The non-straightness of the vertebral arteries is often determined by scanning or duplex examination of the cerebral blood vessels. This pathology is very dangerous in terms of the development of transient or permanent cerebrovascular accident. Patients experience serious difficulties with mental performance, mood swings occur, and secondary hypertensive syndrome may develop.
Non-straightness of the vertebral arteries is always a consequence of pathology of the spinal column in the cervical region. This may be curvature, rotation of the vertebral body, destruction of intervertebral discs against the background of long-term osteochondrosis, deposition of calcium salts and many other diseases. The normal course of the vertebral artery is ensured by the anatomical structure of the cervical vertebrae, in which there are special openings for these blood vessels. They are reliably protected from external traumatic influences. However, when the vertebral bodies or the cartilage tissue separating them, the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc, is deformed, serious deformation and curvature occurs.
Any deformation of the course of the vertebral arteries leads to serious consequences, manifested by various cerebral symptoms. We will talk about how to recognize the disease, diagnose it and treat it without surgery using manual therapy techniques.
What is non-straightness of the vertebral arteries?
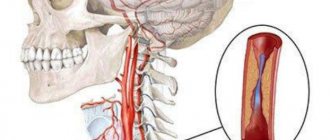
The vertebral arteries stretch from the prevertebral to the intracranial region, passing through the canal of the transverse processes of the cervical portion of the spinal column. If a person has received any injury, has a curvature of the spine or other diseases, this also affects the vertebral artery - it becomes bent. Blood flow is disrupted, the occipital part of the brain does not receive enough nutrition and oxygen. Irregular tortuosity of the artery is called “non-straightness of the VA”. In most cases, both arteries are affected, but non-straightness of the left vertebral artery or non-straightness of the right vertebral artery may also occur. This happens after a serious injury or the growth of a bone callus.
When a person has a non-linear course of VA on both sides, it is easier to make a diagnosis, and clear symptoms of the disease appear. If this pathology develops only on one side, the body tries to cope with the problem itself by increasing blood flow in the other vertebral artery. In this case, there will be practically no symptoms of the disease, but if the patient was examined for another disease, the doctor may notice this deviation.
Anatomical features of the vertebral arteries
The vertebral artery branches from the subclavian towards the central part of the inner edge of the scalene muscle in the neck.
It is important that no more than 1–1.5 cm remains to the adjacent mouth of the thyrocervical trunk, which is also a branch of the subclavian artery. This creates an additional mechanism of “stealing” (redistribution of blood) in case of hypoplasia or stenosis of the vertebral artery
Heading upward, the artery at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra (less often the fifth) enters a protected bone canal formed by the spinous processes of the vertebrae.
It is customary to distinguish sections or segments of the vertebral artery:
- I - the entire area from VI to II cervical vertebrae, where the vessel exits the foramen;
- II - outside the canal, at an angle of 450, it deflects posteriorly and goes to the transverse process of the first cervical vertebra (atlas);
- III - passing through the opening of the atlas on its back side, the artery forms loops, their role is to prevent disruption of blood flow when turning the head;
- IV - heading into the foramen magnum, the artery is located inside a dense ligament, with ossification of the receptacle or bone outgrowths on the occipital bone, conditions are created for traumatizing the walls of the vessel during movements in the cervical region;
- V - inside the foramen magnum (intracranial segment), the vertebral artery passes through the dura mater and lies on the surface of the medulla oblongata.
The fusion of the left and right arteries into a single trunk (basilar artery) ensures participation in the formation of the circle of Willis at the base of the brain
20% of cases of pathology of vertebral arteries are due to developmental anomalies:
- originating directly from the aorta;
- entry into the bony spinal canal higher than usual (at the level of the third to fifth cervical vertebrae);
- displacement of the mouth outward.
More often, the lesions are combined and are divided into the following options:
- up to 34% is due to the combined effect of developmental anomalies and extravasal muscle compression;
- 39% are stenoses of atherosclerotic and thrombotic nature;
- the maximum part - 57% - represents compression by various displacements of the vertebrae in combination with atherosclerosis.
Based on the presence of symptoms and the determination of its connection with neck movements, a suspicion of pathology of the vertebral arteries arises from a general practitioner or therapist. Timely referral to a neurologist and examination is a matter of experience.
