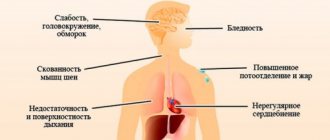
Cardiovascular diseases have remained the leading cause of death worldwide for centuries. An average of 17 million people die from CVDs every year. The scientific community claims that the situation will worsen and the number of victims will rapidly increase. In order to protect your body as much as possible and stop illnesses in a timely manner, you should regularly visit a doctor and undergo diagnostics. MRI examination is considered modern, informative and accurate. How often should a study be carried out, does the magnetic field affect the human body and what do you need to know about cardiac tomography?
Specifics of the scanned area
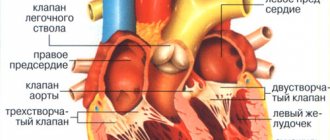
MRI involves scanning the entire cardiovascular system, and not just a separate organ. The heart is a fibromuscular organ that is responsible for the flow of blood through the blood vessels. This is possible through constant rhythmic contractions followed by relaxation (the combination of actions creates a cardiac cycle).
Content:
- Specifics of the scanned area
- The principle of operation of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner
- Virtual endoscopy
- Contrast tomography
- Indications and contraindications for the procedure
- How does a heart and blood vessel scan work?
- Methodology
The heart of vertebrate living organisms consists of endothelium, cardiac and connective tissue. In this case, the cardiac muscle is distinguished as a special type of striated muscle tissue, since it is found only in the heart.
The average person's heart beats 72 times per minute. Over 66 years, the organ will complete approximately 2.5 billion cardiac cycles of contraction and relaxation.
The MRI scanner faces a difficult task. The equipment must record several types of tissues and differentiate them.
Moreover, the organ is in constant motion, which also affects the scanning performance. How exactly is the diagnosis carried out and how informative are the resulting images?
The principle of operation of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner
The operating principle of MRI is based on the study of the magnetic properties of human tissues that are saturated with hydrogen. It is known that a person consists largely of water, and it contains elementary particles protons.
If you place a proton in a powerful magnetic field, the particles will change their spatial orientation and begin to emit radio waves with different intensities and frequencies. The MRI machine is this powerful magnetic field. Moreover, it detects radio waves, calculates the location of the protons to which they are attached, and therefore finds the hydrogen atom itself.
Modern tomographs are equipped with sources of strong magnetic fields, which improves diagnostic information. In medical practice, both permanent neodymium and electromagnets operating in liquid helium are used.
They differ in the strength of the magnetic field. In constants it reaches up to 0.7 Tesla, in electromagnets - from 1 to 3 Tesla. Typically, the accuracy of MRI images is identical when using different sources.
Only the “response” of the tissues to the study differs. The quality of the picture largely depends on the settings and size of the equipment. For cardiac tomography, only electromagnets from 3 Tesla are ideal.
Indications
The main indication for the study is the need for detailed visualization of the circulatory organs in the event of an inaccurate result of cardiac ultrasound. The method can also be used as an alternative to multislice computed tomography (MSCT).
In cardiological practice, it is important to correctly calculate the mass of the myocardium, chamber volumes, ejection fraction, and also to establish the cause of the development and progression of heart failure, which is clearly shown by cardiac MRI.
The high resolution of tomography allows for optimal assessment of the contractile function of the heart. Breath-hold techniques help track the location of the coronary artery. The method makes it possible to evaluate the operation of the valve and indicate backflow of blood or stenosis. Tomography is the gold standard for assessing pericardial thickness. The method allows you to obtain clear images of the aorta, pulmonary arteries and veins, and assess myocardial perfusion.
Indications for cardiac MRI are formed if the following conditions are suspected:
- ventricular aneurysm and pseudoaneurysm;
- dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- myocarditis;
- cardiac fibrosis;
- arrhythmogenic myocardial dysplasia;
- hemochromatosis is an infiltrative cardiomyopathy in which iron accumulates in the myocardium;
- cardiac remodeling;
- amyloidosis;
- sarcoidosis;
- Chagas disease;
- Tumors in the heart are also easily detected, which helps to recognize the disease in the early stages.
