3 times a day.
Chamomile decoction is used in the treatment of many diseases, including cystitis.
Birch
Birch leaves are a natural diuretic, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent. They are often used for inflammatory pathologies of the urinary system. A decoction is prepared from 2 tsp. crushed leaves and 200 ml of hot water. The product is infused for 20 minutes, then filtered. Take 100 ml before meals twice a day.
Linden
Linden normalizes digestion, removes moisture through the bladder and skin pores, and reduces body temperature. A compress of flowers relieves headaches and treats burns. 1 tbsp. l. dried raw materials are poured with 200 ml of boiling water. The product is drunk warm before meals. This is done 2-3 times a day.
Valerian
Valerian is a weak diuretic. It copes better with edema than with cystitis or pyelonephritis. However, the plant has a beneficial effect on the heart. It is recommended to be used together with other herbs. You can add mint in a 1:1 ratio. 1 tbsp. l. collection pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, drink 200 ml once a day.
Motherwort
Motherwort has general strengthening properties. It improves the condition of the immune and nervous system, relieves swelling, relieves cramps, cough and inflammation. The product reduces pain. 1 tbsp. l. motherwort is poured with 300 ml of boiling water. The finished infusion is drunk 150 ml twice a day.
Motherwort decoction is used to treat diseases of the nervous system.
Mint
Mint not only helps remove moisture, but also disinfects tissues. It helps with flu and colds, relieves pain, and improves digestion. Tea is prepared from mint: 2 tsp. crushed raw materials, pour 200 ml of boiling water for 20 minutes. After filtering, drink the product up to 2-3 times a day.
Oregano
Oregano is often used in gynecology. It normalizes hormonal levels, protects the genitourinary system from tumors, and relieves inflammation. Men treat urethritis, prostatitis and infections with oregano. Tea is prepared from 2 tsp. dry herbs and 250 ml of hot water. The mixture is infused for half an hour. It is drunk before meals or between meals, 50-100 ml three times a day.
The course of treatment should not exceed 1 week.
Herbal diuretic tablets
Taking medications to relieve swelling is necessary. They remove excess exudate, which is located in the subcutaneous tissue and puts pressure on the nerve endings. As a result, severe pain occurs.
Herbal diuretic tablets
Name and effect of the medicine:
- Flaronin. It has a powerful diuretic effect and improves blood circulation in the kidneys. Used for a month, 3 times a day.
- Lespenefril. Increases filtration in the renal tubules, reduces the ratio of nitrogenous substances in the blood, improves urination. Indicated for use in kidney diseases. Available in tincture form.
- Aflazin or hibiscus extract. Has anti-inflammatory, diuretic effect. Do not use for children under 6 years of age and pregnant women. Allergic reactions are possible.
- Phytolysin. Without chemical components, plant based, available in the form of a paste. For use: dissolve 0.5 teaspoon in a glass of warm water. Apply 3 times a day.
Flaronin
Lespenefril
Aflazin
Phytolysin
Rules for preparing herbs
Decoctions
It is recommended to consume all decoctions and infusions before 16:00. This advice is necessary because there will be no regular toilet visits due to the diuretic effect of the herbs, which will allow you to get a good night's sleep. It is also recommended to follow all doctor’s orders and take into account that diuretics have a cumulative effect. Therefore, the first results can be expected only some time after the start of regular treatment.
Sodium, potassium, and all electrolyte levels should be checked during recommended therapy.
Tea
Drinking tea as a medicinal product is recommended after lunch, when the gastrointestinal tract is in the active phase. It is prohibited to independently select drinks for the elderly, children and pregnant women. If you drink tea for a long time, you need to change its composition and first consult a doctor. To avoid dehydration, you need to drink more clean water.