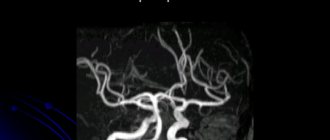
Duplex scanning allows you to see the structure of the vessel, determine the nature of the stenosis, the degree of damage to the artery walls
- Ultrasound Dopplerography - an assessment of all anatomical characteristics of the vertebral arteries on both sides, diameter along the length, speed of the blood flow wave is carried out; it is important as a way to determine cerebral circulatory reserve;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and neck vessels will indicate emerging lesions with impaired blood supply, the formation of cysts, aneurysms;
- An x-ray of the cervical spine can be used to judge the participation of pathological growths of bone tissue in pinching of the vertebral arteries;
- Angiography of the neck vessels is performed by injecting a contrast agent into the subclavian artery. The technique is informative, but is carried out only in specialized departments.
The vertebral artery, which is a paired vessel and located on both sides of the human body, originates from the subclavian artery. The sections (or segments) of the vertebral artery pass in the canal of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, which is why the vessel got its name.
- Three forms of vertebral artery hypoplasia - symptoms, causes and treatment
The following sections of the vertebral artery are distinguished:
- Prevertebral department. This segment occupies the area from the beginning of the artery at the subclavian vessel to the entrance to the canal of the vertebral processes;
- The cervical region occupies a section of the artery passing in the canal of the processes of the cervical vertebrae;
- Cervico-occipital segment. This section is located in the interval from the exit from the canal of the transverse processes of the vertebrae to the entrance to the cranium;
- The intracranial section extends from the skull to the junction of the two vertebral arteries into the basilar vessel.
Thus, more than half of the cases of death from cerebral vascular insufficiency are associated with pathology of the vertebral arteries. One of these disorders is the non-straightness of the vertebral arteries between the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Causes of pathology
Why might a person develop this disease? Non-straightness of the course of the vertebral arteries between the transverse processes and in other areas (there are several sections of the VA: prevertebral, cervical, cervico-occipital, intracranial) appears due to a number of diseases:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- congenital anomalies;
- injuries in which the cervical spine was damaged;
- hypothermia, which causes muscle spasm, which affects the location of the artery;
- tumor;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- scarring of tissue after surgery.
These are the main reasons, but there may be others.
Diagnosis and treatment
To determine the presence of non-straightness of the vertebral arteries, you need to contact a neurologist and undergo an examination, including:
- MRI and X-ray to determine the presence of osteochondrosis and other diseases.
- Doppler ultrasound to assess blood flow velocity.
- Angiography using the injection of a radiopaque contrast agent into the vessels.
- Rheoencephalogram.
For vertebrogenic causes of non-rectilinear course of the vertebral arteries, the following treatment methods are used:
- Massage, osteopathy.
- Acupuncture.
- Electrophoresis for pain relief.
- Sanatorium-resort treatment using baths and compresses.
- Exercise therapy.
- Wearing a Shants orthopedic collar.
- Drug therapy.
- Herbal medicine.
Manual therapy in some cases helps to straighten the vertebrae, and with it the arteries.
The specialist performing these manipulations must have the appropriate license for this type of activity. Massage helps combat tension in the neck muscles due to neuralgia and relieves pain. Gels and ointments used in this case must contain anti-inflammatory components. Acupuncture works through the effector muscles on the corresponding areas of the brain to relax these tense muscles. As a result, the vertebral arteries are not pinched and perform their function normally.
Electrophoresis with zinc hyaluronate, vitamins B1, B12 has an anti-inflammatory effect, improves the condition of the peripheral nervous system, which performs a trophic function. Novocaine relieves pain in osteochondrosis, and when it decomposes in tissues, para-aminobenzoic acid is released, which increases tissue resistance to hypoxia during transient ischemic attacks.
Sanatorium-resort treatment with turpentine baths and mud wraps has an anti-inflammatory effect on blood vessels and the spine. Physical therapy, especially in childhood, helps correct the curvature of the axial skeleton.
Symptoms
When a person has a non-linear course of the vertebral arteries, symptoms can only indicate that blood circulation in the brain is impaired. Only a complete examination will help make the correct diagnosis.
Stage of functional impairment (dystonic)
The main symptoms that show that the patient has a non-straightforward course of the vertebral arteries:
- the back of the head hurts, the pain is bursting and aching;
- there is a feeling of pressure in the back of the head;
- neck pain regularly;
- dizzy when getting out of bed;
- blood pressure rises, it is not possible to lower it with medications;
- there is no strength to do everyday work, you constantly want to sleep, it’s hard to wake up in the morning;
- nausea bothers me, nosebleeds appear, although there are no problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- weakness in the arms and legs, even if the person has not played sports;
- Vision and hearing deteriorate, tinnitus appears, and “spots” flash before the eyes.