Information content
The information content of the method directly depends on the type of device used, its power and settings.
An open (low-field) tomograph is recommended for examining patients with claustrophobia and other conditions that complicate the process. The power of the device usually ranges from 0.23 to 0.5 Tesla. Whether to do cardiac MRI with such low settings is a question of rationality, because the quality of the images is low.
High-field installations have a power of 1-1.5-3 Tesla, which provides thin slices and, therefore, a more detailed picture. In addition, this type of device works much faster.
Virtual endoscopy
The development of computer technology has led to the emergence of a new diagnostic method - virtual endoscopy. What is it and how does it work? Virtual endoscopy is performed using a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scanner. This is a non-invasive technique that allows you to view internal cavities without inserting an endoscope. Special computer programs broadcast the image of the scanned area in real time. The specialist can observe the diagnosed area through the monitor screen from any angle, as with a standard endoscopic examination.
Virtual endoscopy is indicated for severe pathologies of the cardiovascular or respiratory system, when manipulation with an endoscope is impossible. The method is used in oncology, urology, angiology and other branches of medicine. Diagnostic results are provided to the patient in DICOM format for further examination by other specialists.
Diagnostic capabilities of SM-Clinic
CT and MRI are performed using modern high-tech equipment
The clinic uses European equipment. MRI is performed on the new generation Siemens MAGNETOM ESSENZA 1.5 Tesla and Siemens SOMATOM AERA 1.5 Tesla devices. The center has modern computed tomographs, including Siemens SOMATOM Perspective (128 slices).
Specialists in the field of radiology diagnostics with many years of experience
The effectiveness of modern diagnostic methods largely depends on the skills and experience of the specialists who interpret the images. SM-Clinic radiologists regularly improve their skills and join forces in difficult clinical situations.
Contrast tomography
Tomography using contrast is used to improve the differentiation of tissues and organs. This way the picture becomes clearer and more informative, and it is much easier for the doctor to navigate the resulting images. The vast majority of MRI contrast agents contain gadolinium. It enters the body intravenously, spreads through the bloodstream, staining all organs in its path.
Cardiac MRI uses an intravenous injection method. Gadolinium interacts with hydrogen protons, which increases the contrast of the three-dimensional image. The substance is considered completely safe for the human body and is excreted naturally through the kidneys.
The decision to perform contrast tomography is made by the doctor. In most cases, standard diagnostics without the use of auxiliary manipulations is sufficient.
Moreover, contrast agents are associated with a high risk of side effects.
Alternative diagnostic methods
If there are doubts whether it is possible to do cardiac MRI in a particular situation, the method can be replaced by other types of studies. The procedure can be replaced by computed tomography or MSCT, which do not require the use of a contrast solution, however, such methods are suitable for confirming previously made diagnoses that do not require differentiation from other diseases. Also, echocardiography or cardiac ultrasound is often used to assess structural and functional changes. PET-CT is used to track the dynamics of a malignant tumor and metastases.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
MRI is considered a safe procedure with a minimal list of contraindications. There are absolute and relative contraindications. The first category includes the presence of a pacemaker, a ferromagnetic or electronic middle ear implant, a ferromagnetic Ilizarov apparatus, large metal implants, or ferromagnetic fragments. What is this connected with? All these devices can influence the magnetic field, distorting the final result. As a result, the diagnosis will turn out to be uninformative, and the person will waste personal time and financial resources.
Indications for cardiac MRI:
- congenital or acquired organ defects;
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system;
- thrombosis, cysts, cancerous tumors, regardless of nature and stage;
- assessment of cardiac functionality after a heart attack;
- general diagnostics of the organ before/after surgery, assessment of the effectiveness of the therapeutic course, monitoring the recovery process.