Infusions
Herbs that have a diuretic effect are used as a basis for preparing tinctures with alcohol or vodka. The raw materials must be thoroughly washed and crushed. Fill a container with a lid two-thirds full with herbs. Then add high-quality vodka or alcohol. Infuse for a month. Store in a dark place. If you experience pain in the kidneys or in the heart area, allergic reactions, unstable blood pressure (jumps), you should stop taking the herbal mixture and consult a specialist for medical help.
Ice
Frozen herbal infusions have a deep effect on the skin, moisturize it and provide it with nutrients. Apply these ice cubes in the morning and rub the face for 3 minutes. After the ice procedure, you need to apply cream.
For dry skin, dilated blood vessels, inflammation and scratches, frozen infusions should not be used. It is also not recommended to use ice before going outside in the winter.
How to prepare: for the decoction it is better to use water, having previously filtered it. Pour the infused broth into ice molds and let it harden in the freezer.
note
Complaints that the legs swell during pregnancy are perhaps the most common complaints that doctors who observe the expectant mother hear.
And here you need to know a number of important nuances. Edema during pregnancy can be hidden or obvious. A woman can easily identify obvious swelling: during pregnancy, ankles swell, marks from the elastic bands of socks or knee socks remain on the legs for a long time, shoes are difficult to put on. But with hidden edema, the situation is more complicated: they do not immediately attract attention, so the woman takes measures late to get rid of them. The expectant mother needs to keep an eye on the following points:
- weight increases by more than 300-400 grams per week
- Ankle circumference increases approximately 1 cm per week
- the volume of fluid excreted is less than 75% of the volume of fluid consumed (measurements are usually made in a medical facility)
Also, to detect edema, the doctor can conduct a blister test, in which a saline solution is injected under the skin on the arm, and the presence of internal edema can be judged by the speed of its resorption.
Please note: a pregnant woman should also carefully monitor the location of swelling. Unfortunately, swelling of the legs occurs in almost all expectant mothers. However, if they begin to spread higher, moving to the stomach, chest, face, you need to urgently consult a doctor!
Other anti-edema remedies
To take all medications for edema, you must consult a doctor. You need to make sure that the composition does not contain parabens, fragrances, dyes, animal or mineral fats. Such substances can accumulate and cause harm to the body. Problem areas with swelling should be treated twice a day, in the evening two hours before bedtime. Cleanse facial skin, remove makeup. Do not stretch the skin, rub the eyelids, put pressure on the eye area, or apply medications to the edge of the eyelid.
Ointments and gels
Blepharogel is the most popular.
It contains hyaluronic acid and aloe juice, glycerin. These substances help remove puffiness, fine wrinkles, moisturize the skin, and heal small wounds. Heparin ointment, in addition to its main use, is used by cosmetologists. The components included in its composition promote the resorption of bruises and bruises under the eyes, and reduce wrinkles.
Traumeel is a homeopathic ointment. Chamomile, belladonna, arnica, witch hazel, which are part of it, have a regenerating and calming effect
Troxevasin - gel. Can be used as a remedy against edema, promotes the resorption of hematomas.
Troxerutin. Decongestant, anti-inflammatory, venotonic, angioprotective and antioxidant agent.
Blefarogel
Heparin ointment
Traumeel
Troxevasin
Troxerutin
Cosmetical tools
The line of cosmetics for bags and puffiness under the eyes is presented in the form of firming or moisturizing creams that are applied under basic makeup. There are also cooling ointments and creams for the delicate area around the eyes. Before the first use of care products, it is necessary to conduct a test to exclude the occurrence of allergic reactions. You need to apply a small amount of cream or ointment to your wrist and observe for half an hour. The lack of reaction makes it possible to use the care product. If allergies occur, it should not be used.
Cosmetic masks help eliminate swelling. You can choose one that suits you, both in a pharmacy and in a chain of stores. Massaging the area around the eyes and the entire face will help cope with swelling. It improves skin elasticity, reduces muscle tension, promotes tissue regeneration and activation of cellular metabolism, and eliminates swelling of the eyelids. Massage should be carried out after cleansing the facial skin with special products. After the procedure, apply cream or use a mask.