Ischemic stage
It is advisable to consult a doctor as soon as the above symptoms occur. He will refer you for examination and prescribe a course of treatment. If symptoms are ignored, irreversible changes may occur. With severe deformities, a spinal stroke develops. Its main symptoms:
- gait becomes unsteady;
- facial expressions change;
- the tongue deviates to one side;
- there may be paralysis of the legs or arms on the left or right side;
- the patient cannot speak.
In this case, we are talking about life and death, the patient must be urgently taken to a neurological or special vascular hospital.
Symptoms and treatment of tortuosity of the vertebral arteries
Very often, people susceptible to high blood pressure and neurocirculatory dystonia do not know the main cause of the disease.
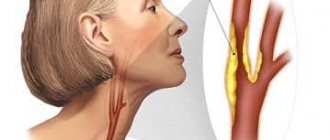
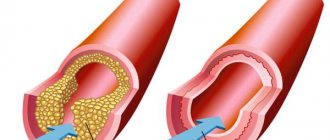
Behind the pathology is often tortuosity of the vertebral arteries, which increases the risk of stroke several times due to deterioration of blood flow in vital vessels. Such consequences can disrupt the activity of the brain and the entire central nervous system. Typically, tortuosity of the vertebral arteries is a hereditary disease and develops when the arterial tissue contains predominantly elastic fibers. As a result, the vascular walls quickly wear out, become thinner and become deformed.
The situation is aggravated if a person suffers from atherosclerosis. In this situation, plaques form on the walls, reducing the overall patency of the vessels. This in turn causes improper blood flow in the brain and other organs of the body. Usually, the bend does not manifest itself in any way, and only over time does the patient experience a circulatory disorder.
As a result, if the pathology is not diagnosed in time, the risk of strokes increases. It happens that the disease is detected during a standard medical examination. In this case, it is necessary to immediately begin competent treatment.
Prevention
To avoid a problem such as a deformed artery, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- control the level of cholesterol in the blood, exclude unhealthy foods (spicy, salty, fatty, fried, etc.) from the daily diet;
- get rid of bad habits (nicotine addiction). Smoking has a negative effect on the condition of the vascular walls and is the main cause of the formation of plaques and narrowing of the arteries;
- control body weight. For these purposes, physical exercises are used for all parts of the spine.
In addition, try not to lift heavy objects and limit your participation in professional sports. Also, you should not make sudden rotations, turns or tilts of your head.
Diagnosis of vertebral artery syndrome
If unpleasant symptoms appear, go to the doctor: the sooner the better. a therapist first
, he will give a referral to
a neurologist
. Even an experienced doctor will not be able to diagnose you without an examination, because... he needs to study the pictures to make sure that the blood flow is disrupted. Each doctor himself makes a list of examinations, but most often it includes the following components:
- Doppler ultrasound
, which shows the speed and direction of blood flow, arterial patency; - compression-functional tests;
- duplex scanning showing the condition of the vessel walls;
- MRI
; - radiography.
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will determine whether the course of the vertebral arteries is really disrupted or whether it is another syndrome, another disease.
Arterial tortuosity and its causes
The non-straightness of the arteries (tortuosity) is very often a congenital feature, the reason for which is the predominance of elastic fibers over collagen. The result of this predominance is deformation, thinning and tortuosity of the walls of the arteries; due to such changes in the vessel, a narrowing of the lumen occurs and, as a consequence, deterioration of blood flow, which can cause stroke and other diseases. Most often, tortuosity of the intracranial (intracranial) segments of the arteries occurs.
At the same time, very often such a congenital anomaly does not bother a person in any way, however, in a situation where the bend site is affected by atherosclerotic plaques, the lumen narrows even more, which can cause a severe oxygen deficiency in the brain and vertebral artery syndrome. That is why people with congenital tortuosity of the arteries need to carefully monitor the condition of the blood vessels.
Also, non-straightness of the vertebral arteries can be an acquired pathology. So, quite often its causes are pathologies of the spine - osteochondrosis, scoliosis and other diseases that cause spinal deformation. Often, tortuosity occurs when an artery is impacted by a spinal process. The greatest number of tortuosity of the artery occurs at the level of the I-II vertebrae of the neck. In this section of the artery, kinks, loops, aneurysms and spurs of the vessel walls can occur.
Also, the occurrence of non-straightness of the arteries is facilitated by their compression by intervertebral hernias, the occurrence of various tumors in the vertebrae, etc.