Do not undergo an MRI scan without first consulting your doctor.
Even preventive examinations should be carried out as prescribed. Self-medication can only harm both psychological and physical health. Trust your doctor and strictly follow his instructions.
Relative contraindications include:
- insulin pumps, non-ferromagnetic implants, prosthetic heart valves, hemostatic clips (are not a contraindication if the device does not contain metal elements);
- decompensated heart failure;
- first trimester of pregnancy (the scientific community still does not have enough evidence about the harm, benefit or neutral effect of the magnetic field on the fetus. But MRI is still preferable to X-ray or CT for a pregnant woman);
- claustrophobia, panic attacks, unstable psycho-emotional state, inappropriate behavior (the patient simply will not be able to follow the instructions of the medical professional, will receive enormous stress and will not allow the examination to be carried out);
- the need for physiological monitoring, the patient’s serious condition (be sure to inform the medical professional of even the slightest deterioration in the condition. The decision to postpone or refuse scanning or replace the method is made only by the attending physician);
- installed braces or dentures (can distort the MRI result and affect the functionality of the magnetic field);
- tattoos (provided that the tattoo ink contains metallic compounds. Such ink is rarely found in modern tattoo parlors. Metallic ink was common about 20 years ago).
Contraindications to contrast diagnostics are included in a separate category. The first thing you need to pay attention to is the patient’s individual reaction.
Before scanning, a person is required to take allergy tests for contrast agent intolerance, on the basis of which a decision on further diagnosis is made.
Contrast tomography is contraindicated in case of serious kidney pathologies, as this will complicate the removal of the drug from the body. Also, diagnosis is contraindicated in severe renal, liver and heart failure.
What does an MRI of the heart show?
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to:
- determine the site of heart damage, assess the degree of damage and the extent of the pathological process;
- assess the size of the atria and ventricles, diagnose hypertrophic changes in the wall of the left and right ventricles;
- detect calcified and atherosclerotic deposits in large vessels of the heart (atherosclerosis of the aorta, atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries);
- see post-traumatic complications, such as hemopericardium, developed aneurysm, rupture of tissues surrounding the heart;
- determine the effectiveness of conservative and surgical treatment and approximate terms of rehabilitation.
How does a heart and blood vessel scan work?
MRI of the heart and blood vessels is no different from scanning any other organ or system and does not require specific preparation. When using contrast enhancement, it is advisable that the gadolinium-based drug be administered on an empty stomach to avoid side effects such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and others.
Immediately before the tomography, the patient is asked to remove all metal-containing items (jewelry, watches, belts, glasses) to prevent distortion of the results.
The patient must also provide the laboratory technician with medical documentation. It includes a doctor’s referral for an MRI, a preliminary diagnosis, specific instructions to the x-ray technician (scanning area with or without contrast, individual characteristics of the patient). Diagnostics lasts 25-30 minutes. With contrast enhancement, the time frame increases to 40-50 minutes.
Contrast tomography is performed under the strict supervision of a specialist.
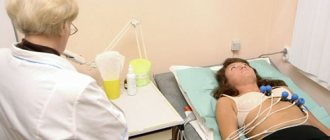
After all preparatory manipulations, the patient is positioned on the retractable tomograph table. During the procedure, the body must be motionless. If you are afraid of making a careless movement, ask the laboratory assistant to secure you with soft straps.
Order of conduct
The procedure requires calm, measured work of the heart, because The faster it beats and the more movements the chest makes, the more noise there is in the image. To even out the functioning of the heart, the doctor may prescribe appropriate medications before the procedure.
During the examination, electrodes (3 pieces) are glued to the patient’s chest to take ECG readings. To do this, men often have to shave the areas of skin to which the electrodes are attached.
The examination is performed in the supine position. The examination time depends on the diagnosis and takes from 30 minutes to an hour. When using contrast, the examination time increases.
During the examination, the patient receives commands to take in air and not breathe for 10 - 30 seconds, for a better scan.