How to treat?
If you have non-straightness of the vertebral arteries, treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms. In the early stages, conservative treatment can also help. It is necessary to figure out what caused the pathology and first cure the underlying disease. If the cause of this pathology is a spasm of the cervical muscles, it needs to be removed. Physical therapy or massage may help. Conservative treatment did not help? Then the doctor prescribes surgery.
Drug treatment
The doctor also decides which medications to prescribe, but most often drugs that improve venous outflow, painkillers, pills that lower blood pressure, etc. are prescribed. Such treatment cannot solve the problem itself, i.e. correct changes in the vessel, but it improves the patient’s well-being.
Surgical
The operation is prescribed if the doctor fears that the patient will have an ischemic stroke. The surgeon decides what exactly needs to be done. Sometimes he shortens and straightens the artery, sometimes he performs prosthetics or stenting.
Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology
Blood enters the brain through four large arteries: the left and right common carotid and the left and right vertebral. It is worth noting that 70-85% of the blood passes through the carotid arteries, so disruption of blood flow in them often leads to acute cerebrovascular accidents, that is, ischemic strokes.
cerebellum, hypothalamus, corpus callosum, midbrain, partly the temporal, parietal, occipital lobes, as well as the dura mater of the posterior cranial fossa. Before entering the cranial cavity, branches depart from the vertebral artery, carrying blood to the spinal cord and its membranes. Consequently, when blood flow in the vertebral artery is disrupted, symptoms arise that indicate hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the areas of the brain that it supplies.
- Asymmetry of intracranial segments of the vertebral arteries and how to treat?
Treatment
In order to eliminate the symptoms caused by tortuosity of both arteries, first of all, it is worth getting rid of the cause that caused this pathology. So, if non-straightness is caused by osteochondrosis, then non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Dicloberl, Nurofen, Pentalgin) and drugs that reduce muscle tone (Mydocalm, Baclofen) are prescribed. It is also necessary to take drugs that restore cartilage tissue (Arteparon, Structum).
After treatment for an orthopedic disease that has caused a non-straightforward course of the artery is completed, measures must be taken to improve blood flow and reduce the severity of symptoms. For this purpose, therapeutic massage is used, that is, a direct effect is applied to the vertebra and ligaments of the deformed part of the spine.
In addition, for tortuosity of the vertebral arteries, drug therapy is used; it is recommended to take medications that improve venous outflow, for example, Anavenol, Antistax, Aescusan. Local medications are also prescribed - vascular ointments (Capilar, etc.).
Also, if necessary, painkillers, drugs that lower blood pressure and drugs that eliminate signs of vestibular disorders are used. It is worth noting that drug treatment is not able to completely correct the deformation of the vessel, but it significantly makes a person’s life easier.
Surgical intervention to eliminate arterial tortuosity is carried out only if there is a high risk of ischemic stroke; most often, such a threat occurs in the first (prevertebral) segment of the artery.
Surgical treatment can occur using several methods. So, if the reason for the non-straightness of the artery is its lengthening, then in this case the vessel shortens and straightens.
Also in some situations, artery replacement is used, which consists of removing the affected area and replacing it with an artificial vessel - a prosthesis. However, it is worth noting that such an intervention is a very traumatic method of treatment, which entails a number of complications, such as bleeding, increased pressure, etc.
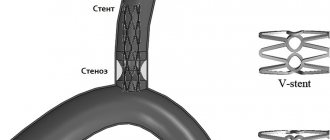
Recently, the popularity of operations involving stenting has increased. A stent is a metal product that is inserted into an artery in a folded state using a balloon catheter. After correct placement of the stent in the artery, it opens, which allows the lumen of the vessel to expand and blood flow to normalize.
Stenting is a less traumatic method of surgical intervention, as it is performed through a micro cut. However, this operation is only possible with modern equipment.
Any pathology of blood vessels can cause serious complications and even cause death, which is why if you detect any sign indicating a disturbance in blood flow and non-straightness of the vertebral arteries, you should immediately contact a specialist for consultation. In addition, you need to regularly undergo preventive examinations of the condition of blood vessels, which will help you undergo treatment on time and avoid many problems.
Vessels
Vessels of the Neck and Head: Anatomy, Diseases, Symptoms
Feb 03, 2021 Kokh V. A.
45341
Vessels
Small Diameter of Vertebral Arteries: Normal, What It Is
Feb 03, 2021 Kokh V. A.
77254
Vessels